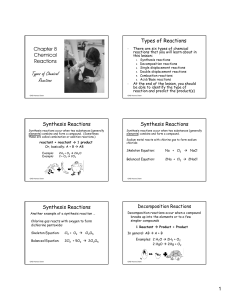
Exam Review Packet Table of Contents
... -‐2,240 kilojoules per mole. Account for this difference. ...
... -‐2,240 kilojoules per mole. Account for this difference. ...
Gas-Phase Reactions of Fe (CH2O)+ and Fe (CH2S)+ with Small
... do this, product ion structures were probed by collision-induced dissociation, specific ion-molecule reactions, and use of labeled compounds, and experimental bond energies were obtained by using ion-molecule bracketing and competitive collisioninduced dissociation methods. Formaldehyde was chosen s ...
... do this, product ion structures were probed by collision-induced dissociation, specific ion-molecule reactions, and use of labeled compounds, and experimental bond energies were obtained by using ion-molecule bracketing and competitive collisioninduced dissociation methods. Formaldehyde was chosen s ...
Illumination Intensity Dependence of the Photovoltage in
... with a profilometer (Mitutoyo Co., Sueftest SV 500), was 3 µm. To avoid electrochemical reactions via the exposed surface of the FTO, the possible pinholes (FTO areas uncovered with TiO2) were electrochemically blocked with an isolating polyphenoxide (PPO) polymer thin layer. The electrochemical dep ...
... with a profilometer (Mitutoyo Co., Sueftest SV 500), was 3 µm. To avoid electrochemical reactions via the exposed surface of the FTO, the possible pinholes (FTO areas uncovered with TiO2) were electrochemically blocked with an isolating polyphenoxide (PPO) polymer thin layer. The electrochemical dep ...
organonitrogen compounds i. amines
... To be consistent and logical in naming amines as substituted ammonias, they strictly should be called allcanamines and arenamines, according.to the nature of the hydrocarbon grouping. Unfortunately, the term alkylamine is used very commonly in place of alkanamine, while a host of trivial names are u ...
... To be consistent and logical in naming amines as substituted ammonias, they strictly should be called allcanamines and arenamines, according.to the nature of the hydrocarbon grouping. Unfortunately, the term alkylamine is used very commonly in place of alkanamine, while a host of trivial names are u ...
CfE Advanced Higher Chemistry
... Try Question 1, basing your method on the last example shown. The full working is available in the answer at the end of this booklet and can be used if you have difficulty. You are strongly advised to try these questions on paper. Seeing the solution is not the same as solving the problem! Obtaining ...
... Try Question 1, basing your method on the last example shown. The full working is available in the answer at the end of this booklet and can be used if you have difficulty. You are strongly advised to try these questions on paper. Seeing the solution is not the same as solving the problem! Obtaining ...
Question Bank Topic 5
... 20.1: The nature of oxidation and reduction processes 20.2: Oxidizing agent and reducing agent 20.3: Oxidation and reduction in terms of electron transfer 20.5: Ionic half-equations 20.6: The reducing power of metals 20.8: The oxidizing power of non-metals 20.9: Chemical changes of common oxidizing ...
... 20.1: The nature of oxidation and reduction processes 20.2: Oxidizing agent and reducing agent 20.3: Oxidation and reduction in terms of electron transfer 20.5: Ionic half-equations 20.6: The reducing power of metals 20.8: The oxidizing power of non-metals 20.9: Chemical changes of common oxidizing ...
A Few Things You Might Want To Know
... Mixtures can be heterogeneous or homogeneous (= solutions). They consist of substances that can be separated by physical changes (distillation, crystallization, chromatography). Substances can be either elements or compounds. Compounds can be separated into elements by chemical changes (redox reacti ...
... Mixtures can be heterogeneous or homogeneous (= solutions). They consist of substances that can be separated by physical changes (distillation, crystallization, chromatography). Substances can be either elements or compounds. Compounds can be separated into elements by chemical changes (redox reacti ...
Chemical Equilibrium Equilibrium A state where the reactants and
... Knowing the equilibrium constant allows us to predict several important features of the reaction. 1) the tendency of the reaction to ___________ (but not the _______________) 2) whether a given set of concentrations represent an __________________ condition 3) the equilibrium position that will be ...
... Knowing the equilibrium constant allows us to predict several important features of the reaction. 1) the tendency of the reaction to ___________ (but not the _______________) 2) whether a given set of concentrations represent an __________________ condition 3) the equilibrium position that will be ...
industry: applying chemical reactions
... chemical operations of EKS Nitrogen Products Company and WYE Battery Technology Corporation. This knowledge will help you later as you debate whether or not a new chemical plant should locate in Riverwood, and, if so, which one. ...
... chemical operations of EKS Nitrogen Products Company and WYE Battery Technology Corporation. This knowledge will help you later as you debate whether or not a new chemical plant should locate in Riverwood, and, if so, which one. ...
K eq
... 1. Each student wads up two paper wads. 2. You must start and stop as the timekeeper says. 3. Throw only one paper wad at a time. 4. If a paper wad lands next to you, you must throw it back. ...
... 1. Each student wads up two paper wads. 2. You must start and stop as the timekeeper says. 3. Throw only one paper wad at a time. 4. If a paper wad lands next to you, you must throw it back. ...
PAGE PROOFS
... reactions, which you met in chapter 000. Often these groups are so large that they are further divided into smaller groups, as is the case with the reactions involved in organic chemistry. Two further such groups are acid–base reactions and redox reactions. Although both of these large groups of rea ...
... reactions, which you met in chapter 000. Often these groups are so large that they are further divided into smaller groups, as is the case with the reactions involved in organic chemistry. Two further such groups are acid–base reactions and redox reactions. Although both of these large groups of rea ...
Reaction Rates
... When the orientation of colliding molecules is correct, as shown in Figure 4c, a reaction can occur. An oxygen atom is transferred from an NO 2 molecule to a CO molecule. When this occurs, a short-lived entity called an activated complex is formed, in this case OCONO. An activated complex, sometimes ...
... When the orientation of colliding molecules is correct, as shown in Figure 4c, a reaction can occur. An oxygen atom is transferred from an NO 2 molecule to a CO molecule. When this occurs, a short-lived entity called an activated complex is formed, in this case OCONO. An activated complex, sometimes ...
chemistry-subject test5 w. solutions
... The ideal gas law assumes (among other things) that there are no intermolecular forces among the gas particles, which hold the molecules tighter together, leading to a smaller volume than that predicted by the ideal gas law. Intermolecular forces among neutral particles are due to hydrogen bonding, ...
... The ideal gas law assumes (among other things) that there are no intermolecular forces among the gas particles, which hold the molecules tighter together, leading to a smaller volume than that predicted by the ideal gas law. Intermolecular forces among neutral particles are due to hydrogen bonding, ...
Equilibrium notes (complete)
... products at the other. • If you dump some water at one end of the tub the water flows towards the other end of the tub to reestablish equilibrium • If you scoop out some water at one end of the tub the water flows back towards the “hole” to reestablish equilibrium. The effect of temperature changes: ...
... products at the other. • If you dump some water at one end of the tub the water flows towards the other end of the tub to reestablish equilibrium • If you scoop out some water at one end of the tub the water flows back towards the “hole” to reestablish equilibrium. The effect of temperature changes: ...
Chapter 16: Reaction Rates
... When the orientation of colliding molecules is correct, as shown in Figure 16.4c, a reaction can occur. An oxygen atom is transferred from an NO 2 molecule to a CO molecule. When this occurs, a short-lived entity called an activated complex is formed, in this case OCONO. An activated complex, someti ...
... When the orientation of colliding molecules is correct, as shown in Figure 16.4c, a reaction can occur. An oxygen atom is transferred from an NO 2 molecule to a CO molecule. When this occurs, a short-lived entity called an activated complex is formed, in this case OCONO. An activated complex, someti ...
Reaction Kinetics - National Open University of Nigeria
... CHM 407: Reaction Kinetics concerns with the speed or rates of chemical reactions. The study of reaction rates allows for the prediction of how fast it will take a reaction mixture to reach equilibrium. It also account for how the reaction rate would be optimised by controlling certain factors such ...
... CHM 407: Reaction Kinetics concerns with the speed or rates of chemical reactions. The study of reaction rates allows for the prediction of how fast it will take a reaction mixture to reach equilibrium. It also account for how the reaction rate would be optimised by controlling certain factors such ...
Chapter 9 Stoichiometry
... d) When the reaction is done, is there any Fe2O3 left over? How much? ...
... d) When the reaction is done, is there any Fe2O3 left over? How much? ...
technical report 91 -32
... adsorbed radionuclides directly and/or they are dissolved and reduce the radionuclides in solution. For this reason, the redox conditions can be simulated best by letting the minerals/rocks equilibrate with the water at the desired pH, carbon dioxide concentration and water chemistry. This is what h ...
... adsorbed radionuclides directly and/or they are dissolved and reduce the radionuclides in solution. For this reason, the redox conditions can be simulated best by letting the minerals/rocks equilibrate with the water at the desired pH, carbon dioxide concentration and water chemistry. This is what h ...
Answers - logo Pre-U Chemistry Textbook
... Two electrons would have to go into an antibonding molecular orbital. This is energetically unfavourable because the increase in energy of the antibonding orbital is greater than the decrease in energy of the bonding orbital. Helium molecules do not form because they would be at higher energy than t ...
... Two electrons would have to go into an antibonding molecular orbital. This is energetically unfavourable because the increase in energy of the antibonding orbital is greater than the decrease in energy of the bonding orbital. Helium molecules do not form because they would be at higher energy than t ...
431 KB / 47 pages
... Solutions for Chapter 10 End-of-Chapter Problems Problem 10.1. (a) We have seen (Investigate This 10.2) that electrolysis of a dilute aqueous solution of an ionic compound (magnesium sulfate) produces a gas at both electrodes and a basic solution at the cathode and acidic solution at the anode, just ...
... Solutions for Chapter 10 End-of-Chapter Problems Problem 10.1. (a) We have seen (Investigate This 10.2) that electrolysis of a dilute aqueous solution of an ionic compound (magnesium sulfate) produces a gas at both electrodes and a basic solution at the cathode and acidic solution at the anode, just ...
M.Sc. Chemistry - Periyar University
... Theories of Reaction rates – Arrhenius theory – effect of temperature on reaction rate – Hard – Sphere collision theory of reaction rates – molecular beams – Reaction cross section – effectiveness of collisions – Probability factor. Transition state theory of reaction rates – Potential energy surfac ...
... Theories of Reaction rates – Arrhenius theory – effect of temperature on reaction rate – Hard – Sphere collision theory of reaction rates – molecular beams – Reaction cross section – effectiveness of collisions – Probability factor. Transition state theory of reaction rates – Potential energy surfac ...
document
... d. Define Brønsted–Lowry acid and Brønsted–Lowry base. e. Write the chemical equation of a Brønsted–Lowry base in aqueous solution f. Write the chemical equation of an acid in aqueous solution using the hydronium ion. g. Learn the common strong acids and strong ...
... d. Define Brønsted–Lowry acid and Brønsted–Lowry base. e. Write the chemical equation of a Brønsted–Lowry base in aqueous solution f. Write the chemical equation of an acid in aqueous solution using the hydronium ion. g. Learn the common strong acids and strong ...
1.8 M - Thierry Karsenti
... Most chemical reactions and virtually all biological processes take place not between pure solids, liquids or gases, but rather among ions and molecules dissolved in water or other solvents (i.e. in solution). In this module we will therefore examine the various types of solutions and their properti ...
... Most chemical reactions and virtually all biological processes take place not between pure solids, liquids or gases, but rather among ions and molecules dissolved in water or other solvents (i.e. in solution). In this module we will therefore examine the various types of solutions and their properti ...
Photoredox catalysis
_Schematic.png?width=300)
Photoredox catalysis is a branch of catalysis that harnesses the energy of visible light to accelerate a chemical reaction via a single-electron transfer. This area is named as a combination of ""photo-"" referring to light and redox, a condensed expression for the chemical processes of reduction and oxidation. In particular, photoredox catalysis employs small quantities of a light-sensitive compound that, when excited by light, can mediate the transfer of electrons between chemical compounds that otherwise would not react. Photoredox catalysts are generally drawn from three classes of materials: transition-metal complexes, organic dyes and semiconductors. While each class of materials has advantages, soluble transition-metal complexes are used most often.Study of this branch of catalysis led to the development of new methods to accomplish known and new chemical transformations. One attraction to the area is that photoredox catalysts are often less toxic than other reagents often used to generate free radicals, such as organotin reagents. Furthermore, while photoredox catalysts generate potent redox agents while exposed to light, they are innocuous under ordinary conditions Thus transition-metal complex photoredox catalysts are in some ways more attractive than stoichiometric redox agents such as quinones. The properties of photoredox catalysts can be modified by changing ligands and the metal, reflecting the somewhat modular nature of the catalyst.While photoredox catalysis has most often been applied to generate known reactive intermediates in a novel way, the study of this mode of catalysis led to the discovery of new organic reactions, such as the first direct functionalization of the β-arylation of saturated aldehydes. Although the D3-symmetric transition-metal complexes used in many photoredox-catalyzed reactions are chiral, the use of enantioenriched photoredox catalysts led to low levels of enantioselectivity in a photoredox-catalyzed aryl-aryl coupling reaction, suggesting that the chiral nature of these catalysts is not yet a highly effective means of transmitting stereochemical information in photoredox reactions. However, while synthetically useful levels of enantioselectivity have not been achieved using chiral photoredox catalysts alone, optically-active products have been obtained through the synergistic combination of photoredox catalysis with chiral organocatalysts such as secondary amines and Brønsted acids.