Year 10 Chemistry Exam June 2011 Multiple Choice Section A
... d. water is removed from a substance 2. The graph shows the relative amount of chemical substances which can be taken up by plants at different pH levels. The narrower the bar the harder it is for plants to take up elements. ...
... d. water is removed from a substance 2. The graph shows the relative amount of chemical substances which can be taken up by plants at different pH levels. The narrower the bar the harder it is for plants to take up elements. ...
AP Chemistry 2013 Semester 1 Final Exam Review Problems
... b. BrF5 c. OSF4 d. Central Br in Br320. Nitrogen, N2, can ionize to form N2+ or add an electron to give N2-1 Using molecular orbital theory, compare these species with regard to a. Their magnetic character b. Net number of pi bonds c. Bond order d. bond length e. Bond strength ...
... b. BrF5 c. OSF4 d. Central Br in Br320. Nitrogen, N2, can ionize to form N2+ or add an electron to give N2-1 Using molecular orbital theory, compare these species with regard to a. Their magnetic character b. Net number of pi bonds c. Bond order d. bond length e. Bond strength ...
Problem
... • The Pauli exclusion principle states that no two electrons in an atom can have the same set of four quantum numbers n, l, ml and ms. – For a given orbital the values of n, l, and ml ...
... • The Pauli exclusion principle states that no two electrons in an atom can have the same set of four quantum numbers n, l, ml and ms. – For a given orbital the values of n, l, and ml ...
Remember Question words
... Law of Conservation of Mass = no detectable gain or loss in mass occurs in chemical reactions. However, the state of a substance may change in a chemical reaction. For example, substances in a chemical reaction can change from solid states to gaseous states but the total mass will not change. Or mor ...
... Law of Conservation of Mass = no detectable gain or loss in mass occurs in chemical reactions. However, the state of a substance may change in a chemical reaction. For example, substances in a chemical reaction can change from solid states to gaseous states but the total mass will not change. Or mor ...
Semester Exam Review Guide
... a. elements are arranged by atomic number. b. metallic elements are placed on the right-hand side. c. elements in the same group have the same number of valence electrons. d. both a and c. 19. __________ brought back the concept of the atom in the_____century. a. Bernoulli, 18th. b. Boyle, 17th. c. ...
... a. elements are arranged by atomic number. b. metallic elements are placed on the right-hand side. c. elements in the same group have the same number of valence electrons. d. both a and c. 19. __________ brought back the concept of the atom in the_____century. a. Bernoulli, 18th. b. Boyle, 17th. c. ...
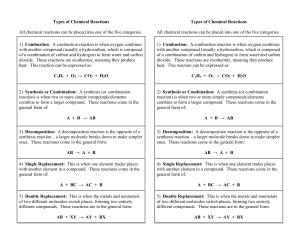
Types of Chemical Reactions
... of a combination of carbon and hydrogen) to form water and carbon dioxide. These reactions are exothermic, meaning they produce heat. This reaction can be expressed as: ...
... of a combination of carbon and hydrogen) to form water and carbon dioxide. These reactions are exothermic, meaning they produce heat. This reaction can be expressed as: ...
A1982NU66300001
... These were exciting times at University College London, with many new complexes being produced each week with the enthusiastic encouragementof Ron Nyholm. It was clear that there was a real need, in order to support this synthetic programme, for a rapid spectroscopic method for telling the likely ox ...
... These were exciting times at University College London, with many new complexes being produced each week with the enthusiastic encouragementof Ron Nyholm. It was clear that there was a real need, in order to support this synthetic programme, for a rapid spectroscopic method for telling the likely ox ...
Too Hot to Handle Lab
... from, a reacting substance during an exothermic reaction. A reaction that involves burning, or a combustion reaction, is an example of an exothermic reaction. The combustion of methane gas, which occurs in a gas stove, releases a large amount of heat energy. The energy that is released in an exother ...
... from, a reacting substance during an exothermic reaction. A reaction that involves burning, or a combustion reaction, is an example of an exothermic reaction. The combustion of methane gas, which occurs in a gas stove, releases a large amount of heat energy. The energy that is released in an exother ...
Advanced Placement (AP) Chemistry 2012 – 2013 Ramsay High
... required. The course meets 5 days a week for ninety-six (96) minutes. Much of the work involves solving math-type word problems. It is highly recommended that AP Chemistry students be concurrently enrolled in one of the highest-level mathematics courses available. With the exception of laboratory ex ...
... required. The course meets 5 days a week for ninety-six (96) minutes. Much of the work involves solving math-type word problems. It is highly recommended that AP Chemistry students be concurrently enrolled in one of the highest-level mathematics courses available. With the exception of laboratory ex ...
Chemical Synthesis (sat6)
... A1: MgO and H2 -> Mg and H2O; A2: C and O2 -> CO2; A3: CO2 and H2O -> H2CO3; A4: MgO and H2 and O2 and C; minimize obj: H2CO3; Write(’Yes, H2CO3 is produced’); Write(’No, H2CO3 is not produced’); ...
... A1: MgO and H2 -> Mg and H2O; A2: C and O2 -> CO2; A3: CO2 and H2O -> H2CO3; A4: MgO and H2 and O2 and C; minimize obj: H2CO3; Write(’Yes, H2CO3 is produced’); Write(’No, H2CO3 is not produced’); ...
Name________________ Hour____ Chapter 11 Review 1. Name
... 2 atoms of solid aluminum react with 6 molecules of liquid water to produce 3 molecules of hydrogen gas and 2 formula units of solid aluminum hydroxide. 4. Write in symbols: 2 formula units of solid lead (IV) oxide decomposes in the presence of heat to produce 2 formula units of solid lead (II) oxid ...
... 2 atoms of solid aluminum react with 6 molecules of liquid water to produce 3 molecules of hydrogen gas and 2 formula units of solid aluminum hydroxide. 4. Write in symbols: 2 formula units of solid lead (IV) oxide decomposes in the presence of heat to produce 2 formula units of solid lead (II) oxid ...
Begin Chemical Equations Practice
... molecule that follows, so 6CO2 shows that there are 6 Carbon atoms and 12 Oxygen atoms. ...
... molecule that follows, so 6CO2 shows that there are 6 Carbon atoms and 12 Oxygen atoms. ...
rules for predicting products of chemical reactions
... In order for a double replacement reaction to take place: - Both of the reactants must be soluble in water - If a compound contains at least one of the ions that is proven soluble, then the compound will be at least moderately soluble - One product must be soluble and one product must be insoluble o ...
... In order for a double replacement reaction to take place: - Both of the reactants must be soluble in water - If a compound contains at least one of the ions that is proven soluble, then the compound will be at least moderately soluble - One product must be soluble and one product must be insoluble o ...
03. The Theoretic bases of bioenergetics
... 2.Н(formation)= ΣnНf298(products) - ΣnНf298(reactants) 3.Н(combustion) = ΣnНс298(reactants) - ΣnНс298(products) ...
... 2.Н(formation)= ΣnНf298(products) - ΣnНf298(reactants) 3.Н(combustion) = ΣnНс298(reactants) - ΣnНс298(products) ...
Earth Science - Green Local Schools
... Average atomic mass energy levels Metal Valence electron Nonmetal Period Semiconductor Group Alkali metal Ion Alkaline-earth metal Atomic number Transition metal Mass number Noble gases Electron Cloud Model / Bohr Model Be able to find the number of neutrons, protons, and electrons in an atom Be ...
... Average atomic mass energy levels Metal Valence electron Nonmetal Period Semiconductor Group Alkali metal Ion Alkaline-earth metal Atomic number Transition metal Mass number Noble gases Electron Cloud Model / Bohr Model Be able to find the number of neutrons, protons, and electrons in an atom Be ...
1) Which of the following correctly lists the atoms in order of
... 1) Which of the following correctly lists the atoms in order of increasing size (smallest to largest)? a) F< K < Ge < Br < Rb b) F < Br < Ge < K < Rb c) F < Ge < Br < K < Rb d) F < K < Br < Ge < Rb e) F < Br < Ge < Rb < K 2). The first six ionization energies for an element are: 786 kJ, 1580 kJ, 323 ...
... 1) Which of the following correctly lists the atoms in order of increasing size (smallest to largest)? a) F< K < Ge < Br < Rb b) F < Br < Ge < K < Rb c) F < Ge < Br < K < Rb d) F < K < Br < Ge < Rb e) F < Br < Ge < Rb < K 2). The first six ionization energies for an element are: 786 kJ, 1580 kJ, 323 ...
Seminario Tunable electronic properties of self
... In novel organic optoelectronics applications, the device efficiency depends crucially on the energy barrier that controls charge carrier injection at molecule/electrode interfaces. These processes are determined by the chemical interaction between the deposited species and the inorganic surface, as ...
... In novel organic optoelectronics applications, the device efficiency depends crucially on the energy barrier that controls charge carrier injection at molecule/electrode interfaces. These processes are determined by the chemical interaction between the deposited species and the inorganic surface, as ...
Semester 1 Exam Review Part 1
... 10. Vertical column in the Periodic Table. 11. Elements in the same family have similar ___. 12. Horizontal row on the Periodic Table. 13. Elements on the right side of the Periodic Table. ...
... 10. Vertical column in the Periodic Table. 11. Elements in the same family have similar ___. 12. Horizontal row on the Periodic Table. 13. Elements on the right side of the Periodic Table. ...
Discussion 9, Mahaffy et al., Chapter 15
... Oxidation Reduction Reactions a. Oxidation is loss of electrons (acts as a reducing agent) b.Reduction is gain of electrons (acts as a oxidizing agent) Assigning Oxidation numbers c. Oxidation number is 0 for atoms in an element. d.The sum of all oxidation numbers in a molecule or ion must add up to ...
... Oxidation Reduction Reactions a. Oxidation is loss of electrons (acts as a reducing agent) b.Reduction is gain of electrons (acts as a oxidizing agent) Assigning Oxidation numbers c. Oxidation number is 0 for atoms in an element. d.The sum of all oxidation numbers in a molecule or ion must add up to ...
No Slide Title
... A Closer Look at the Equation 2Al(s) + 3Br2(l) Al2Br6(s) • The chemicals on the left are the reactants and the right are the products. • The coefficient in front of the chemical denotes the stoichiometric relationship. • The numerical subscript represents the number of atoms present in the molecu ...
... A Closer Look at the Equation 2Al(s) + 3Br2(l) Al2Br6(s) • The chemicals on the left are the reactants and the right are the products. • The coefficient in front of the chemical denotes the stoichiometric relationship. • The numerical subscript represents the number of atoms present in the molecu ...
Chemistry Review: Unit2 - Menno Simons Christian School
... Heat is produced or absorbed, starting material is used up, there is a change in colour, a material with new properties is formed, gas bubbles form in a liquid, a precipitate forms in a liquid and the change is difficult to reverse. 7) In the table below list whether there is a chemical or physical ...
... Heat is produced or absorbed, starting material is used up, there is a change in colour, a material with new properties is formed, gas bubbles form in a liquid, a precipitate forms in a liquid and the change is difficult to reverse. 7) In the table below list whether there is a chemical or physical ...
CHEMICAL REACTIONS OBJECTIVES 1. To study reactions
... When two ionic solutions are mixed and there is not an ion combination that is insoluble or gaseous, no reaction will be observed. For example, no reaction occurs between NaCl and KNO3 because all ionic combinations are soluble compounds. Part II. Exothermic and endothermic reactions Reactions that ...
... When two ionic solutions are mixed and there is not an ion combination that is insoluble or gaseous, no reaction will be observed. For example, no reaction occurs between NaCl and KNO3 because all ionic combinations are soluble compounds. Part II. Exothermic and endothermic reactions Reactions that ...
The Photosynthesis Process
... the process doesn't require light directly, the inputs needed for this process come from the light reactions. Since the light reactions cannot occur without light, the Calvin cycle will not be able to ...
... the process doesn't require light directly, the inputs needed for this process come from the light reactions. Since the light reactions cannot occur without light, the Calvin cycle will not be able to ...
Chemistry Final Exam Test Yourself I
... electrons. Composed of non-metals (Covalent) A compound is this when the atoms in it give or take electrons. Composed of at least one non-metal and one metal (Ionic) ...
... electrons. Composed of non-metals (Covalent) A compound is this when the atoms in it give or take electrons. Composed of at least one non-metal and one metal (Ionic) ...
Photoredox catalysis
_Schematic.png?width=300)
Photoredox catalysis is a branch of catalysis that harnesses the energy of visible light to accelerate a chemical reaction via a single-electron transfer. This area is named as a combination of ""photo-"" referring to light and redox, a condensed expression for the chemical processes of reduction and oxidation. In particular, photoredox catalysis employs small quantities of a light-sensitive compound that, when excited by light, can mediate the transfer of electrons between chemical compounds that otherwise would not react. Photoredox catalysts are generally drawn from three classes of materials: transition-metal complexes, organic dyes and semiconductors. While each class of materials has advantages, soluble transition-metal complexes are used most often.Study of this branch of catalysis led to the development of new methods to accomplish known and new chemical transformations. One attraction to the area is that photoredox catalysts are often less toxic than other reagents often used to generate free radicals, such as organotin reagents. Furthermore, while photoredox catalysts generate potent redox agents while exposed to light, they are innocuous under ordinary conditions Thus transition-metal complex photoredox catalysts are in some ways more attractive than stoichiometric redox agents such as quinones. The properties of photoredox catalysts can be modified by changing ligands and the metal, reflecting the somewhat modular nature of the catalyst.While photoredox catalysis has most often been applied to generate known reactive intermediates in a novel way, the study of this mode of catalysis led to the discovery of new organic reactions, such as the first direct functionalization of the β-arylation of saturated aldehydes. Although the D3-symmetric transition-metal complexes used in many photoredox-catalyzed reactions are chiral, the use of enantioenriched photoredox catalysts led to low levels of enantioselectivity in a photoredox-catalyzed aryl-aryl coupling reaction, suggesting that the chiral nature of these catalysts is not yet a highly effective means of transmitting stereochemical information in photoredox reactions. However, while synthetically useful levels of enantioselectivity have not been achieved using chiral photoredox catalysts alone, optically-active products have been obtained through the synergistic combination of photoredox catalysis with chiral organocatalysts such as secondary amines and Brønsted acids.