Final Exam - W09
... A civil engineer wants to reduce odors at a wastewater treatment plant by adding hydrogen peroxide to the sewage. The hydrogen peroxide is delivered as 50% by mass solution, but for maintenance and safety issues, the H2O2 is diluted to a 3% by mass solution. If the engineer needs 20.0 gallons of the ...
... A civil engineer wants to reduce odors at a wastewater treatment plant by adding hydrogen peroxide to the sewage. The hydrogen peroxide is delivered as 50% by mass solution, but for maintenance and safety issues, the H2O2 is diluted to a 3% by mass solution. If the engineer needs 20.0 gallons of the ...
Chapter 2
... “nonliniarity” and “feedback”. If the first term is related to the mathematics behind these processes, the feedback arises when the products of later steps in the mechanism influence the rate of some of the earlier reactions steps (and, hence, the rate of their own production). This may take the for ...
... “nonliniarity” and “feedback”. If the first term is related to the mathematics behind these processes, the feedback arises when the products of later steps in the mechanism influence the rate of some of the earlier reactions steps (and, hence, the rate of their own production). This may take the for ...
A Guide to Rate of Reactions
... It is important to note that the CAPS document separates Rate of Reaction and Chemical Equilibrium. This is because the underlying theory of each of these is very different. Rate of reaction is also called Chemical Kinetics and deals with how fast a reaction happens. Chemical equilibrium is based on ...
... It is important to note that the CAPS document separates Rate of Reaction and Chemical Equilibrium. This is because the underlying theory of each of these is very different. Rate of reaction is also called Chemical Kinetics and deals with how fast a reaction happens. Chemical equilibrium is based on ...
Exam 2 Review - Iowa State University
... Sodium Sulfide. Write the balanced equation. State the limiting reagent(s). How much precipitate forms? What is the molarity of the non-precipitate product? ...
... Sodium Sulfide. Write the balanced equation. State the limiting reagent(s). How much precipitate forms? What is the molarity of the non-precipitate product? ...
ch19 MSJ jlm
... (This is also called electromotive force (emf) Why is this reaction spontaneous? Why is the voltage 0.46 volt? ...
... (This is also called electromotive force (emf) Why is this reaction spontaneous? Why is the voltage 0.46 volt? ...
Chemical Reactions PPT
... Since oxidation is the loss of electrons and reduction is the gain of electrons, they must occur simultaneously. ** Any chemical process in which elements undergo changes in oxidation number is an oxidation – reduction reaction , or redox reaction for short.** ...
... Since oxidation is the loss of electrons and reduction is the gain of electrons, they must occur simultaneously. ** Any chemical process in which elements undergo changes in oxidation number is an oxidation – reduction reaction , or redox reaction for short.** ...
Chemistry Standards Review
... 81. Describe the bonding characteristics of carbon. How many bonds can carbon form? What types of covalent bonds can carbon form? 82. What type of bond is found in most large organic molecules? 83. What monomers make up proteins? What monomers make up DNA? 84. What is the chemical structure of an am ...
... 81. Describe the bonding characteristics of carbon. How many bonds can carbon form? What types of covalent bonds can carbon form? 82. What type of bond is found in most large organic molecules? 83. What monomers make up proteins? What monomers make up DNA? 84. What is the chemical structure of an am ...
Gibbs Free Energy and chemical equilibrium
... 2. If Q/K = 1, then ΔG = 0 and the system is at equilibrium. 3. If Q/K > 1, then ΔG is positive, and the reaction is spontaneous in the opposite direction as written. ...
... 2. If Q/K = 1, then ΔG = 0 and the system is at equilibrium. 3. If Q/K > 1, then ΔG is positive, and the reaction is spontaneous in the opposite direction as written. ...
97KB - NZQA
... If the solution turns pale green and a grey deposit forms on the iron metal, then the solution contains lead ions, as Fe is higher on the activity series than Pb. The pale green solution is due to iron(II) ions being formed. The grey deposit is lead. Fe + Pb2+ Fe2+ + Pb If the solution remains col ...
... If the solution turns pale green and a grey deposit forms on the iron metal, then the solution contains lead ions, as Fe is higher on the activity series than Pb. The pale green solution is due to iron(II) ions being formed. The grey deposit is lead. Fe + Pb2+ Fe2+ + Pb If the solution remains col ...
The d-block elements are commonly known as transition
... Ligand-to-Metal Charge-Transfer (LMCT) Transition Color in transition-series metal compounds is generally due to the electronic transitions of two principal types of charge transfer transitions. An electron may jump from a predominantly ligand orbital to a predominantly metal orbital, giving rise t ...
... Ligand-to-Metal Charge-Transfer (LMCT) Transition Color in transition-series metal compounds is generally due to the electronic transitions of two principal types of charge transfer transitions. An electron may jump from a predominantly ligand orbital to a predominantly metal orbital, giving rise t ...
View flyer - Tufts University School of Engineering
... The catalytic semi-hydrogenation of acetylene to produce ethylene is a common method for the removal of trace acetylene (~1%) in ethylene feed streams destined for ethylene polymerization. An effective catalyst for this reaction converts all of the acetylene to ethylene without further conversion of ...
... The catalytic semi-hydrogenation of acetylene to produce ethylene is a common method for the removal of trace acetylene (~1%) in ethylene feed streams destined for ethylene polymerization. An effective catalyst for this reaction converts all of the acetylene to ethylene without further conversion of ...
Chapter 8
... Electron Configurations of Cations of Transition Metals When a cation is formed from an atom of a transition metal, electrons are always removed first from the ns orbital and then from the (n – 1)d orbitals. ...
... Electron Configurations of Cations of Transition Metals When a cation is formed from an atom of a transition metal, electrons are always removed first from the ns orbital and then from the (n – 1)d orbitals. ...
Masterton and Hurley Chapter 4
... • When an ionic solid is dissolved in a solvent, the ions separate from each other • MgCl2 (s) → Mg2+ (aq) + 2 Cl-1 (aq) • The concentrations of ions are related to each other by the formula of the compound: • Molarity of MgCl2 = Molarity of Mg2+ • Molarity of Cl-1 = 2 X Molarity of MgCl2 • Total nu ...
... • When an ionic solid is dissolved in a solvent, the ions separate from each other • MgCl2 (s) → Mg2+ (aq) + 2 Cl-1 (aq) • The concentrations of ions are related to each other by the formula of the compound: • Molarity of MgCl2 = Molarity of Mg2+ • Molarity of Cl-1 = 2 X Molarity of MgCl2 • Total nu ...
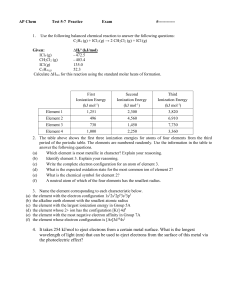
AP Chem Test 5-7 Practice Exam - mvhs
... 3. Name the element corresponding to each characteristic below. the element with the electron configuration 1s22s22p63s23p3 the alkaline earth element with the smallest atomic radius the element with the largest ionization energy in Group 5A the element whose 2+ ion has the configuration [Kr] 4d5 th ...
... 3. Name the element corresponding to each characteristic below. the element with the electron configuration 1s22s22p63s23p3 the alkaline earth element with the smallest atomic radius the element with the largest ionization energy in Group 5A the element whose 2+ ion has the configuration [Kr] 4d5 th ...
Grade XII Foreign SET 2 Chemistry (Theory)
... In N2, the two nitrogen atoms form a triple bond. This triple bond has very high bond strength, which is very difficult to break. It is because of nitrogen’s small size that it is able to form p– p bonds with itself. This property is not exhibited by phosphorus. (ii)Sulphur hexafluoride (SF6) is k ...
... In N2, the two nitrogen atoms form a triple bond. This triple bond has very high bond strength, which is very difficult to break. It is because of nitrogen’s small size that it is able to form p– p bonds with itself. This property is not exhibited by phosphorus. (ii)Sulphur hexafluoride (SF6) is k ...
Oxidation numbers
... In fact, oxidation never takes place on its own - nor does reduction. When one substance is oxidised in a reaction, another one is reduced. A Redox reaction is one in which both reduction and oxidation take place. To work out which element is oxidised and which is reduced in a reaction, we go throug ...
... In fact, oxidation never takes place on its own - nor does reduction. When one substance is oxidised in a reaction, another one is reduced. A Redox reaction is one in which both reduction and oxidation take place. To work out which element is oxidised and which is reduced in a reaction, we go throug ...
Chemical Equations
... • 2. If at least one INSOLUBLE product is formed (which means a precipitate will form) the reaction will occur! • 3. If only SOUBLE products are formed then the reaction will NOT occur (because no precipitate is formed)! • 4. If water is produced the reaction will occur! • 5. If the reaction occurs ...
... • 2. If at least one INSOLUBLE product is formed (which means a precipitate will form) the reaction will occur! • 3. If only SOUBLE products are formed then the reaction will NOT occur (because no precipitate is formed)! • 4. If water is produced the reaction will occur! • 5. If the reaction occurs ...
Catalytic, Enantioselective Alkylation of r
... (MeCN)n (3c)16 performed the best, giving high yield (91%) and selectivity at 0 °C (98% ee, entry 3). Demonstrating the utility of our process, similarly good ee was obtained eVen when this reaction was conducted at 0 °C in the presence of only 2 mol % catalyst (96% ee, entry 4). At this temperature ...
... (MeCN)n (3c)16 performed the best, giving high yield (91%) and selectivity at 0 °C (98% ee, entry 3). Demonstrating the utility of our process, similarly good ee was obtained eVen when this reaction was conducted at 0 °C in the presence of only 2 mol % catalyst (96% ee, entry 4). At this temperature ...
Bonding. A. Ionic bonds form when anions and cations arise
... Because of the electronegativity differences between atoms, it is not always possible for the octet rules to be followed rigorously. Oxidation numbers offer a summary of the octet rule each atom followed in the bonding process. Follow these rules to determine the oxidation number of any atom: 1. The ...
... Because of the electronegativity differences between atoms, it is not always possible for the octet rules to be followed rigorously. Oxidation numbers offer a summary of the octet rule each atom followed in the bonding process. Follow these rules to determine the oxidation number of any atom: 1. The ...
CHEM 5142
... experimental results for the Fe(aq)2+/3+ electron exchange rate, k22, and the calculated value obtained from cross reactions by the Marcus theory? c) What is the role of the sulfate ion in this reaction? VII. Activation, Addition and Insertion Reactions and Catalysis. ...
... experimental results for the Fe(aq)2+/3+ electron exchange rate, k22, and the calculated value obtained from cross reactions by the Marcus theory? c) What is the role of the sulfate ion in this reaction? VII. Activation, Addition and Insertion Reactions and Catalysis. ...
The Born-Haber Cycle
... Consider the strongly exothermic reaction between sodium metal and chlorine gas… ...
... Consider the strongly exothermic reaction between sodium metal and chlorine gas… ...
Inorganic Chemistry 412 / 512
... number of vertices, n, is the number of B atoms (4), sp this is an (n+3) or arachnotype structure. (b) Sketch the geometry of B4H10. (just show the arrangement of B atoms) [5 pts] See the butterfly structure in Figure 12.11 (c) Give the point group for the closo [B6H6]2- ion and describe the expecte ...
... number of vertices, n, is the number of B atoms (4), sp this is an (n+3) or arachnotype structure. (b) Sketch the geometry of B4H10. (just show the arrangement of B atoms) [5 pts] See the butterfly structure in Figure 12.11 (c) Give the point group for the closo [B6H6]2- ion and describe the expecte ...
lecture slides of chap8
... A metal ion with a net +3 charge has five electrons in the 3d subshell. What is this metal? (a) Cr (b) Mn (c) Fe (d) Co (e) Ni This species has +3 charges, which indicates that it has three more protons than the electrons. According to the question that it has five electrons in the 3d subshell, and ...
... A metal ion with a net +3 charge has five electrons in the 3d subshell. What is this metal? (a) Cr (b) Mn (c) Fe (d) Co (e) Ni This species has +3 charges, which indicates that it has three more protons than the electrons. According to the question that it has five electrons in the 3d subshell, and ...
Photoredox catalysis
_Schematic.png?width=300)
Photoredox catalysis is a branch of catalysis that harnesses the energy of visible light to accelerate a chemical reaction via a single-electron transfer. This area is named as a combination of ""photo-"" referring to light and redox, a condensed expression for the chemical processes of reduction and oxidation. In particular, photoredox catalysis employs small quantities of a light-sensitive compound that, when excited by light, can mediate the transfer of electrons between chemical compounds that otherwise would not react. Photoredox catalysts are generally drawn from three classes of materials: transition-metal complexes, organic dyes and semiconductors. While each class of materials has advantages, soluble transition-metal complexes are used most often.Study of this branch of catalysis led to the development of new methods to accomplish known and new chemical transformations. One attraction to the area is that photoredox catalysts are often less toxic than other reagents often used to generate free radicals, such as organotin reagents. Furthermore, while photoredox catalysts generate potent redox agents while exposed to light, they are innocuous under ordinary conditions Thus transition-metal complex photoredox catalysts are in some ways more attractive than stoichiometric redox agents such as quinones. The properties of photoredox catalysts can be modified by changing ligands and the metal, reflecting the somewhat modular nature of the catalyst.While photoredox catalysis has most often been applied to generate known reactive intermediates in a novel way, the study of this mode of catalysis led to the discovery of new organic reactions, such as the first direct functionalization of the β-arylation of saturated aldehydes. Although the D3-symmetric transition-metal complexes used in many photoredox-catalyzed reactions are chiral, the use of enantioenriched photoredox catalysts led to low levels of enantioselectivity in a photoredox-catalyzed aryl-aryl coupling reaction, suggesting that the chiral nature of these catalysts is not yet a highly effective means of transmitting stereochemical information in photoredox reactions. However, while synthetically useful levels of enantioselectivity have not been achieved using chiral photoredox catalysts alone, optically-active products have been obtained through the synergistic combination of photoredox catalysis with chiral organocatalysts such as secondary amines and Brønsted acids.