NOTES CHEMICAL REACTIONS:
... reaction (left side of arrow) • Law of Conservation of Mass must be satisfied! ...
... reaction (left side of arrow) • Law of Conservation of Mass must be satisfied! ...
James W. Whittaker - Oxygen reactions of the copper oxidases
... electrons a complex can deliver, as well as the redox potential of the metal complex. The importance of nuclearity is illustrated by the binuclear Cu(I)–Cu(I) centre of the oxygen-reactive site in haemocyanin, which is capable of reducing O2 by two electrons; this enables haemocyanin to carry oxygen ...
... electrons a complex can deliver, as well as the redox potential of the metal complex. The importance of nuclearity is illustrated by the binuclear Cu(I)–Cu(I) centre of the oxygen-reactive site in haemocyanin, which is capable of reducing O2 by two electrons; this enables haemocyanin to carry oxygen ...
Oxidation and Reduction
... Fictive charges which are given to an element by some rules. The oxidation number is described by positive or negative roman numbers and they are written above or in brackets after the element they are assigned to. Rules of the assignment of the oxidation number: *the sum of the ON’s of all the atom ...
... Fictive charges which are given to an element by some rules. The oxidation number is described by positive or negative roman numbers and they are written above or in brackets after the element they are assigned to. Rules of the assignment of the oxidation number: *the sum of the ON’s of all the atom ...
Microsoft Word
... One of the major current challenges before chemists to develop synthetic methods that are less polluting i.e. to design clean or green chemicals transformations. The chemical manufacturing processes should be such that they don’t cause permanent damage to the environment or disturb the ecological ba ...
... One of the major current challenges before chemists to develop synthetic methods that are less polluting i.e. to design clean or green chemicals transformations. The chemical manufacturing processes should be such that they don’t cause permanent damage to the environment or disturb the ecological ba ...
Final Exam Practice 2016 (MC)
... d) There are too many electrons in this diagram. The lone pair on carbon should instead be a double bond with one of oxygen’s lone pairs. 23. The molecules CO2 and SO2 have very similar formulas yet make a different shape. What is different about their Lewis structures that give them a different sha ...
... d) There are too many electrons in this diagram. The lone pair on carbon should instead be a double bond with one of oxygen’s lone pairs. 23. The molecules CO2 and SO2 have very similar formulas yet make a different shape. What is different about their Lewis structures that give them a different sha ...
effective nuclear charge
... in a multi-electron system, electrons are simultaneously attracted to the nucleus and repelled by each other outer electrons are shielded from full strength of nucleus ◦ screening effect effective nuclear charge is net positive charge that is attracting a particular electron Z is nuclear charge, S i ...
... in a multi-electron system, electrons are simultaneously attracted to the nucleus and repelled by each other outer electrons are shielded from full strength of nucleus ◦ screening effect effective nuclear charge is net positive charge that is attracting a particular electron Z is nuclear charge, S i ...
File - IGCSE STUDY BANK
... I was once asked "what is the opposite of a catalyst?" There is no real opposite to a catalyst, other than the uncatalysed reaction! The word catalyst means changing the rate of a reaction with some other material 'added to' or in 'contact with' the reaction mixture. There are the two phrases you ma ...
... I was once asked "what is the opposite of a catalyst?" There is no real opposite to a catalyst, other than the uncatalysed reaction! The word catalyst means changing the rate of a reaction with some other material 'added to' or in 'contact with' the reaction mixture. There are the two phrases you ma ...
Document
... 37. ___ The radius of an ion is always larger than the atomic radius of the original atom. 38. ___Most of the metals found above hydrogen in the activity series are found as elements in the ground. 39. __ Gold is a highly reactive metal. 40. ___ Barium hydroxide produced in a double displacement rea ...
... 37. ___ The radius of an ion is always larger than the atomic radius of the original atom. 38. ___Most of the metals found above hydrogen in the activity series are found as elements in the ground. 39. __ Gold is a highly reactive metal. 40. ___ Barium hydroxide produced in a double displacement rea ...
AP Chemistry Syllabus 2013 Mawhiney
... Labs form a foundation for student understanding of the chemical principles discussed in lectures but are also chosen to reflect the diversity of lab work generally completed in a first year course. Analysis of data from AP Chemistry examinees shows that increased laboratory time is correlated with ...
... Labs form a foundation for student understanding of the chemical principles discussed in lectures but are also chosen to reflect the diversity of lab work generally completed in a first year course. Analysis of data from AP Chemistry examinees shows that increased laboratory time is correlated with ...
Section 3: Modern Atomic Theory Atoms Section 3
... atom and that determines the atom’s chemical properties ...
... atom and that determines the atom’s chemical properties ...
Homogeneous and Heterogeneous Catalysis
... the surface, forming a mobile precursor state. The molecule B then collides with A on the surface, they react, bind and the new molecule desorbs. Any surface reaction can be described as following one of these mechanisms, or some combination of these mechanisms. In addition, all of these above mecha ...
... the surface, forming a mobile precursor state. The molecule B then collides with A on the surface, they react, bind and the new molecule desorbs. Any surface reaction can be described as following one of these mechanisms, or some combination of these mechanisms. In addition, all of these above mecha ...
Unit 13: Electrochemistry (Link to Prentice Hall Text: Chapters 22
... If you have 2 electrodes made of different metals connected, how can you tell which one is oxidized and which one is reduced? Table J! Oxidation If the metal is ______________ on Table J. (More active = easier to lose electrons) Reduction If the metal is ______________ on Table J. (Less active = har ...
... If you have 2 electrodes made of different metals connected, how can you tell which one is oxidized and which one is reduced? Table J! Oxidation If the metal is ______________ on Table J. (More active = easier to lose electrons) Reduction If the metal is ______________ on Table J. (Less active = har ...
chm5423chapter5notes..
... reaction. Finally, molecules with no significant removal processes in the troposphere can migrate into the stratosphere. In this chapter, we focus on the chemical reactions of organic molecules. Organic molecules are an important trace constituent in the lower atmosphere of the Earth. Organic molecu ...
... reaction. Finally, molecules with no significant removal processes in the troposphere can migrate into the stratosphere. In this chapter, we focus on the chemical reactions of organic molecules. Organic molecules are an important trace constituent in the lower atmosphere of the Earth. Organic molecu ...
Properties of Metals vs. Nonmetals vs. Metalloids
... Refer to your class notes, worksheets, and the textbook to complete this review sheet. Study early so that you will have time to ask questions about what you don’t understand. Do not forget to use your study guide from the first quarter exam to also help you review for your semester final. If you do ...
... Refer to your class notes, worksheets, and the textbook to complete this review sheet. Study early so that you will have time to ask questions about what you don’t understand. Do not forget to use your study guide from the first quarter exam to also help you review for your semester final. If you do ...
Properties of Metals vs. Nonmetals vs. Metalloids
... Refer to your class notes, worksheets, and the textbook to complete this review sheet. Study early so that you will have time to ask questions about what you don’t understand. Do not forget to use your study guide from the first quarter exam to also help you review for your semester final. If you do ...
... Refer to your class notes, worksheets, and the textbook to complete this review sheet. Study early so that you will have time to ask questions about what you don’t understand. Do not forget to use your study guide from the first quarter exam to also help you review for your semester final. If you do ...
CBSE/12th Class/2010/CHEMISTRY
... Ionic solids Ionic solids are insulators in solid state but conductors in molten state and in aqueous solutions. Ans.2 In chemical kinetics, the order of reaction with respect to a given substance (such as reactant, catalyst or product) is defined as the index, or exponent, to which its concentratio ...
... Ionic solids Ionic solids are insulators in solid state but conductors in molten state and in aqueous solutions. Ans.2 In chemical kinetics, the order of reaction with respect to a given substance (such as reactant, catalyst or product) is defined as the index, or exponent, to which its concentratio ...
Practice with Chemical Equilibrium (Chapter 14) (Due 2/17)
... C. The two reagents react to form PCl5 according to the reaction below: PCl3 + Cl2 = PCl5 At equilibrium, 0.0173 mol of PCl5 are present and the total gas pressure is 2.00 atm. What is the reaction's equilibrium constant? 2. K has a value of 50.0 at 448 oC for the reaction H2 + I2 = 2 HI. If 45 g of ...
... C. The two reagents react to form PCl5 according to the reaction below: PCl3 + Cl2 = PCl5 At equilibrium, 0.0173 mol of PCl5 are present and the total gas pressure is 2.00 atm. What is the reaction's equilibrium constant? 2. K has a value of 50.0 at 448 oC for the reaction H2 + I2 = 2 HI. If 45 g of ...
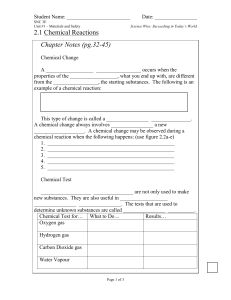
Chemical Reactions
... The ___________ of which a new substances forms is called the ___________ of __________________. Different chemical substances will produce _______________ at _________________ rates. Factor that affects rate of reaction Temperature ...
... The ___________ of which a new substances forms is called the ___________ of __________________. Different chemical substances will produce _______________ at _________________ rates. Factor that affects rate of reaction Temperature ...
Resource for Final Exam Prep
... 1 nm = 1 10-9 m Photoelectric effect kinetic energy of ejected electron Uncertainty principle you can estimate accurately the position and the momentum of an electron at the same time Quantum numbers (n, l, ml, ms), what do they each define? Value of l for s, p, d and f orbitals Energies of di ...
... 1 nm = 1 10-9 m Photoelectric effect kinetic energy of ejected electron Uncertainty principle you can estimate accurately the position and the momentum of an electron at the same time Quantum numbers (n, l, ml, ms), what do they each define? Value of l for s, p, d and f orbitals Energies of di ...
Molecular Geometry Why?
... is based on the premise that electrons around a central atom repel each other. Electron domains are areas of high electron density such as bonds (single, double or triple) and lone-pairs of electrons. In simple terms VSEPR means that all electron bonding domains and electron nonbonding domains aroun ...
... is based on the premise that electrons around a central atom repel each other. Electron domains are areas of high electron density such as bonds (single, double or triple) and lone-pairs of electrons. In simple terms VSEPR means that all electron bonding domains and electron nonbonding domains aroun ...
Fall Final Review Honors
... 4.84 10-19 J Hydrogen atoms have specific energy levels. Therefore, the atoms can only gain or lose certain amounts of energy. When atoms lose energy, they emit photons which correspond to the lines in the emission spectrum. The more energy lost, the more energy the photon has. Bohr’s model stated ...
... 4.84 10-19 J Hydrogen atoms have specific energy levels. Therefore, the atoms can only gain or lose certain amounts of energy. When atoms lose energy, they emit photons which correspond to the lines in the emission spectrum. The more energy lost, the more energy the photon has. Bohr’s model stated ...
CHE 101– Chapter 8 – Study Guide Terms: Products, reactants
... 4. Steps to Complete a Reaction – Be able to fill in the missing products or reactants for chemical reactions a. Identify the type of reaction b. Determine the reaction mechanism c. Determine if the reaction will occur i. Combination, Decomposition, Acid/Base and Combustion reactions are presumed to ...
... 4. Steps to Complete a Reaction – Be able to fill in the missing products or reactants for chemical reactions a. Identify the type of reaction b. Determine the reaction mechanism c. Determine if the reaction will occur i. Combination, Decomposition, Acid/Base and Combustion reactions are presumed to ...
Ch 7: Reactions
... • Questions to ask yourself if you cannot figure out the type of reaction: • Follow this series of questions. When you can answer "yes" to a question, then stop! • 1) Does your reaction have oxygen as one of it's reactants and carbon dioxide and water as products? If yes, then it's a combustion rea ...
... • Questions to ask yourself if you cannot figure out the type of reaction: • Follow this series of questions. When you can answer "yes" to a question, then stop! • 1) Does your reaction have oxygen as one of it's reactants and carbon dioxide and water as products? If yes, then it's a combustion rea ...
4. - period2chem
... always record one estimate digit 1200 m 4.84 10-19 J Hydrogen atoms have specific energy levels. Therefore, the atoms can only gain or lose certain amounts of energy. When atoms lose energy, they emit photons which correspond to the lines in the emission spectrum. The more energy lost, the more en ...
... always record one estimate digit 1200 m 4.84 10-19 J Hydrogen atoms have specific energy levels. Therefore, the atoms can only gain or lose certain amounts of energy. When atoms lose energy, they emit photons which correspond to the lines in the emission spectrum. The more energy lost, the more en ...
Photoredox catalysis
_Schematic.png?width=300)
Photoredox catalysis is a branch of catalysis that harnesses the energy of visible light to accelerate a chemical reaction via a single-electron transfer. This area is named as a combination of ""photo-"" referring to light and redox, a condensed expression for the chemical processes of reduction and oxidation. In particular, photoredox catalysis employs small quantities of a light-sensitive compound that, when excited by light, can mediate the transfer of electrons between chemical compounds that otherwise would not react. Photoredox catalysts are generally drawn from three classes of materials: transition-metal complexes, organic dyes and semiconductors. While each class of materials has advantages, soluble transition-metal complexes are used most often.Study of this branch of catalysis led to the development of new methods to accomplish known and new chemical transformations. One attraction to the area is that photoredox catalysts are often less toxic than other reagents often used to generate free radicals, such as organotin reagents. Furthermore, while photoredox catalysts generate potent redox agents while exposed to light, they are innocuous under ordinary conditions Thus transition-metal complex photoredox catalysts are in some ways more attractive than stoichiometric redox agents such as quinones. The properties of photoredox catalysts can be modified by changing ligands and the metal, reflecting the somewhat modular nature of the catalyst.While photoredox catalysis has most often been applied to generate known reactive intermediates in a novel way, the study of this mode of catalysis led to the discovery of new organic reactions, such as the first direct functionalization of the β-arylation of saturated aldehydes. Although the D3-symmetric transition-metal complexes used in many photoredox-catalyzed reactions are chiral, the use of enantioenriched photoredox catalysts led to low levels of enantioselectivity in a photoredox-catalyzed aryl-aryl coupling reaction, suggesting that the chiral nature of these catalysts is not yet a highly effective means of transmitting stereochemical information in photoredox reactions. However, while synthetically useful levels of enantioselectivity have not been achieved using chiral photoredox catalysts alone, optically-active products have been obtained through the synergistic combination of photoredox catalysis with chiral organocatalysts such as secondary amines and Brønsted acids.