transition metals
... 11.) Does the Qc for the formation of 1 mole of NO from its elements differ from the Qc of the decomposition of 1 mole of NO into its elements? Explain and give the relationship between the two Qc values. 12.) Balance the reaction and write the Qc a. ________NaHCO3 (s) ________Na2CO3 (s) + _______ ...
... 11.) Does the Qc for the formation of 1 mole of NO from its elements differ from the Qc of the decomposition of 1 mole of NO into its elements? Explain and give the relationship between the two Qc values. 12.) Balance the reaction and write the Qc a. ________NaHCO3 (s) ________Na2CO3 (s) + _______ ...
chemical reaction
... • Mole ratios: – how many moles of products are produced with given a number of moles of reactants. ...
... • Mole ratios: – how many moles of products are produced with given a number of moles of reactants. ...
2013 Final Exam Answers
... b) different because in each case there are a different number of electron pairs around the central atom. ...
... b) different because in each case there are a different number of electron pairs around the central atom. ...
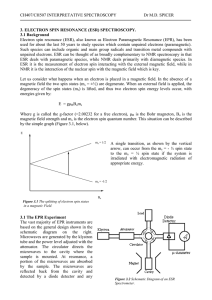
ESR Theory - Personal WWW Pages
... Interpretation of ESR spectra at a superficial level is fairly straightforward. Approximate values of g and A can be extracted, although second order effects and anisotropy can make it difficult to obtain accurate parameters. The g-values are indicative of the electron environment. The magnitude of ...
... Interpretation of ESR spectra at a superficial level is fairly straightforward. Approximate values of g and A can be extracted, although second order effects and anisotropy can make it difficult to obtain accurate parameters. The g-values are indicative of the electron environment. The magnitude of ...
CHEMISTRY I Final..#1..rev 4KEY
... the outer energy levels of the bonding metallic atoms are free to move from one atom to the next. Because they are free to move, these electrons are often referred to delocalized electrons and give metals ALL of the following properties EXCEPT. a. Malleable and ductile. c. Conduct heat and electrici ...
... the outer energy levels of the bonding metallic atoms are free to move from one atom to the next. Because they are free to move, these electrons are often referred to delocalized electrons and give metals ALL of the following properties EXCEPT. a. Malleable and ductile. c. Conduct heat and electrici ...
Topic 9 - Anderson High School
... • Negative chloride ions are attracted to the positive ions. There they lose electrons and are oxidized to chlorine gas: 2Cl-(l) → Cl2(g) + 2e• Positive sodium ions are attracted to the negative cathode. They gain electrons and are reduced to sodium metal: ...
... • Negative chloride ions are attracted to the positive ions. There they lose electrons and are oxidized to chlorine gas: 2Cl-(l) → Cl2(g) + 2e• Positive sodium ions are attracted to the negative cathode. They gain electrons and are reduced to sodium metal: ...
Key To T2 Review For Final Study Guide File - District 196 e
... 8. What is a limiting reactant? Why is this reactant so important? The limiting reactant is the reactant that runs out first in a chemical reaction, therefore determining the amount of product produced. 9. What is an excess reactant? The reactant that there is more than enough of to complete the lim ...
... 8. What is a limiting reactant? Why is this reactant so important? The limiting reactant is the reactant that runs out first in a chemical reaction, therefore determining the amount of product produced. 9. What is an excess reactant? The reactant that there is more than enough of to complete the lim ...
Define:
... 65. Write the electron configuration and the orbital diagram for phosphorus. How many unpaired electrons does phosphorus have? 66. Write the electron configurations for potassium, oxygen, and selenium. 67. Write the components of the electromagnetic spectrum in order of highest frequency to lowest f ...
... 65. Write the electron configuration and the orbital diagram for phosphorus. How many unpaired electrons does phosphorus have? 66. Write the electron configurations for potassium, oxygen, and selenium. 67. Write the components of the electromagnetic spectrum in order of highest frequency to lowest f ...
+ CuO Cu + O
... 2- The substance which loses an electron or more during a chemical reaction. (…………………………………………) 3- The substance which takes oxygen away or gives hydrogen during a chemical reaction. (………………………………………..) 4- A chemical process in which an atom loses an electron or more. ...
... 2- The substance which loses an electron or more during a chemical reaction. (…………………………………………) 3- The substance which takes oxygen away or gives hydrogen during a chemical reaction. (………………………………………..) 4- A chemical process in which an atom loses an electron or more. ...
Redox Reactions and Electrochemistry
... must equal the number gained by the reduced one) 7) Add half-reactions and cancel electrons and other common species on left and right sides of the equation. 8) Check Reaction! It should be balanced in terms of oxidation states, charge and atoms. IF NOT, YOU HAVE MADE A MISTAKE! ...
... must equal the number gained by the reduced one) 7) Add half-reactions and cancel electrons and other common species on left and right sides of the equation. 8) Check Reaction! It should be balanced in terms of oxidation states, charge and atoms. IF NOT, YOU HAVE MADE A MISTAKE! ...
Chapter 11
... more simpler products. ► AB A + B ► Decomposition reactions will always start with a single reactant. Most require energy. ► These are the opposite of combination reactions. ...
... more simpler products. ► AB A + B ► Decomposition reactions will always start with a single reactant. Most require energy. ► These are the opposite of combination reactions. ...
Redox Reactions and Electrochemistry
... must equal the number gained by the reduced one) 7) Add half-reactions and cancel electrons and other common species on left and right sides of the equation. 8) Check Reaction! It should be balanced in terms of oxidation states, charge and atoms. IF NOT, YOU HAVE MADE A MISTAKE! ...
... must equal the number gained by the reduced one) 7) Add half-reactions and cancel electrons and other common species on left and right sides of the equation. 8) Check Reaction! It should be balanced in terms of oxidation states, charge and atoms. IF NOT, YOU HAVE MADE A MISTAKE! ...
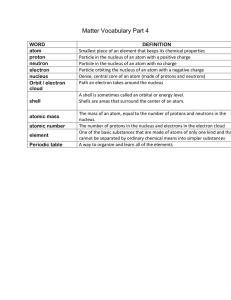
Matter Vocab Part 4
... Particle in the nucleus of an atom with a positive charge Particle in the nucleus of an atom with no charge Particle orbiting the nucleus of an atom with a negative charge Dense, central core of an atom (made of protons and neutrons) Path an electron takes around the nucleus A shell is sometimes cal ...
... Particle in the nucleus of an atom with a positive charge Particle in the nucleus of an atom with no charge Particle orbiting the nucleus of an atom with a negative charge Dense, central core of an atom (made of protons and neutrons) Path an electron takes around the nucleus A shell is sometimes cal ...
Chem. 121, Sec 11 Name: Student I.D. Please Show Your Work
... 17. Choose the paramagnetic atom or ion: Ca, Ne, Sc3+, Cl-, Na. Show Orbital diagrams. (5 marks) ...
... 17. Choose the paramagnetic atom or ion: Ca, Ne, Sc3+, Cl-, Na. Show Orbital diagrams. (5 marks) ...
In situ Raman Spectroscopic Study of Supported Molten Salt
... giving rise to formation of vanadium oxosulfato complexes ...
... giving rise to formation of vanadium oxosulfato complexes ...
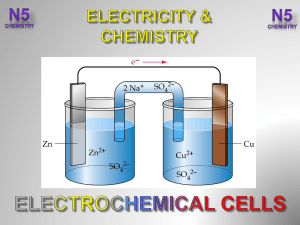
3.-Electrochemical-Cells-V2-
... Electrons flow in the external circuit from the species higher in the electrochemical series to the one lower in the electrochemical series. ...
... Electrons flow in the external circuit from the species higher in the electrochemical series to the one lower in the electrochemical series. ...
C1a - Mr Corfe
... Gold Au silver Ag RULE: An metal is more reactive if it is further to the left of the periodic table or further down in the group (not including groups 3-8) TYPES OF REACTIONS PHYSICAL – changing of states EXOTHERMIC – gives out heat ENDOTHERMIC – take in heat from it surrounding THERMAL DECOMPOSI ...
... Gold Au silver Ag RULE: An metal is more reactive if it is further to the left of the periodic table or further down in the group (not including groups 3-8) TYPES OF REACTIONS PHYSICAL – changing of states EXOTHERMIC – gives out heat ENDOTHERMIC – take in heat from it surrounding THERMAL DECOMPOSI ...
Electrochemistry
... oxidation number increases from 0 to +2, and H+ is reduced, because its oxidation number decreases from +1 to 0. The reducing agent is the substance that gives away electrons, thereby going to a higher oxidation number, and the oxidizing agent is the substance that accepts electrons, thereby going t ...
... oxidation number increases from 0 to +2, and H+ is reduced, because its oxidation number decreases from +1 to 0. The reducing agent is the substance that gives away electrons, thereby going to a higher oxidation number, and the oxidizing agent is the substance that accepts electrons, thereby going t ...
Chem 30A Final Exam
... 3. One set of reactants for rocket fuel is hydrazine, N2H4, and hydrogen peroxide, H2O2 which react vigorously when mixed: N2H4(l) + 2H2O2(l) N2(g) + 4H2O(g). A chemist mixes 2.0 mol N2H4 with 3.0 mol H2O2. What is the limiting reactant? How many moles of water ...
... 3. One set of reactants for rocket fuel is hydrazine, N2H4, and hydrogen peroxide, H2O2 which react vigorously when mixed: N2H4(l) + 2H2O2(l) N2(g) + 4H2O(g). A chemist mixes 2.0 mol N2H4 with 3.0 mol H2O2. What is the limiting reactant? How many moles of water ...
Redox
... Before metallurgy, humans discovered fire. The technology of fire has been crucial in the development of human cultures, but only relatively recently (18th century) have we come to realize the role of oxygen in burning. Understanding the connection of corrosion (rusting, tarnishing, etc.) and burnin ...
... Before metallurgy, humans discovered fire. The technology of fire has been crucial in the development of human cultures, but only relatively recently (18th century) have we come to realize the role of oxygen in burning. Understanding the connection of corrosion (rusting, tarnishing, etc.) and burnin ...
Final Exam Practice-2017
... 92. What is the element that is reduced in the following reaction? Br2 (g) + 2HI (aq) 2HBr (aq) + I2 (l) a) Br b) H c) I 93. Which of the following is the correct balanced half reaction for I2O5 I2 in a basic solution? a) 10H+ + I2O5 + 5e- I2 + 5H2O c) 5H2O + I2O5 + 5e- I2 + 10 OHb) 10H+ + I ...
... 92. What is the element that is reduced in the following reaction? Br2 (g) + 2HI (aq) 2HBr (aq) + I2 (l) a) Br b) H c) I 93. Which of the following is the correct balanced half reaction for I2O5 I2 in a basic solution? a) 10H+ + I2O5 + 5e- I2 + 5H2O c) 5H2O + I2O5 + 5e- I2 + 10 OHb) 10H+ + I ...
Coordination chemistry with selected topics in bioinorganic chemistry
... The lecture starts with the brief outline of the history of coordination chemistry. The basic concepts of coordination chemistry are defined including coordination compound, central atom, ligands, coordination bond, coordination number and coordination sphere. Special attention is given to the supra ...
... The lecture starts with the brief outline of the history of coordination chemistry. The basic concepts of coordination chemistry are defined including coordination compound, central atom, ligands, coordination bond, coordination number and coordination sphere. Special attention is given to the supra ...
3. atomic structure
... When an electron returns from a higher energy state to a lower energy state, it emits a specific amount of energy usually in the form of light. This is known as a bright line spectrum, and can be used to identify an element like a fingerprint. ...
... When an electron returns from a higher energy state to a lower energy state, it emits a specific amount of energy usually in the form of light. This is known as a bright line spectrum, and can be used to identify an element like a fingerprint. ...
IB Definitions
... The mass number is the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom The atomic number is equivalent to the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom Isotopes are atoms which have the same atomic number but different mass numbers (due to the presence of different numbers of neutro ...
... The mass number is the total number of protons and neutrons in the nucleus of an atom The atomic number is equivalent to the number of protons in the nucleus of an atom Isotopes are atoms which have the same atomic number but different mass numbers (due to the presence of different numbers of neutro ...
The chemical master equation
... Let N(t) = (N1 (t), N2 (t), . . . , Nn (t)) be the composition vector of the system, where Ni is the number of molecules of type i and n is the number of distinct chemical species. Let N be the space of all possible vectors N. Let P(N , t) be the probability distribution over the space N , i.e. the ...
... Let N(t) = (N1 (t), N2 (t), . . . , Nn (t)) be the composition vector of the system, where Ni is the number of molecules of type i and n is the number of distinct chemical species. Let N be the space of all possible vectors N. Let P(N , t) be the probability distribution over the space N , i.e. the ...
Photoredox catalysis
_Schematic.png?width=300)
Photoredox catalysis is a branch of catalysis that harnesses the energy of visible light to accelerate a chemical reaction via a single-electron transfer. This area is named as a combination of ""photo-"" referring to light and redox, a condensed expression for the chemical processes of reduction and oxidation. In particular, photoredox catalysis employs small quantities of a light-sensitive compound that, when excited by light, can mediate the transfer of electrons between chemical compounds that otherwise would not react. Photoredox catalysts are generally drawn from three classes of materials: transition-metal complexes, organic dyes and semiconductors. While each class of materials has advantages, soluble transition-metal complexes are used most often.Study of this branch of catalysis led to the development of new methods to accomplish known and new chemical transformations. One attraction to the area is that photoredox catalysts are often less toxic than other reagents often used to generate free radicals, such as organotin reagents. Furthermore, while photoredox catalysts generate potent redox agents while exposed to light, they are innocuous under ordinary conditions Thus transition-metal complex photoredox catalysts are in some ways more attractive than stoichiometric redox agents such as quinones. The properties of photoredox catalysts can be modified by changing ligands and the metal, reflecting the somewhat modular nature of the catalyst.While photoredox catalysis has most often been applied to generate known reactive intermediates in a novel way, the study of this mode of catalysis led to the discovery of new organic reactions, such as the first direct functionalization of the β-arylation of saturated aldehydes. Although the D3-symmetric transition-metal complexes used in many photoredox-catalyzed reactions are chiral, the use of enantioenriched photoredox catalysts led to low levels of enantioselectivity in a photoredox-catalyzed aryl-aryl coupling reaction, suggesting that the chiral nature of these catalysts is not yet a highly effective means of transmitting stereochemical information in photoredox reactions. However, while synthetically useful levels of enantioselectivity have not been achieved using chiral photoredox catalysts alone, optically-active products have been obtained through the synergistic combination of photoredox catalysis with chiral organocatalysts such as secondary amines and Brønsted acids.