M.Sc.Course - Department of Chemistry, IIT Bombay
... CH211/CH 229 Chemical thermodynamics Thermodynamic functions, laws of thermodynamics, properties of entropy, criteria for spontaneity and equilibrium, properties of free energy, Gibbs and Maxwell's relations. Chemical potential, ideal and real gases, properties of fugacity, mixing and excess functio ...
... CH211/CH 229 Chemical thermodynamics Thermodynamic functions, laws of thermodynamics, properties of entropy, criteria for spontaneity and equilibrium, properties of free energy, Gibbs and Maxwell's relations. Chemical potential, ideal and real gases, properties of fugacity, mixing and excess functio ...
Influence of Storage on the Composition of Clarified Apple Juice
... to 5, hydrolysis appeared to be the major cause of sucrose reduction (and reducing sugars increase) at a rate determined by pH and temperature. Akhavan and Wrolstad (1980) verified that slight losses (6%) in total sugars occur after 112 days of storage at 37°C of pear concentrate. Stadtman (1948) co ...
... to 5, hydrolysis appeared to be the major cause of sucrose reduction (and reducing sugars increase) at a rate determined by pH and temperature. Akhavan and Wrolstad (1980) verified that slight losses (6%) in total sugars occur after 112 days of storage at 37°C of pear concentrate. Stadtman (1948) co ...
Unit 6 Chemical Energy
... Everything humans do requires energy. It is a major factor in social change on our planet. Technologies, which inevitably consume energy, are developed for a social purpose. These technologies, however, often have drawbacks related to their use of energy. The control and use of our present sources o ...
... Everything humans do requires energy. It is a major factor in social change on our planet. Technologies, which inevitably consume energy, are developed for a social purpose. These technologies, however, often have drawbacks related to their use of energy. The control and use of our present sources o ...
Chemical Reaction Equations
... Reactions are fast – the reaction must occur within a reasonable time (see pg. 280) Reactions are quantitative – one that is more than 99% complete; in other words, at least one reactant is completely used up Reactions are stoichiometric – means that there is a simple whole-number ratio of chemical ...
... Reactions are fast – the reaction must occur within a reasonable time (see pg. 280) Reactions are quantitative – one that is more than 99% complete; in other words, at least one reactant is completely used up Reactions are stoichiometric – means that there is a simple whole-number ratio of chemical ...
Cold interactions between an Yb ion and a Li atom
... Equations (6), (7), and (9) give rate constants for a single scattering energy E. In practice, we have an ensemble of thermally populated states and the rate constants at a temperature T are obtained by performing a Boltzmann average, ...
... Equations (6), (7), and (9) give rate constants for a single scattering energy E. In practice, we have an ensemble of thermally populated states and the rate constants at a temperature T are obtained by performing a Boltzmann average, ...
Electronic state dependence in dissociation of core
... water was suggested to be one of the four fundamental elements in nature [1]. The theory of the four elements was the standard dogma for nearly two thousand years. During the 19th century it became evident that water was a substance made up by small molecules consisting of even smaller atoms. The di ...
... water was suggested to be one of the four fundamental elements in nature [1]. The theory of the four elements was the standard dogma for nearly two thousand years. During the 19th century it became evident that water was a substance made up by small molecules consisting of even smaller atoms. The di ...
data table - Tenafly Public Schools
... the same? _______________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 4. How many characteristic properties of two substances must be different for the two substances to be the different? ___________________________ ...
... the same? _______________________________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________________ 4. How many characteristic properties of two substances must be different for the two substances to be the different? ___________________________ ...
Higher Chemistry Resources Guide - Glow Blogs
... thiosufate and acid to investigate the effect of concentration on reaction rate. http://rsc.li/1icyVlR Details of RSC experiment using potassium iodate and bisulfite/starch solution to investigate the effect of concentration and temperature on reaction rate. http://rsc.li/1gtJVXZ ...
... thiosufate and acid to investigate the effect of concentration on reaction rate. http://rsc.li/1icyVlR Details of RSC experiment using potassium iodate and bisulfite/starch solution to investigate the effect of concentration and temperature on reaction rate. http://rsc.li/1gtJVXZ ...
chemistry
... 54 Determine the total number of neutrons in an atom of Si-29. [1] 55 In the space in your answer booklet, show a correct numerical setup for calculating the atomic mass of Si. [1] 56 A scientist calculated the percent natural abundance of Si-30 in a sample to be 3.29%. Determine the percent error f ...
... 54 Determine the total number of neutrons in an atom of Si-29. [1] 55 In the space in your answer booklet, show a correct numerical setup for calculating the atomic mass of Si. [1] 56 A scientist calculated the percent natural abundance of Si-30 in a sample to be 3.29%. Determine the percent error f ...
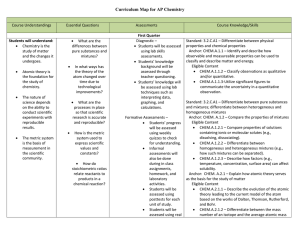
AP Chemistry Curriculum Map - Belle Vernon Area School District
... selected elements by using their locations on the periodic table and known trends. Standard: 3.2.C.A1 – Use electronegativity to explain the difference between polar and non-polar covalent bonds. Anchor: CHEM.A.2.3 – Explain how periodic trends in the properties of atoms allow for the prediction of ...
... selected elements by using their locations on the periodic table and known trends. Standard: 3.2.C.A1 – Use electronegativity to explain the difference between polar and non-polar covalent bonds. Anchor: CHEM.A.2.3 – Explain how periodic trends in the properties of atoms allow for the prediction of ...
Transition state theory
Transition state theory (TST) explains the reaction rates of elementary chemical reactions. The theory assumes a special type of chemical equilibrium (quasi-equilibrium) between reactants and activated transition state complexes.TST is used primarily to understand qualitatively how chemical reactions take place. TST has been less successful in its original goal of calculating absolute reaction rate constants because the calculation of absolute reaction rates requires precise knowledge of potential energy surfaces, but it has been successful in calculating the standard enthalpy of activation (Δ‡Hɵ), the standard entropy of activation (Δ‡Sɵ), and the standard Gibbs energy of activation (Δ‡Gɵ) for a particular reaction if its rate constant has been experimentally determined. (The ‡ notation refers to the value of interest at the transition state.)This theory was developed simultaneously in 1935 by Henry Eyring, then at Princeton University, and by Meredith Gwynne Evans and Michael Polanyi of the University of Manchester. TST is also referred to as ""activated-complex theory,"" ""absolute-rate theory,"" and ""theory of absolute reaction rates.""Before the development of TST, the Arrhenius rate law was widely used to determine energies for the reaction barrier. The Arrhenius equation derives from empirical observations and ignores any mechanistic considerations, such as whether one or more reactive intermediates are involved in the conversion of a reactant to a product. Therefore, further development was necessary to understand the two parameters associated with this law, the pre-exponential factor (A) and the activation energy (Ea). TST, which led to the Eyring equation, successfully addresses these two issues; however, 46 years elapsed between the publication of the Arrhenius rate law, in 1889, and the Eyring equation derived from TST, in 1935. During that period, many scientists and researchers contributed significantly to the development of the theory.