Chapter 15a
... hydrolysis. We will go through examples of each of these types of problems one at a time. Strong Acids and Strong Bases The strength of the acid is determined by how far the equilibrium lies to the right. Qualitatively, this may be judged by the Ka of the acid. A large Ka indicates a strong acid; a ...
... hydrolysis. We will go through examples of each of these types of problems one at a time. Strong Acids and Strong Bases The strength of the acid is determined by how far the equilibrium lies to the right. Qualitatively, this may be judged by the Ka of the acid. A large Ka indicates a strong acid; a ...
Document
... out of first. The excess reagent is the one you have left over. The limiting reagent determines how much product you can make ...
... out of first. The excess reagent is the one you have left over. The limiting reagent determines how much product you can make ...
AQA GCSE Chemistry My Revision Notes
... ethene. Ethene is then converted into ethanol. (h) Describe how ethanol, C2H5OH, can be produced from ethene. (2 marks) (i) Ethanol can be made using either sugar or alkanes as the starting material. Evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of using these two starting materials to produce ethanol. ...
... ethene. Ethene is then converted into ethanol. (h) Describe how ethanol, C2H5OH, can be produced from ethene. (2 marks) (i) Ethanol can be made using either sugar or alkanes as the starting material. Evaluate the advantages and disadvantages of using these two starting materials to produce ethanol. ...
Chapter 4
... This was written as a molecular equation in which all reactants and products are shown as complete, neutral chemical formulas. ...
... This was written as a molecular equation in which all reactants and products are shown as complete, neutral chemical formulas. ...
Kool Colors
... may turn black or may show signs of rust. Steel is primarily made from iron, and, when iron oxidizes, we call it rust. If something loses electrons, something else must gain those electrons. In this case, the dye in the Kool-Aid solution is gaining electrons and is said to be reduced. When the dye r ...
... may turn black or may show signs of rust. Steel is primarily made from iron, and, when iron oxidizes, we call it rust. If something loses electrons, something else must gain those electrons. In this case, the dye in the Kool-Aid solution is gaining electrons and is said to be reduced. When the dye r ...
The Complete Notes - Joliet Junior College
... reads: “Do not exceed a 150 N load” and you must use this information to determine the maximum weight a child must not exceed in order to be protected during a collision at 55 mph. Can you do it? A child’s life, not to mention the financial future of your employer, may depend on your ability to solv ...
... reads: “Do not exceed a 150 N load” and you must use this information to determine the maximum weight a child must not exceed in order to be protected during a collision at 55 mph. Can you do it? A child’s life, not to mention the financial future of your employer, may depend on your ability to solv ...
Disproportionation of Gold(II)
... spin contamination as measured by the 〈S2〉 expectation value was minimal. Isolation of the disproportionation transition state used the QST3 method.32 Other stationary points (all minima, i.e., zero imaginary frequencies as confirmed by calculation of the energy Hessian at the calculated stationary ...
... spin contamination as measured by the 〈S2〉 expectation value was minimal. Isolation of the disproportionation transition state used the QST3 method.32 Other stationary points (all minima, i.e., zero imaginary frequencies as confirmed by calculation of the energy Hessian at the calculated stationary ...
exam2gc1sum11+key
... 394 kJ/mol, ΔH°f[H2O(l)] = –286 kJ/mol) C8H8 + 10O2(g) → 8CO2(g) + 4H2O(l) ΔH°rxn = –4439 kJ/mol A. 143 kJ/mol B. -143 kJ/mol C. 8735 kJ/mol D. –3759 kJ/mol ____18. A gas is allowed to expand doing 5 J of work. If the gas absorbs 250 J of heat from the surroundings, what is the change in internal en ...
... 394 kJ/mol, ΔH°f[H2O(l)] = –286 kJ/mol) C8H8 + 10O2(g) → 8CO2(g) + 4H2O(l) ΔH°rxn = –4439 kJ/mol A. 143 kJ/mol B. -143 kJ/mol C. 8735 kJ/mol D. –3759 kJ/mol ____18. A gas is allowed to expand doing 5 J of work. If the gas absorbs 250 J of heat from the surroundings, what is the change in internal en ...
Task 4 6 points - Austrian Chemistry Olympiad
... 5.14. One of the following MO-schemes shows the energies for the molecular orbitals of CO in correct sequence. Choose the right scheme by correctly „occupying“ it with electrons (arrows) and indicating the LUMO. ...
... 5.14. One of the following MO-schemes shows the energies for the molecular orbitals of CO in correct sequence. Choose the right scheme by correctly „occupying“ it with electrons (arrows) and indicating the LUMO. ...
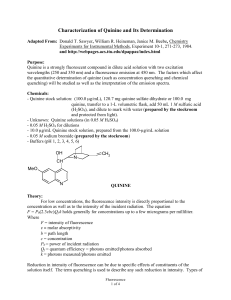
Characterization of Quinine and Its Determination
... quinine.) If a significant number of molecules are already in a vibrationally excited state before excitation, some overlap occurs in the absorption and emission spectra because less energy is needed to excite these molecules to the S1 level. The types of transitions associated with fluorescence inc ...
... quinine.) If a significant number of molecules are already in a vibrationally excited state before excitation, some overlap occurs in the absorption and emission spectra because less energy is needed to excite these molecules to the S1 level. The types of transitions associated with fluorescence inc ...
Transition state theory
Transition state theory (TST) explains the reaction rates of elementary chemical reactions. The theory assumes a special type of chemical equilibrium (quasi-equilibrium) between reactants and activated transition state complexes.TST is used primarily to understand qualitatively how chemical reactions take place. TST has been less successful in its original goal of calculating absolute reaction rate constants because the calculation of absolute reaction rates requires precise knowledge of potential energy surfaces, but it has been successful in calculating the standard enthalpy of activation (Δ‡Hɵ), the standard entropy of activation (Δ‡Sɵ), and the standard Gibbs energy of activation (Δ‡Gɵ) for a particular reaction if its rate constant has been experimentally determined. (The ‡ notation refers to the value of interest at the transition state.)This theory was developed simultaneously in 1935 by Henry Eyring, then at Princeton University, and by Meredith Gwynne Evans and Michael Polanyi of the University of Manchester. TST is also referred to as ""activated-complex theory,"" ""absolute-rate theory,"" and ""theory of absolute reaction rates.""Before the development of TST, the Arrhenius rate law was widely used to determine energies for the reaction barrier. The Arrhenius equation derives from empirical observations and ignores any mechanistic considerations, such as whether one or more reactive intermediates are involved in the conversion of a reactant to a product. Therefore, further development was necessary to understand the two parameters associated with this law, the pre-exponential factor (A) and the activation energy (Ea). TST, which led to the Eyring equation, successfully addresses these two issues; however, 46 years elapsed between the publication of the Arrhenius rate law, in 1889, and the Eyring equation derived from TST, in 1935. During that period, many scientists and researchers contributed significantly to the development of the theory.