Review Packet
... ____ 94. According to kinetic molecular theory, gas particles a. are spaced far apart. b. are constantly moving. c. have mass. d. all of the above. ____ 95. Kinetic energy a. is energy associated with movement. b. increases with increasing temperature. c. is given by ½mv2 d. all of the above. ____ 9 ...
... ____ 94. According to kinetic molecular theory, gas particles a. are spaced far apart. b. are constantly moving. c. have mass. d. all of the above. ____ 95. Kinetic energy a. is energy associated with movement. b. increases with increasing temperature. c. is given by ½mv2 d. all of the above. ____ 9 ...
CHEM121 Exam 4 ObjectivesW16
... 25.0 mL of hydrochloric acid were titrated with 0.125M sodium hydroxide. 35.6 mL of the base were required to reach the equivalence point. a. Write a balanced equation . ...
... 25.0 mL of hydrochloric acid were titrated with 0.125M sodium hydroxide. 35.6 mL of the base were required to reach the equivalence point. a. Write a balanced equation . ...
Document
... 2HCl(aq) + Cr(s) H2(g)+ CrCl2(aq) A. composition B. single-displacement C. decomposition D. double-displacement ...
... 2HCl(aq) + Cr(s) H2(g)+ CrCl2(aq) A. composition B. single-displacement C. decomposition D. double-displacement ...
Chemical Reactions and Enzymes
... “lock and key” model effect of temp. and pH on enzyme activity effect of concentration on enzyme activity ...
... “lock and key” model effect of temp. and pH on enzyme activity effect of concentration on enzyme activity ...
Sample
... 2- Explain the relationship between temperature and the rate of a chemical reaction in terms of collision theory? ...
... 2- Explain the relationship between temperature and the rate of a chemical reaction in terms of collision theory? ...
CCN2275 Physical Chemistry
... Gibbs energy function and equilibrium constants, phase rule, ClausiusClapeyron equation; Effect of change in state variables on some state/path functions. ...
... Gibbs energy function and equilibrium constants, phase rule, ClausiusClapeyron equation; Effect of change in state variables on some state/path functions. ...
國立嘉義大學95學年度
... 19. Which conditions of P, T, and n, respectively, are most ideal? (A) high P, highT, high n. (B) low P, lowT, low n. (C) high P, lowT, high n. 20. At STP, Which gas has the highest density? (A) H2 21. At STP, Which gas has the slowest average speed? ...
... 19. Which conditions of P, T, and n, respectively, are most ideal? (A) high P, highT, high n. (B) low P, lowT, low n. (C) high P, lowT, high n. 20. At STP, Which gas has the highest density? (A) H2 21. At STP, Which gas has the slowest average speed? ...
Chemical Reactions presentation
... Chemical Bonds and Energy The heat produced by a propane grill is a form of energy. When you write the chemical equation for the combustion of propane, you can include “heat” on the right side of the equation. C3H8 + 5O2 3CO2 + 4H2O + Heat ...
... Chemical Bonds and Energy The heat produced by a propane grill is a form of energy. When you write the chemical equation for the combustion of propane, you can include “heat” on the right side of the equation. C3H8 + 5O2 3CO2 + 4H2O + Heat ...
EETopic Coversheet Word document
... Know that an increase in pressure will favour the side with less gas particles for a reaction at equilibrium Know that an increase in temperature will favour the direction which takes in heat (endothermic) for a reaction at equilibrium Know that an increase in concentration of reactants will favour ...
... Know that an increase in pressure will favour the side with less gas particles for a reaction at equilibrium Know that an increase in temperature will favour the direction which takes in heat (endothermic) for a reaction at equilibrium Know that an increase in concentration of reactants will favour ...
Rates of Reaction: Chemical Kinetics 50
... A. increases as temperature decreases. B. decreases when a catalyst is added. C. increases as reactant concentration increases. D. decreases as reactant concentration increases. ...
... A. increases as temperature decreases. B. decreases when a catalyst is added. C. increases as reactant concentration increases. D. decreases as reactant concentration increases. ...
國立嘉義大學九十二學年度
... (A) The average kinetic energies of molecules from samples of different "ideal" gases is the same at the same temperature. (B) The molecules of an ideal gas are relatively far apart. (C) All molecules of an ideal gas have the same kinetic energy at constant temperature. (D) Molecules of a gas underg ...
... (A) The average kinetic energies of molecules from samples of different "ideal" gases is the same at the same temperature. (B) The molecules of an ideal gas are relatively far apart. (C) All molecules of an ideal gas have the same kinetic energy at constant temperature. (D) Molecules of a gas underg ...
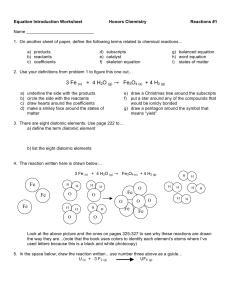
Equation Intro Worksheet 1213
... Look at the above picture and the ones on pages 325-327 to see why these reactions are drawn the way they are…(note that the book uses colors to identify each element’s atoms where I’ve used letters because this is a black and white photocopy) 5. In the space below, draw the reaction written…use num ...
... Look at the above picture and the ones on pages 325-327 to see why these reactions are drawn the way they are…(note that the book uses colors to identify each element’s atoms where I’ve used letters because this is a black and white photocopy) 5. In the space below, draw the reaction written…use num ...
P2-Equilibrium Activity
... Not all chemical reactions reach completion where the limiting reactant is consumed completely. In fact, most chemical reactions that occur in living systems never reach completion. Rather, they produce some amount of product then appear to stop reacting in the forward direction, never fully consumi ...
... Not all chemical reactions reach completion where the limiting reactant is consumed completely. In fact, most chemical reactions that occur in living systems never reach completion. Rather, they produce some amount of product then appear to stop reacting in the forward direction, never fully consumi ...
Transition state theory
Transition state theory (TST) explains the reaction rates of elementary chemical reactions. The theory assumes a special type of chemical equilibrium (quasi-equilibrium) between reactants and activated transition state complexes.TST is used primarily to understand qualitatively how chemical reactions take place. TST has been less successful in its original goal of calculating absolute reaction rate constants because the calculation of absolute reaction rates requires precise knowledge of potential energy surfaces, but it has been successful in calculating the standard enthalpy of activation (Δ‡Hɵ), the standard entropy of activation (Δ‡Sɵ), and the standard Gibbs energy of activation (Δ‡Gɵ) for a particular reaction if its rate constant has been experimentally determined. (The ‡ notation refers to the value of interest at the transition state.)This theory was developed simultaneously in 1935 by Henry Eyring, then at Princeton University, and by Meredith Gwynne Evans and Michael Polanyi of the University of Manchester. TST is also referred to as ""activated-complex theory,"" ""absolute-rate theory,"" and ""theory of absolute reaction rates.""Before the development of TST, the Arrhenius rate law was widely used to determine energies for the reaction barrier. The Arrhenius equation derives from empirical observations and ignores any mechanistic considerations, such as whether one or more reactive intermediates are involved in the conversion of a reactant to a product. Therefore, further development was necessary to understand the two parameters associated with this law, the pre-exponential factor (A) and the activation energy (Ea). TST, which led to the Eyring equation, successfully addresses these two issues; however, 46 years elapsed between the publication of the Arrhenius rate law, in 1889, and the Eyring equation derived from TST, in 1935. During that period, many scientists and researchers contributed significantly to the development of the theory.