Entropy and reaction spontaneity Gibbs free energy
... coefficient. For perfect solutions f=1. For real solutions f→1 when c→0. Standard state for compounds in solutions is when a=1. Physical Chemistry EPM/04 ...
... coefficient. For perfect solutions f=1. For real solutions f→1 when c→0. Standard state for compounds in solutions is when a=1. Physical Chemistry EPM/04 ...
MCQ plus answers
... Use a dark lead pencil so that you can use an eraser if you make an error. Errors made in ink cannot be corrected – you will need to ask the examination supervisor for another sheet. Boxes with faint or incomplete lines or not completed in the prescribed manner may not be read. Be sure to complete t ...
... Use a dark lead pencil so that you can use an eraser if you make an error. Errors made in ink cannot be corrected – you will need to ask the examination supervisor for another sheet. Boxes with faint or incomplete lines or not completed in the prescribed manner may not be read. Be sure to complete t ...
Chapter 14 – Chemical Reactions
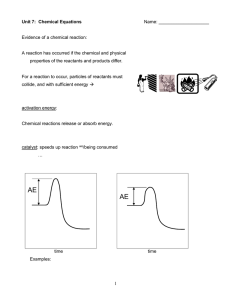
... Reactants – the _____________ materials of a chemical _____________ Products – the substances _____________ as a _____________ of a chemical _____________ Coefficient – a _____________ placed in _____________ of a chemical _____________ or _____________ All chemical equations must be balanced. Steps ...
... Reactants – the _____________ materials of a chemical _____________ Products – the substances _____________ as a _____________ of a chemical _____________ Coefficient – a _____________ placed in _____________ of a chemical _____________ or _____________ All chemical equations must be balanced. Steps ...
Reversible and irreversible reactions - Chemwiki
... reversible reactions the reaction takes place in both the forward and backward directions. The reversible reaction may be expressed as: ...
... reversible reactions the reaction takes place in both the forward and backward directions. The reversible reaction may be expressed as: ...
CHEM 313 - Suraj @ LUMS
... surfaces and their inequalities; canonical ensemble and partition function Q; relation to molecular partition function and thermodynamic quantities. Entropy and probability; mixtures of gases and entropy changes at low temperatures. ...
... surfaces and their inequalities; canonical ensemble and partition function Q; relation to molecular partition function and thermodynamic quantities. Entropy and probability; mixtures of gases and entropy changes at low temperatures. ...
this PDF file
... reaction. However it is not easy to accurately calculate and plot the standard free energy changes and equilibrium constants for reactions due to the calculation complexity of reactions and phase transitions. It is found in the literature (Li, 2001) that it is not simple and convenient for calculati ...
... reaction. However it is not easy to accurately calculate and plot the standard free energy changes and equilibrium constants for reactions due to the calculation complexity of reactions and phase transitions. It is found in the literature (Li, 2001) that it is not simple and convenient for calculati ...
CH 115 Exam 2 - UAB General Chemistry Supplemental Instruction
... Assume the chemical equations on this exam are NOT balanced unless stated otherwise. 1. Balance the equation and give the stoichiometric coefficient for HCl ...
... Assume the chemical equations on this exam are NOT balanced unless stated otherwise. 1. Balance the equation and give the stoichiometric coefficient for HCl ...
THERMOCHEMISTRY ENERGETICS/ENTHALPY
... than the reactants, so energy is given out Also in an exothermic reaction more bonds are made than are broken, so overall energy is given out Activation energy (Ea) – is the minimal amount of energy needed to start the reaction (i.e. minimum amount of energy to break bonds in the reactants). ...
... than the reactants, so energy is given out Also in an exothermic reaction more bonds are made than are broken, so overall energy is given out Activation energy (Ea) – is the minimal amount of energy needed to start the reaction (i.e. minimum amount of energy to break bonds in the reactants). ...
Ch. 15 Study Guide
... 19. half-life, t1/2 : time required for the concentration of a reactant to decrease to half its initial value. 20. First-order reaction half-lives do not depend on the initial concentration. 21. Second-order and zero-order reaction half-lives do depend on initial concentration. 22. Generally, reacti ...
... 19. half-life, t1/2 : time required for the concentration of a reactant to decrease to half its initial value. 20. First-order reaction half-lives do not depend on the initial concentration. 21. Second-order and zero-order reaction half-lives do depend on initial concentration. 22. Generally, reacti ...
UNIT 1 - StudyGuide.PK
... www.studyguide.pk energy cycles, and carry out calculations involving such cycles and relevant energy ...
... www.studyguide.pk energy cycles, and carry out calculations involving such cycles and relevant energy ...
Transition state theory
Transition state theory (TST) explains the reaction rates of elementary chemical reactions. The theory assumes a special type of chemical equilibrium (quasi-equilibrium) between reactants and activated transition state complexes.TST is used primarily to understand qualitatively how chemical reactions take place. TST has been less successful in its original goal of calculating absolute reaction rate constants because the calculation of absolute reaction rates requires precise knowledge of potential energy surfaces, but it has been successful in calculating the standard enthalpy of activation (Δ‡Hɵ), the standard entropy of activation (Δ‡Sɵ), and the standard Gibbs energy of activation (Δ‡Gɵ) for a particular reaction if its rate constant has been experimentally determined. (The ‡ notation refers to the value of interest at the transition state.)This theory was developed simultaneously in 1935 by Henry Eyring, then at Princeton University, and by Meredith Gwynne Evans and Michael Polanyi of the University of Manchester. TST is also referred to as ""activated-complex theory,"" ""absolute-rate theory,"" and ""theory of absolute reaction rates.""Before the development of TST, the Arrhenius rate law was widely used to determine energies for the reaction barrier. The Arrhenius equation derives from empirical observations and ignores any mechanistic considerations, such as whether one or more reactive intermediates are involved in the conversion of a reactant to a product. Therefore, further development was necessary to understand the two parameters associated with this law, the pre-exponential factor (A) and the activation energy (Ea). TST, which led to the Eyring equation, successfully addresses these two issues; however, 46 years elapsed between the publication of the Arrhenius rate law, in 1889, and the Eyring equation derived from TST, in 1935. During that period, many scientists and researchers contributed significantly to the development of the theory.