entropy - KFUPM Faculty List
... The second law of thermodynamics says that for a process to be spontaneous as written (in the for- ward direction), Suniv must be positive. An equilibrium process is one that does not occur spontaneously in either the net forward or net reverse direction but can be made to occur by the addition or ...
... The second law of thermodynamics says that for a process to be spontaneous as written (in the for- ward direction), Suniv must be positive. An equilibrium process is one that does not occur spontaneously in either the net forward or net reverse direction but can be made to occur by the addition or ...
Branham
... interactions lead to slower crystal growth because of the repulsion [8]. However, it should be noted that while these factors are important, it has already been discussed that other factors such as concentration and agitation influence crystal growth, and certain factors may be more important than o ...
... interactions lead to slower crystal growth because of the repulsion [8]. However, it should be noted that while these factors are important, it has already been discussed that other factors such as concentration and agitation influence crystal growth, and certain factors may be more important than o ...
Fulltext
... Fig. 1. Kink and jog models for a lipid bilayer (DPPC), Here we show lipids only with one chain. The circles indicate the head groups and zig-zag lines indicate the CH2 chains. All the summations in this equation are over all various states of DPPC. Where N is the t.%tl number of lipid molecules, A ...
... Fig. 1. Kink and jog models for a lipid bilayer (DPPC), Here we show lipids only with one chain. The circles indicate the head groups and zig-zag lines indicate the CH2 chains. All the summations in this equation are over all various states of DPPC. Where N is the t.%tl number of lipid molecules, A ...
Kinetics and Mechanism of Uncatalyzed and Ag (I) Catalyzed
... The rate initially increases, and then tends towards a limiting value with increasing hydrogen ion concentration in uncatalyzed reaction. Similarly, in case of silver (I) catalyzed reaction, the hydrogen ion concentration was varied from 0.5-2.5 mol dm-3, employing perchloric acid at fixed concentra ...
... The rate initially increases, and then tends towards a limiting value with increasing hydrogen ion concentration in uncatalyzed reaction. Similarly, in case of silver (I) catalyzed reaction, the hydrogen ion concentration was varied from 0.5-2.5 mol dm-3, employing perchloric acid at fixed concentra ...
Chapter 5HW_Ans
... b) conversion factor: x X moles of C2H2; therefore 7 moles of O2 2molesC 2 H 2 as moles of C2H2 cancel as they are in both numerator and denominator 2molesC 2 H 2 c) conversion factor: x X moles of H2O; therefore 0.5 moles of 2molesH 2 O C2H2 as moles of H2O cancel as they are in both numerator and ...
... b) conversion factor: x X moles of C2H2; therefore 7 moles of O2 2molesC 2 H 2 as moles of C2H2 cancel as they are in both numerator and denominator 2molesC 2 H 2 c) conversion factor: x X moles of H2O; therefore 0.5 moles of 2molesH 2 O C2H2 as moles of H2O cancel as they are in both numerator and ...
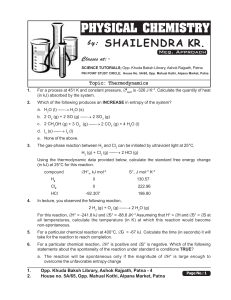
Thermodynamics - Shailendra Kumar Chemistry
... Which of the following statements concerning the change in ∆G° and ∆G during a chemical reaction is most correct? a. ∆G° remains constant while ∆G changes and becomes equal to ∆G° at equilibrium. b. Both ∆G° and ∆G remain constant during a chemical reaction. c. Initially both ∆G and ∆G° are equal to ...
... Which of the following statements concerning the change in ∆G° and ∆G during a chemical reaction is most correct? a. ∆G° remains constant while ∆G changes and becomes equal to ∆G° at equilibrium. b. Both ∆G° and ∆G remain constant during a chemical reaction. c. Initially both ∆G and ∆G° are equal to ...
Sample Exercise 15.1 Writing Equilibrium
... (b) In (i) we have 0.60 mol/L product and 0.40 mol/L reactant, Kc = 0.600/0.40 = 1.5. (You will get the same result by merely dividing the number of spheres of each kind: 6 spheres/4 spheres = 1.5.) In (ii) we have 0.10 mol/L product and 0.90 mol/L reactant, giving Kc = 0.10/0.90 = 0.11 (or 1 sphere ...
... (b) In (i) we have 0.60 mol/L product and 0.40 mol/L reactant, Kc = 0.600/0.40 = 1.5. (You will get the same result by merely dividing the number of spheres of each kind: 6 spheres/4 spheres = 1.5.) In (ii) we have 0.10 mol/L product and 0.90 mol/L reactant, giving Kc = 0.10/0.90 = 0.11 (or 1 sphere ...
Copyright © 2004 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Benjamin
... Biochemistry—chemistry of living organisms ; essential for understanding physiology because body functions involve chemical changes that occur within cells. ...
... Biochemistry—chemistry of living organisms ; essential for understanding physiology because body functions involve chemical changes that occur within cells. ...
3 CO 2 (g) + 4 H 2 O(l)
... Every chemical species has what chemists call enthalpy. The enthalpy of a substance is the ability of that species to produce Heat. Almost every chemical reaction produces or absorbs heat and we will learn how to calculate the amount of heat associated with any particular chemical change. When we he ...
... Every chemical species has what chemists call enthalpy. The enthalpy of a substance is the ability of that species to produce Heat. Almost every chemical reaction produces or absorbs heat and we will learn how to calculate the amount of heat associated with any particular chemical change. When we he ...
Mechanistic Studies of the Reactions of Silicon
... concentrations. The results are consistent with a two-step mechanism involving reversible formation of a silene-alcohol complex, followed by intracomplex proton transfer. The latter is rate-determining in all cases but acetic acid, for which it is proposed that complexation is the rate-determining s ...
... concentrations. The results are consistent with a two-step mechanism involving reversible formation of a silene-alcohol complex, followed by intracomplex proton transfer. The latter is rate-determining in all cases but acetic acid, for which it is proposed that complexation is the rate-determining s ...
ConcepTest On Simple Redox Reactions
... Comment to Instructor: Correct answer is 3. HCl. Since the oxidation number of H is decreasing from +1 to 0, it is undergoing reduction. Zn is being oxidized, and HCl is the “agent” that is causing the Zn to be oxidized. #4 indicates that the student is thinking that the Zn+2in ZnCl2 is undergoing r ...
... Comment to Instructor: Correct answer is 3. HCl. Since the oxidation number of H is decreasing from +1 to 0, it is undergoing reduction. Zn is being oxidized, and HCl is the “agent” that is causing the Zn to be oxidized. #4 indicates that the student is thinking that the Zn+2in ZnCl2 is undergoing r ...
Chem101 - Lecture 5 Introduction Introduction
... • In this reaction the sulfur is oxidized while the oxygen is reduced. University of Wisconsin-Eau Claire ...
... • In this reaction the sulfur is oxidized while the oxygen is reduced. University of Wisconsin-Eau Claire ...
June 01, 2008
... As a chemist working in the forensics department of the SAPS, you were called upon to identify an unknown powder that was found at 3 different crime scenes. Your preliminary examination of the powder samples obtained from Scene 1 and Scene 2 might suggest it being an illegal drug (a date-rape drug). ...
... As a chemist working in the forensics department of the SAPS, you were called upon to identify an unknown powder that was found at 3 different crime scenes. Your preliminary examination of the powder samples obtained from Scene 1 and Scene 2 might suggest it being an illegal drug (a date-rape drug). ...
20. Chemical Equilibrium
... In most of the chemical reactions we have studied so far, it appears as though all of the reactants are converted to products before a reaction stops. In truth, however, experiments show that the conversion of reactants into products is often incomplete in chemical reactions. This is the case no mat ...
... In most of the chemical reactions we have studied so far, it appears as though all of the reactants are converted to products before a reaction stops. In truth, however, experiments show that the conversion of reactants into products is often incomplete in chemical reactions. This is the case no mat ...
10th CBSE {SA - 1} Revision Pack Booklet - 3
... No, all metals do not react with caustic soda. 8. To an aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide, a few drops of phenolphthalein were added. What do you observe? To this solution small amount of dilute HCl was added. What do you observe now? Explain your answer. ...
... No, all metals do not react with caustic soda. 8. To an aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide, a few drops of phenolphthalein were added. What do you observe? To this solution small amount of dilute HCl was added. What do you observe now? Explain your answer. ...
Energy Flow and Chemical Change
... reversed: In the chemical change, the reactants (wax and O2) contain more energy than the products (CO2 and H2O), and the difference in energy is released as heat and light. Then, during the physical change, some of that heat is absorbed when lower energy ice melts and forms higher energy water. Thi ...
... reversed: In the chemical change, the reactants (wax and O2) contain more energy than the products (CO2 and H2O), and the difference in energy is released as heat and light. Then, during the physical change, some of that heat is absorbed when lower energy ice melts and forms higher energy water. Thi ...
Transition state theory
Transition state theory (TST) explains the reaction rates of elementary chemical reactions. The theory assumes a special type of chemical equilibrium (quasi-equilibrium) between reactants and activated transition state complexes.TST is used primarily to understand qualitatively how chemical reactions take place. TST has been less successful in its original goal of calculating absolute reaction rate constants because the calculation of absolute reaction rates requires precise knowledge of potential energy surfaces, but it has been successful in calculating the standard enthalpy of activation (Δ‡Hɵ), the standard entropy of activation (Δ‡Sɵ), and the standard Gibbs energy of activation (Δ‡Gɵ) for a particular reaction if its rate constant has been experimentally determined. (The ‡ notation refers to the value of interest at the transition state.)This theory was developed simultaneously in 1935 by Henry Eyring, then at Princeton University, and by Meredith Gwynne Evans and Michael Polanyi of the University of Manchester. TST is also referred to as ""activated-complex theory,"" ""absolute-rate theory,"" and ""theory of absolute reaction rates.""Before the development of TST, the Arrhenius rate law was widely used to determine energies for the reaction barrier. The Arrhenius equation derives from empirical observations and ignores any mechanistic considerations, such as whether one or more reactive intermediates are involved in the conversion of a reactant to a product. Therefore, further development was necessary to understand the two parameters associated with this law, the pre-exponential factor (A) and the activation energy (Ea). TST, which led to the Eyring equation, successfully addresses these two issues; however, 46 years elapsed between the publication of the Arrhenius rate law, in 1889, and the Eyring equation derived from TST, in 1935. During that period, many scientists and researchers contributed significantly to the development of the theory.