MINDS-ON 3: Fuel Combustion
... Develop students’ understanding that in an incomplete combustion reaction, a number of different products can form which include carbon, carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, and water. Explain that which products are actually formed depend on the amount of oxygen present. Carbon monoxide (CO), a toxic g ...
... Develop students’ understanding that in an incomplete combustion reaction, a number of different products can form which include carbon, carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, and water. Explain that which products are actually formed depend on the amount of oxygen present. Carbon monoxide (CO), a toxic g ...
Chemical Engineering Principles of CVD Processes
... EXHAUST SYSTEM The exhaust system usually includes - a vacuum pump - a total pressure control system & - a scrubber The selection of vacuum pump depends - The process e.g. pumping capacity required - pressure range to be used & - gases to be pumped ...
... EXHAUST SYSTEM The exhaust system usually includes - a vacuum pump - a total pressure control system & - a scrubber The selection of vacuum pump depends - The process e.g. pumping capacity required - pressure range to be used & - gases to be pumped ...
CH 8 blackboard
... Mass Moles Moles Mass However, since the original quantity of NO2 is given in kilograms, you must first convert to grams. Since the final quantity is requested in kilograms, you must convert back to kilograms at the end. The main conversion factor is the stoichiometric relationship between mol ...
... Mass Moles Moles Mass However, since the original quantity of NO2 is given in kilograms, you must first convert to grams. Since the final quantity is requested in kilograms, you must convert back to kilograms at the end. The main conversion factor is the stoichiometric relationship between mol ...
Chemistry General v. 2016
... 3.2.10.A1 Predict properties of elements using trends of the periodic table. Bohr Model- The simplest modern picture of the structure of the atom, according to which electrons move in orbits around the nucleus; Electron Configuration- The arrangement of electrons in an atom; Electromagnetic Radiatio ...
... 3.2.10.A1 Predict properties of elements using trends of the periodic table. Bohr Model- The simplest modern picture of the structure of the atom, according to which electrons move in orbits around the nucleus; Electron Configuration- The arrangement of electrons in an atom; Electromagnetic Radiatio ...
Teaching to Standards: Science
... of the bags and to touch the pictures in the Student Response Guide. For example, say: You’re looking at salt. This is salt. Review the concept of solute. While holding the bags, say: This is flour. This is salt. This is baking soda. They are solids and are the solutes for our experiment today. Then ...
... of the bags and to touch the pictures in the Student Response Guide. For example, say: You’re looking at salt. This is salt. Review the concept of solute. While holding the bags, say: This is flour. This is salt. This is baking soda. They are solids and are the solutes for our experiment today. Then ...
CHEMISTRY / ELECTROCHEMISTRY OF THE SULPHUR
... Tarnishing of Cu and alloys, including these metals by H2S in air of varying relative humidity in the concentration range 2% down to ppb, has been studied by various authors. In the main, when oxidising gases are absent, the rates appear to follow a parabolic law. Exceptions to this statement are th ...
... Tarnishing of Cu and alloys, including these metals by H2S in air of varying relative humidity in the concentration range 2% down to ppb, has been studied by various authors. In the main, when oxidising gases are absent, the rates appear to follow a parabolic law. Exceptions to this statement are th ...
Part II - American Chemical Society
... Part II of this test requires that student answers be written in a response booklet of blank pages. Only this “Blue Book” is graded for a score on Part II. Testing materials, scratch paper, and the “Blue Book” should be made available to the student only during the examination period. All testing ma ...
... Part II of this test requires that student answers be written in a response booklet of blank pages. Only this “Blue Book” is graded for a score on Part II. Testing materials, scratch paper, and the “Blue Book” should be made available to the student only during the examination period. All testing ma ...
C:\My Documents\My Documents\Teaching\chem130\hunt
... to provide you with practice at solving quantitative problems. It is in your best interests to work through all these questions independently before the exam. Please note that the first midterm exam may also include questions related to Chapter 1 (Introduction) and Chapter 4 ...
... to provide you with practice at solving quantitative problems. It is in your best interests to work through all these questions independently before the exam. Please note that the first midterm exam may also include questions related to Chapter 1 (Introduction) and Chapter 4 ...
Lecture 10
... August 24, 1888), was a German physicist and mathematician, and was one of thefounders of thermodynamics. His most important paper, on the mechanical theory of heat, published in 1850, first stated the basic ideas of the second law of thermodynamics. In 1865 he introduced the concept of entropy. He ...
... August 24, 1888), was a German physicist and mathematician, and was one of thefounders of thermodynamics. His most important paper, on the mechanical theory of heat, published in 1850, first stated the basic ideas of the second law of thermodynamics. In 1865 he introduced the concept of entropy. He ...
Dynamic modeling of electrochemical systems using linear graph
... to eliminate the branch through and chord across variables from the set of system equations. A compact set of final equations can be obtained by substituting (3) and (4) into the terminal equations. As discussed above, the cutset, circuit, and terminal equations provide a necessary and sufficient set ...
... to eliminate the branch through and chord across variables from the set of system equations. A compact set of final equations can be obtained by substituting (3) and (4) into the terminal equations. As discussed above, the cutset, circuit, and terminal equations provide a necessary and sufficient set ...
Unit 6: Reactions and Stoichiometry
... Big Numbers and Chemistry At the most fundamental level, the chemist needs a unit that describes a very large quantity. One of the most well-known numbers in the study of chemistry is number of units in a mole. The number of units in a mole is called Avogadro’s number (named after the Italian physic ...
... Big Numbers and Chemistry At the most fundamental level, the chemist needs a unit that describes a very large quantity. One of the most well-known numbers in the study of chemistry is number of units in a mole. The number of units in a mole is called Avogadro’s number (named after the Italian physic ...
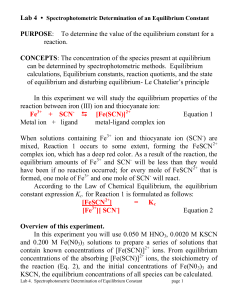
PURPOSE: To determine the value of the equilibrium constant for a
... 8. An error was made in preparing the KSCN solution in Part A. Its concentration was 0.003 molar but was labeled as 0.002 molar. How would the slope of the calibration curve (absorbance on the y-axis versus concentration of Fe(SCN)2+on the x-axis) be affected? How would this impact your Kc in Part C ...
... 8. An error was made in preparing the KSCN solution in Part A. Its concentration was 0.003 molar but was labeled as 0.002 molar. How would the slope of the calibration curve (absorbance on the y-axis versus concentration of Fe(SCN)2+on the x-axis) be affected? How would this impact your Kc in Part C ...
Chapter 19 Chemical Thermodynamics
... which H is estimated: S° = nS°(products) - mS°(reactants) where n and m are the coefficients in the Chemical ...
... which H is estimated: S° = nS°(products) - mS°(reactants) where n and m are the coefficients in the Chemical ...
Transition state theory
Transition state theory (TST) explains the reaction rates of elementary chemical reactions. The theory assumes a special type of chemical equilibrium (quasi-equilibrium) between reactants and activated transition state complexes.TST is used primarily to understand qualitatively how chemical reactions take place. TST has been less successful in its original goal of calculating absolute reaction rate constants because the calculation of absolute reaction rates requires precise knowledge of potential energy surfaces, but it has been successful in calculating the standard enthalpy of activation (Δ‡Hɵ), the standard entropy of activation (Δ‡Sɵ), and the standard Gibbs energy of activation (Δ‡Gɵ) for a particular reaction if its rate constant has been experimentally determined. (The ‡ notation refers to the value of interest at the transition state.)This theory was developed simultaneously in 1935 by Henry Eyring, then at Princeton University, and by Meredith Gwynne Evans and Michael Polanyi of the University of Manchester. TST is also referred to as ""activated-complex theory,"" ""absolute-rate theory,"" and ""theory of absolute reaction rates.""Before the development of TST, the Arrhenius rate law was widely used to determine energies for the reaction barrier. The Arrhenius equation derives from empirical observations and ignores any mechanistic considerations, such as whether one or more reactive intermediates are involved in the conversion of a reactant to a product. Therefore, further development was necessary to understand the two parameters associated with this law, the pre-exponential factor (A) and the activation energy (Ea). TST, which led to the Eyring equation, successfully addresses these two issues; however, 46 years elapsed between the publication of the Arrhenius rate law, in 1889, and the Eyring equation derived from TST, in 1935. During that period, many scientists and researchers contributed significantly to the development of the theory.