Stop-Signal Task - Gemstone Honors Program
... behavior. The stop-signal task, a popular method used in neuroscience and psychology to measure impulsivity, has shown that those with ADHD tend to have slower inhibition response times (Eagle & Baunez, 2010). Poor performance on these tasks is observed after pharmacological manipulation of prefront ...
... behavior. The stop-signal task, a popular method used in neuroscience and psychology to measure impulsivity, has shown that those with ADHD tend to have slower inhibition response times (Eagle & Baunez, 2010). Poor performance on these tasks is observed after pharmacological manipulation of prefront ...
Age-dependent effect of cholinergic lesion on dendritic morphology
... to young adults [46]. Similarly, the axonal sprouting typically seen in hippocampal neurons following partial deafferentation via lesions of entorhinal cortex is reduced in aged rats [52]. Finally, lesions of the nucleus basalis magnocellularis (NBM) attenuate benzodiazepine-induced potentiation of ...
... to young adults [46]. Similarly, the axonal sprouting typically seen in hippocampal neurons following partial deafferentation via lesions of entorhinal cortex is reduced in aged rats [52]. Finally, lesions of the nucleus basalis magnocellularis (NBM) attenuate benzodiazepine-induced potentiation of ...
What creates a valuable cue? The underestimated importance of a
... brain and this trace is then considered to be what we call a memory. Since various cortical areas are activated during the perception and experience of an event, same goes for the retrieval of this memory (Rugg et al., 2008). This means that when we encode an event with phonological and visual metho ...
... brain and this trace is then considered to be what we call a memory. Since various cortical areas are activated during the perception and experience of an event, same goes for the retrieval of this memory (Rugg et al., 2008). This means that when we encode an event with phonological and visual metho ...
Document
... Research in Dr. Jaffe’s lab focuses on the hippocampal formation; a brain region important for certain aspects of learning and memory. It is also one of the first brain structures affected by Alzheimer's disease and medial temporal lobe epilepsy arises in the hippocampus, among other brain structure ...
... Research in Dr. Jaffe’s lab focuses on the hippocampal formation; a brain region important for certain aspects of learning and memory. It is also one of the first brain structures affected by Alzheimer's disease and medial temporal lobe epilepsy arises in the hippocampus, among other brain structure ...
Lecture 1
... Myelinated axons: sheath of Schwann and myelin sheath one Schwann cell myelinates a single axon multiple Schwann cells needed to cover entire length of an axon ...
... Myelinated axons: sheath of Schwann and myelin sheath one Schwann cell myelinates a single axon multiple Schwann cells needed to cover entire length of an axon ...
Ecological dominance, social competition, and coalitionary arms
... evolution of brain and cognitive systems above and beyond more traditional modular systems (Fodor, 1983; Tooby & Cosmides, 1995). These systems have been cast in terms of general intelligence, domain-general abilities, or executive functions that are capable of integrating and co-opting information ...
... evolution of brain and cognitive systems above and beyond more traditional modular systems (Fodor, 1983; Tooby & Cosmides, 1995). These systems have been cast in terms of general intelligence, domain-general abilities, or executive functions that are capable of integrating and co-opting information ...
Does the Conventional Leaky Integrate-and
... 2- Variation of the delay between pre-synaptic spike arrival and post-synaptic channel opening, in different synapses. (Synaptic noise) 3- The noise due to spontaneous firings of the neurons, which is often treated as a Poisson process. (Spontaneous noise) Thus, if the cortical neural groups are ass ...
... 2- Variation of the delay between pre-synaptic spike arrival and post-synaptic channel opening, in different synapses. (Synaptic noise) 3- The noise due to spontaneous firings of the neurons, which is often treated as a Poisson process. (Spontaneous noise) Thus, if the cortical neural groups are ass ...
7 Memory
... just before their house was robbed. If there was little or no other encoding, however, you might not be able to remember the make, model, or color of the car. The second basic memory process is storage, which refers to the maintenance of information in memory over time—often over a very long time. W ...
... just before their house was robbed. If there was little or no other encoding, however, you might not be able to remember the make, model, or color of the car. The second basic memory process is storage, which refers to the maintenance of information in memory over time—often over a very long time. W ...
The formation of novel social category conjunctions in working
... novel. We focus entirely on encounters that are novel, that is when familiarity is at zero and constituent compatibility is the driving mechanism informing representational development (i.e. novel conjunctions). In these cases familiarity of the conjunction is of interest and not the constituent cat ...
... novel. We focus entirely on encounters that are novel, that is when familiarity is at zero and constituent compatibility is the driving mechanism informing representational development (i.e. novel conjunctions). In these cases familiarity of the conjunction is of interest and not the constituent cat ...
Cerebellar Affective Syndrome Expanding Our Thinking About the
... Entirely afferent fibers originating within the pontine nuclei as part of the cerebral cortex>pons>cerebellar tract. ...
... Entirely afferent fibers originating within the pontine nuclei as part of the cerebral cortex>pons>cerebellar tract. ...
Neural Prostheses - Gert Cauwenberghs
... – Inner hair cells excited by basilar membrane vibrations, amplified by outer hair cells, stimulate cochlear nerve fibers in the healthy cochlea. – Electrodes in the cochlear implant stimulate cochlear nerve fibers with alternating current signals, of amplitude representative of sound intensity. ...
... – Inner hair cells excited by basilar membrane vibrations, amplified by outer hair cells, stimulate cochlear nerve fibers in the healthy cochlea. – Electrodes in the cochlear implant stimulate cochlear nerve fibers with alternating current signals, of amplitude representative of sound intensity. ...
How Spike Generation Mechanisms Determine the Neuronal
... sodium channels) determines the speed with which neurons can track changes in input. Key words: populations of spiking neurons; noise; dynamics; sodium channel; integrate-and-fire model; conductance-based model ...
... sodium channels) determines the speed with which neurons can track changes in input. Key words: populations of spiking neurons; noise; dynamics; sodium channel; integrate-and-fire model; conductance-based model ...
Transcripts/01_15 11
... a. Another way to think of this is to group by the nuclei functions. i. So you have relay nuclei (i.e., relay to the cortex), Association nuclei, and “Other” nuclei including the Interlaminar and Reticular. b. Relay Nuclei: i. Note that there is a table in the book that may break these relay nuclei ...
... a. Another way to think of this is to group by the nuclei functions. i. So you have relay nuclei (i.e., relay to the cortex), Association nuclei, and “Other” nuclei including the Interlaminar and Reticular. b. Relay Nuclei: i. Note that there is a table in the book that may break these relay nuclei ...
Quantitative Assessment of the Distributions of Membrane
... pipettes after pulling off the dye-filled pipette. The waveform command signal in pCLAMP 9.2 (Molecular Devices) was used to voltage-clamp the soma using a waveform prerecorded in current clamp in the same neuron. With a second channel in current-clamp mode, the amplitude of the somatic response was ...
... pipettes after pulling off the dye-filled pipette. The waveform command signal in pCLAMP 9.2 (Molecular Devices) was used to voltage-clamp the soma using a waveform prerecorded in current clamp in the same neuron. With a second channel in current-clamp mode, the amplitude of the somatic response was ...
Cortical Maps - White Rose Research Online
... one might graph the excitation of one neuron by another against the distance that separates them in the tissue. Or an interaction may be described in terms of the functional relationships between neurons, as one might graph the correspondence between neurons as a function of the similarity of their ...
... one might graph the excitation of one neuron by another against the distance that separates them in the tissue. Or an interaction may be described in terms of the functional relationships between neurons, as one might graph the correspondence between neurons as a function of the similarity of their ...
Rapid eye movement sleep deprivation induces an increase in
... areas rather than in large ones. There are significant differences in Achase activity among discrete regions (8). These differences are also observed in smaller brain areas such as discrete nuclei (9). Therefore, the small significant differences (11 to 15%) in enzyme activity obtained in our study ...
... areas rather than in large ones. There are significant differences in Achase activity among discrete regions (8). These differences are also observed in smaller brain areas such as discrete nuclei (9). Therefore, the small significant differences (11 to 15%) in enzyme activity obtained in our study ...
Prefrontal Cortex, Emotion, and Approach/Withdrawal Motivation
... suggesting that refinement of the models might be needed to fully account for the relationship between frontal asymmetry, motivation, and emotion. Research has tended to support aspects of both Heller’s (1986, 1990) and Davidson’s (1983) models. Although these models have often been treated as if th ...
... suggesting that refinement of the models might be needed to fully account for the relationship between frontal asymmetry, motivation, and emotion. Research has tended to support aspects of both Heller’s (1986, 1990) and Davidson’s (1983) models. Although these models have often been treated as if th ...
Phantom Limbs and Neural Plasticity
... are important for 2 reasons: First, they suggest that, contrary to the static picture of brain maps provided by neuroanatomists, topography is extremely labile. Even in the adult brain, massive reorganization can occur over extremely short periods, and referred sensations can therefore be used as a ...
... are important for 2 reasons: First, they suggest that, contrary to the static picture of brain maps provided by neuroanatomists, topography is extremely labile. Even in the adult brain, massive reorganization can occur over extremely short periods, and referred sensations can therefore be used as a ...
Brain Oscillations Control Timing of Single
... 5Functional Neurosurgery Unit, Tel-Aviv Medical Center and Sackler Faculty of Medicine, Tel-Aviv University, Tel-Aviv 69978, Israel ...
... 5Functional Neurosurgery Unit, Tel-Aviv Medical Center and Sackler Faculty of Medicine, Tel-Aviv University, Tel-Aviv 69978, Israel ...
Discussion and future directions
... connections link regions with matched characteristic frequencies (Read et al., 2001). Recent modeling of eye–saccades planning in the lateral intraparietal area (Xing and Andersen, 2000) have shown that in order to hold memory activity for a saccades, the neural population develops excitatory connec ...
... connections link regions with matched characteristic frequencies (Read et al., 2001). Recent modeling of eye–saccades planning in the lateral intraparietal area (Xing and Andersen, 2000) have shown that in order to hold memory activity for a saccades, the neural population develops excitatory connec ...
Computational Modelling of Mental Imagery in Chess: A Sensitivity
... Chase & Simon, 1973). The visuo-spatial information stored there can be subjected to visuo-spatial mental operations; in chess, it is the place where, for example, the trajectories of pieces are computed. The information stored in the mind’s eye decays rapidly and needs to be updated either by input ...
... Chase & Simon, 1973). The visuo-spatial information stored there can be subjected to visuo-spatial mental operations; in chess, it is the place where, for example, the trajectories of pieces are computed. The information stored in the mind’s eye decays rapidly and needs to be updated either by input ...
Visuomotor development
... 1987; Cliff, 1990). Research carried out on understanding simpler animals behavior indicated that all sensorimotor systems interact with their immediate surroundings by forming a closed loop with the environment (Cliff, 1995). It was suggested that: • Sensorimotor pathways generating adaptive behavi ...
... 1987; Cliff, 1990). Research carried out on understanding simpler animals behavior indicated that all sensorimotor systems interact with their immediate surroundings by forming a closed loop with the environment (Cliff, 1995). It was suggested that: • Sensorimotor pathways generating adaptive behavi ...
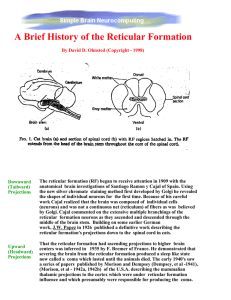
A Brief History of the Reticular Formation
... states that whenever the motivation is the same, a defined set of stimuli will always release a specific motor response. Lorentz was the first to propose this concept in a 1935 German paper but not until 1948 and 1951 did Tinbergen introduce this concept to the English speaking world. The region of ...
... states that whenever the motivation is the same, a defined set of stimuli will always release a specific motor response. Lorentz was the first to propose this concept in a 1935 German paper but not until 1948 and 1951 did Tinbergen introduce this concept to the English speaking world. The region of ...