Respiration in Organisms
... 10. The mountaineers carry oxygen with them becausea. At an altitude of more than 5 km there is no air. b. The amount of air available to a person is less than that available on the ground. c. The temperature of air is higher than that on the ground. d. The pressure of air is higher than that on th ...
... 10. The mountaineers carry oxygen with them becausea. At an altitude of more than 5 km there is no air. b. The amount of air available to a person is less than that available on the ground. c. The temperature of air is higher than that on the ground. d. The pressure of air is higher than that on th ...
Respiratory System
... LUNGS – Paired and cone shaped; right lung- 3 lobes, left lung – two lobes; fill pleural divisions of the thoracic cavity; Pleural Membrane – a serous membrane that encloses and protects, Parietal Pleura – outer layer, Pleural Cavity- small space between membranes; Bronchiopulmonary segment to lobul ...
... LUNGS – Paired and cone shaped; right lung- 3 lobes, left lung – two lobes; fill pleural divisions of the thoracic cavity; Pleural Membrane – a serous membrane that encloses and protects, Parietal Pleura – outer layer, Pleural Cavity- small space between membranes; Bronchiopulmonary segment to lobul ...
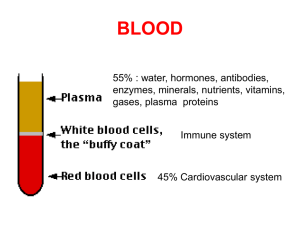
blood
... about a group of related men in a village nearby who bled severely from little wounds or simple surgeries. ...
... about a group of related men in a village nearby who bled severely from little wounds or simple surgeries. ...
ESUHSD Marking Period __2__: September 27th to October 5th
... Use the fluid mosaic model to illustrate and explain the structure and function of the cell membrane. ...
... Use the fluid mosaic model to illustrate and explain the structure and function of the cell membrane. ...
5 Levels of Organization Notes
... Within multi-cellular organisms there is Division of labor. Division of labor - the work (labor) of keeping the organism alive is divided (division) among the different parts of the body. Each part has a job to do and as each part does its special job, it works in harmony with all the other parts. ...
... Within multi-cellular organisms there is Division of labor. Division of labor - the work (labor) of keeping the organism alive is divided (division) among the different parts of the body. Each part has a job to do and as each part does its special job, it works in harmony with all the other parts. ...
Final Exam Review
... Mary Stangler Center for Academic Success This review is meant to highlight basic concepts from the units covered in this course. It does not cover all concepts presented by your instructor. Refer back to your notes, unit objectives, labs, handouts, etc. to further prepare for your exam. ...
... Mary Stangler Center for Academic Success This review is meant to highlight basic concepts from the units covered in this course. It does not cover all concepts presented by your instructor. Refer back to your notes, unit objectives, labs, handouts, etc. to further prepare for your exam. ...
Final Exam Review
... Mary Stangler Center for Academic Success This review is meant to highlight basic concepts from the units covered in this course. It does not cover all concepts presented by your instructor. Refer back to your notes, unit objectives, labs, handouts, etc. to further prepare for your exam. ...
... Mary Stangler Center for Academic Success This review is meant to highlight basic concepts from the units covered in this course. It does not cover all concepts presented by your instructor. Refer back to your notes, unit objectives, labs, handouts, etc. to further prepare for your exam. ...
Responsible for the continuation of the plant species by sexual or
... Homeostasis: regulation of conditions within a cell (like osmosis) or an organism (like blood sugar balance), or system (like ecosystem balance), which allows for stable, internal balance (equilibrium) Internal feedback mechanism: self-regulating process that can help maintain homeostasis. Examples ...
... Homeostasis: regulation of conditions within a cell (like osmosis) or an organism (like blood sugar balance), or system (like ecosystem balance), which allows for stable, internal balance (equilibrium) Internal feedback mechanism: self-regulating process that can help maintain homeostasis. Examples ...
Human Anatomy and Physiology
... 1. Cells ~ the basic unit of structure and function of living organisms 2. Tissues ~ similar cells that are grouped together to perform a similar function 3. Organs ~ tissues grouped together to perform a specific function. One organ may contain more than one type of tissue. The heart contains tissu ...
... 1. Cells ~ the basic unit of structure and function of living organisms 2. Tissues ~ similar cells that are grouped together to perform a similar function 3. Organs ~ tissues grouped together to perform a specific function. One organ may contain more than one type of tissue. The heart contains tissu ...
Honeybee Heart
... Life is an emergent property, defined in terms of a cell, limited by a membrane, which separates the boundary of the living system inside from the non-living outside. This is simply true for the vast world of unicellular organisms. Larger organisms - plants and animals - that are multicellular, have ...
... Life is an emergent property, defined in terms of a cell, limited by a membrane, which separates the boundary of the living system inside from the non-living outside. This is simply true for the vast world of unicellular organisms. Larger organisms - plants and animals - that are multicellular, have ...
Document
... are not in a distinct nucleus. d) Yeast is a single-celled organism. Yeast cells have a nucleus, cytoplasm and a membrane surrounded by a cell wall. e) Cells may be specialised to carry out a particular function. ...
... are not in a distinct nucleus. d) Yeast is a single-celled organism. Yeast cells have a nucleus, cytoplasm and a membrane surrounded by a cell wall. e) Cells may be specialised to carry out a particular function. ...
Click here for printer-friendly sample test questions
... 5. What human body system breaks down food and absorbs nutrients? A. Digestive B. Endocrine C. Respiratory D. Skeletal 6. What two body systems work together to produce movement? A. Circulatory and skeletal B. Muscular and digestive C. Respiration and nervous D. Skeletal and muscular Depth of Knowle ...
... 5. What human body system breaks down food and absorbs nutrients? A. Digestive B. Endocrine C. Respiratory D. Skeletal 6. What two body systems work together to produce movement? A. Circulatory and skeletal B. Muscular and digestive C. Respiration and nervous D. Skeletal and muscular Depth of Knowle ...
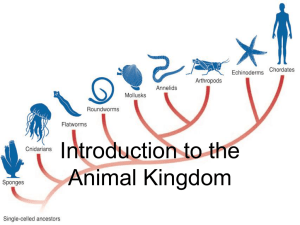
Introduction to the Animal Kingdom
... Introduction to the Animal Kingdom • Animals are multicellular eukaryotic heterotroph whose cells lack cell walls • Vertebrates: 5% of animal species with backbones • Invertebrates: 95% of animal species WITHOUT backbones • Cell specialization – special shape, physical structure, and chemical compo ...
... Introduction to the Animal Kingdom • Animals are multicellular eukaryotic heterotroph whose cells lack cell walls • Vertebrates: 5% of animal species with backbones • Invertebrates: 95% of animal species WITHOUT backbones • Cell specialization – special shape, physical structure, and chemical compo ...
Where is the HIGH oxygen concentration?
... This means there was a greater water concentration inside the cell and it lost water. 2) What can you conclude about the solute concentration inside the cells compared to outside? Because the water concentration was high (see question 1), there must have been a low amount of solutes inside the cell. ...
... This means there was a greater water concentration inside the cell and it lost water. 2) What can you conclude about the solute concentration inside the cells compared to outside? Because the water concentration was high (see question 1), there must have been a low amount of solutes inside the cell. ...
Chemical Composition of Living Cells
... matter of the cell being protein (15% on a wetweight basis). Cells generally contain many more protein molecules than DNA molecules, yet DNA is typically the largest biomolecule in the cell. About 99% of cellular molecules are water molecules, with water normally accounting for approximately 70% of ...
... matter of the cell being protein (15% on a wetweight basis). Cells generally contain many more protein molecules than DNA molecules, yet DNA is typically the largest biomolecule in the cell. About 99% of cellular molecules are water molecules, with water normally accounting for approximately 70% of ...
Study Guide 1st Lab Exam – Monday 7/13/09
... 27. Learn about 3 domains and 4 kingdoms of Eukarya with their characteristics. Bacteria 28. Bacteria have cell wall made of peptidoglycan. These lack a nucleus or any membrane bound organelles; the only organelle present is ribosomes for protein synthesis. They divide by binary fission. Some bacill ...
... 27. Learn about 3 domains and 4 kingdoms of Eukarya with their characteristics. Bacteria 28. Bacteria have cell wall made of peptidoglycan. These lack a nucleus or any membrane bound organelles; the only organelle present is ribosomes for protein synthesis. They divide by binary fission. Some bacill ...
Chapter 1 - The Science of Biology - holyoke
... Occasionally you may have trouble with working your microscope. Here are some common problems and solutions. 1. Image is too dark! Adjust the diaphragm, make sure your light is on. 2. There's a spot in my viewing field, even when I move the slide the spot stays in the same place! Your lens is dirty. ...
... Occasionally you may have trouble with working your microscope. Here are some common problems and solutions. 1. Image is too dark! Adjust the diaphragm, make sure your light is on. 2. There's a spot in my viewing field, even when I move the slide the spot stays in the same place! Your lens is dirty. ...
References - 기초의과학연구센터 MRC
... Mitochondrial dysfunction, often characterized by massive fission and other morphological abnormalities, is a well-known risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease (AD). One causative mechanism underlying AD-associated mitochondrial dysfunction is thought to be amyloid beta (Aβ), yet the pathways between A ...
... Mitochondrial dysfunction, often characterized by massive fission and other morphological abnormalities, is a well-known risk factor for Alzheimer’s disease (AD). One causative mechanism underlying AD-associated mitochondrial dysfunction is thought to be amyloid beta (Aβ), yet the pathways between A ...
Biology Unit 2 - John Madejski Academy
... Cancers (malignant tumours) result from uncontrolled cell division. Cells may invade neighbouring tissues, or break off and spread in blood forming secondary tumours. Benign tumours - growths of abnormal cells, contained in one area, usually within a membrane (do not spread). ...
... Cancers (malignant tumours) result from uncontrolled cell division. Cells may invade neighbouring tissues, or break off and spread in blood forming secondary tumours. Benign tumours - growths of abnormal cells, contained in one area, usually within a membrane (do not spread). ...
File - Different Diseases
... division resumes, the cells that are produced are not all identical – they have differentiated and the mass of cells is referred to as an embryo. Initially, the embryo has three distinct layers: the ectoderm (outermost layer, which becomes nervous tissue and the outer epithelial tissue); the mesoder ...
... division resumes, the cells that are produced are not all identical – they have differentiated and the mass of cells is referred to as an embryo. Initially, the embryo has three distinct layers: the ectoderm (outermost layer, which becomes nervous tissue and the outer epithelial tissue); the mesoder ...
EOCT REVIEW
... the reaction happen faster- called catalysts • If you didn’t have enzymes, reactions would happen too slowly and you might die waiting for the rxn to occur. • Enzymes are used to break down food in your body and to build new molecules & organelles. • Enzymes are used over & over but are very SPECIFI ...
... the reaction happen faster- called catalysts • If you didn’t have enzymes, reactions would happen too slowly and you might die waiting for the rxn to occur. • Enzymes are used to break down food in your body and to build new molecules & organelles. • Enzymes are used over & over but are very SPECIFI ...
Blood cell
... neuron before it B = Cell body – contains nucleus & cytoplasm C = Nucleus – genetic information D = Axon – transmits the message/impulse away from cell body E = Myelin sheath – protective covering that insulates the axon F = Node – gaps in the myelin sheath where the axon is exposed G = Schwann cell ...
... neuron before it B = Cell body – contains nucleus & cytoplasm C = Nucleus – genetic information D = Axon – transmits the message/impulse away from cell body E = Myelin sheath – protective covering that insulates the axon F = Node – gaps in the myelin sheath where the axon is exposed G = Schwann cell ...
Unit 1 Cell Biology Topic 3: Producing new cells
... the new cells. Genes are the basic unit of inheritance, and are responsible for the characteristics of an organism (e.g. what it looks like, its behaviour and all its chemical reactions). Genes are located on chromosomes, which are threadlike structures found in the nucleus of most cells (remember r ...
... the new cells. Genes are the basic unit of inheritance, and are responsible for the characteristics of an organism (e.g. what it looks like, its behaviour and all its chemical reactions). Genes are located on chromosomes, which are threadlike structures found in the nucleus of most cells (remember r ...
NOTES- Inv. 2 Supporting Cells.notebook
... The human body is made of systems, which are made of organs, which are made of tissues, which are made of cells All the human organ systems interact in order for a human to live and carry out life functions. The most important function is servicing cells. In a human, the circulatory system pum ...
... The human body is made of systems, which are made of organs, which are made of tissues, which are made of cells All the human organ systems interact in order for a human to live and carry out life functions. The most important function is servicing cells. In a human, the circulatory system pum ...
Slide 1
... Active transport This is the movement of substances against a concentration gradient (from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration. This process requires energy. This is provided by aerobic respiration which is carried out in mitochondria. Active transport often occurs across c ...
... Active transport This is the movement of substances against a concentration gradient (from an area of low concentration to an area of high concentration. This process requires energy. This is provided by aerobic respiration which is carried out in mitochondria. Active transport often occurs across c ...
Cell theory

In biology, cell theory is a scientific theory which describes the properties of cells. These cells are the basic unit of structure in all organisms and also the basic unit of reproduction. With continual improvements made to microscopes over time, magnification technology advanced enough to discover cells in the 17th century. This discovery is largely attributed to Robert Hooke, and began the scientific study of cells, also known as cell biology. Over a century later, many debates about cells began amongst scientists. Most of these debates involved the nature of cellular regeneration, and the idea of cells as a fundamental unit of life. Cell theory was eventually formulated in 1838. This is usually credited to Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann. However, many other scientists like Rudolf Virchow contributed to the theory. Cell theory has become the foundation of biology and is the most widely accepted explanation of the function of cells.The three tenets to the cell theory are as described below: All living organisms are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the most basic unit of life. All cells arise from pre-existing, living cells, by biogenesis.