Biology Notes-Teacher (chapters 7, 8, 9)
... Cell culture – isolated cells are given nutrients and their growth and division are studied Cell lines – the generations of cells produced from a culture; can be grown indefinitely in a lab Eg. HeLa cells Stem cells – “blank slate” cells that divide to produce all other types of specialized cells - ...
... Cell culture – isolated cells are given nutrients and their growth and division are studied Cell lines – the generations of cells produced from a culture; can be grown indefinitely in a lab Eg. HeLa cells Stem cells – “blank slate” cells that divide to produce all other types of specialized cells - ...
Lecture 4 Tissues V10
... • Three characteristics make connective tissues different from other primary tissues: – All have common embryonic origin: all arise from mesenchyme tissue as their tissue of origin – Have varying degrees of vascularity (cartilage is avascular, bone is highly vascularized) – Cells are suspended/embed ...
... • Three characteristics make connective tissues different from other primary tissues: – All have common embryonic origin: all arise from mesenchyme tissue as their tissue of origin – Have varying degrees of vascularity (cartilage is avascular, bone is highly vascularized) – Cells are suspended/embed ...
What You Absolutely Need to Know To Pass the NYS Living
... which a cell changes to have a special shape and function. 2. Cells specialize by turning specific genes on or off. • Ex: A white blood cell has turned off all genes needed to make skin, bone, or ...
... which a cell changes to have a special shape and function. 2. Cells specialize by turning specific genes on or off. • Ex: A white blood cell has turned off all genes needed to make skin, bone, or ...
YEAR 10 IGCSE BIOLOGY REVISION GUIDE DBGS DIGESTION
... Glucose -> Energy + Lactic Acid (Instead of CO2) Lactic Acid builds up in the muscles and makes them ache. Muscle cramps To get rid of lactic acid, aerobic respiration occurs Lactic acid + O2 -> CO2 + H20 + Energy Amount of oxygen required in the above is called oxygen debt Differences Bet ...
... Glucose -> Energy + Lactic Acid (Instead of CO2) Lactic Acid builds up in the muscles and makes them ache. Muscle cramps To get rid of lactic acid, aerobic respiration occurs Lactic acid + O2 -> CO2 + H20 + Energy Amount of oxygen required in the above is called oxygen debt Differences Bet ...
Respiratory System
... The nose produces a continuous supply of mucus. This mucus, which is replaced every 20 minutes, has two main jobs. One is to add some moisture to the air so that the internal tissues of the respiratory system don’t dry out. The other job is to catch unwanted particles and bacteria from the air. The ...
... The nose produces a continuous supply of mucus. This mucus, which is replaced every 20 minutes, has two main jobs. One is to add some moisture to the air so that the internal tissues of the respiratory system don’t dry out. The other job is to catch unwanted particles and bacteria from the air. The ...
Skeletal System Muscular System
... • Describe how oxygen gets to your cells • What gas waste is created by cells that your body gets rid of? How does it do it? ...
... • Describe how oxygen gets to your cells • What gas waste is created by cells that your body gets rid of? How does it do it? ...
Structure and Function
... are made up of at least one cell and every cell comes from another cell. Energy Energy is the ability to make things move and change. Everything that an organism does needs energy. Energy is obtained from the environment. Plants and animals differ in how they obtain their energy. Plants use the ener ...
... are made up of at least one cell and every cell comes from another cell. Energy Energy is the ability to make things move and change. Everything that an organism does needs energy. Energy is obtained from the environment. Plants and animals differ in how they obtain their energy. Plants use the ener ...
Physiology - Loveland Schools
... 1. Recognize that information stored in DNA provides the instructions for assembling protein molecules used by the cells that determine the characteristics of the organism. 2. Explain why specialized cells/structures are useful to plants and animals (e.g., stoma, phloem, xylem, blood, nerve, muscle, ...
... 1. Recognize that information stored in DNA provides the instructions for assembling protein molecules used by the cells that determine the characteristics of the organism. 2. Explain why specialized cells/structures are useful to plants and animals (e.g., stoma, phloem, xylem, blood, nerve, muscle, ...
What You Absolutely Need to Know To Pass the
... which a cell changes to have a special shape and function. 2. Cells specialize by turning specific genes on or off. • Ex: A white blood cell has turned off all genes needed to make skin, bone, or ...
... which a cell changes to have a special shape and function. 2. Cells specialize by turning specific genes on or off. • Ex: A white blood cell has turned off all genes needed to make skin, bone, or ...
CRT Review Term 2 - Science Page of Mystery
... and then uses radio waves which are transformed into an image. MRI can show the soft tissues and organs since they are mostly made up of water. What does this demonstrate? A. Science provides information which is generally NOT helpful to the health of humans. B. Science affects humans by improving t ...
... and then uses radio waves which are transformed into an image. MRI can show the soft tissues and organs since they are mostly made up of water. What does this demonstrate? A. Science provides information which is generally NOT helpful to the health of humans. B. Science affects humans by improving t ...
1.3.2 Chemical Elements
... • It is a universal solvent for transporting substances in blood (e.g. food and oxygen) or in plants (e.g. minerals) • The medium for metabolism i.e. chemical reactions take place in it. • It is a reactant/product photosynthesis and respiration ...
... • It is a universal solvent for transporting substances in blood (e.g. food and oxygen) or in plants (e.g. minerals) • The medium for metabolism i.e. chemical reactions take place in it. • It is a reactant/product photosynthesis and respiration ...
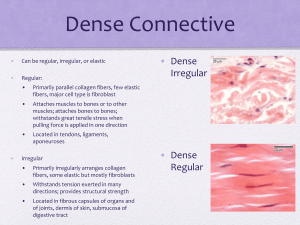
Connective Tissue
... • Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the metabolic rate of an endotherm at rest at a “comfortable” temperature • Standard metabolic rate (SMR) is the metabolic rate of an ectotherm at rest at a specific temperature • Both rates assume a nongrowing, fasting, and nonstressed animal • Ectotherms have much l ...
... • Basal metabolic rate (BMR) is the metabolic rate of an endotherm at rest at a “comfortable” temperature • Standard metabolic rate (SMR) is the metabolic rate of an ectotherm at rest at a specific temperature • Both rates assume a nongrowing, fasting, and nonstressed animal • Ectotherms have much l ...
Unit 1 Higher Human Biology Summary Notes
... Smooth muscle forms part of the walls of large blood vessels and the alimentary canal Cardiac muscle In this type, each cell has one or more branches in contact with adjacent cells 4. Nervous tissue This tissue is composed of a network of neurons which receive and transmit impulses and glial cells w ...
... Smooth muscle forms part of the walls of large blood vessels and the alimentary canal Cardiac muscle In this type, each cell has one or more branches in contact with adjacent cells 4. Nervous tissue This tissue is composed of a network of neurons which receive and transmit impulses and glial cells w ...
The Living Cell - Discovery Education
... Cells are like miniature factories which use raw materials and energy to create their amazing product which is none other than life itself. Large organisms are multicellular and are made from many different cells. The cells of multicellular organisms have become specialized to perform all sorts of t ...
... Cells are like miniature factories which use raw materials and energy to create their amazing product which is none other than life itself. Large organisms are multicellular and are made from many different cells. The cells of multicellular organisms have become specialized to perform all sorts of t ...
N5 Multicellular Organisms Course Notes
... The brain plays a very important part in the way you respond to any factors that may affect your body. Just to read this page, millions of nerve messages are zipping around within your own brain. The brain itself is made up of several different parts or regions, each with its own specialised functio ...
... The brain plays a very important part in the way you respond to any factors that may affect your body. Just to read this page, millions of nerve messages are zipping around within your own brain. The brain itself is made up of several different parts or regions, each with its own specialised functio ...
blood cells - School
... If we now concentrate on one red blood cell, we can see how important the haemoglobin molecule is to the process of transporting oxygen. ...
... If we now concentrate on one red blood cell, we can see how important the haemoglobin molecule is to the process of transporting oxygen. ...
File
... kidney, there are millions Tubes connecting the kidneys to the bladder Smooth muscle bag that stores a solution of wastes called urine Tube where urine passed out of the body ...
... kidney, there are millions Tubes connecting the kidneys to the bladder Smooth muscle bag that stores a solution of wastes called urine Tube where urine passed out of the body ...
Final Exam Review Help
... _____ONE THAT GETS LITTLE TO NO PRECIPITATION (DESERT)_________ 41) Be able to use a dichotomous key to identify an organism. 42) What environmental condition will most likely lead to the adaptations that allow a species of fish to not only survive outside of the water, but to actually travel from o ...
... _____ONE THAT GETS LITTLE TO NO PRECIPITATION (DESERT)_________ 41) Be able to use a dichotomous key to identify an organism. 42) What environmental condition will most likely lead to the adaptations that allow a species of fish to not only survive outside of the water, but to actually travel from o ...
File
... marrow inside bones is site for blood cell formation (hematopoiesis) • Located in bones ...
... marrow inside bones is site for blood cell formation (hematopoiesis) • Located in bones ...
development
... This is the first in a series of complex events that conclude with the birth of a full-grown organism. Following fertilization, the zygote begins a series of mitotic cell divisions know as cleavage. Cleavage- Cells don't grow, just divide; therefore, cell ...
... This is the first in a series of complex events that conclude with the birth of a full-grown organism. Following fertilization, the zygote begins a series of mitotic cell divisions know as cleavage. Cleavage- Cells don't grow, just divide; therefore, cell ...
LAB 16 - Stuyvesant High School
... parallel leaf venation (examples: corn and other members of the grass family). Dicots have branching herbaceous (soft) or woody stems and branching leaf venation (examples: lilacs and other woody flowering trees). An important and unique life function that plants perform is to derive their energy fr ...
... parallel leaf venation (examples: corn and other members of the grass family). Dicots have branching herbaceous (soft) or woody stems and branching leaf venation (examples: lilacs and other woody flowering trees). An important and unique life function that plants perform is to derive their energy fr ...
CellUnitWrapUpNotes
... Example: The Ted Talk guy who lost his feet used prosthetic feet Implants: A device that is placed inside the body to help it do something better or something that was not possible before. Example: Pace-maker (heart), Breast Implants (more appealing), Subcutaneous (under the skin) communication devi ...
... Example: The Ted Talk guy who lost his feet used prosthetic feet Implants: A device that is placed inside the body to help it do something better or something that was not possible before. Example: Pace-maker (heart), Breast Implants (more appealing), Subcutaneous (under the skin) communication devi ...
Cell theory

In biology, cell theory is a scientific theory which describes the properties of cells. These cells are the basic unit of structure in all organisms and also the basic unit of reproduction. With continual improvements made to microscopes over time, magnification technology advanced enough to discover cells in the 17th century. This discovery is largely attributed to Robert Hooke, and began the scientific study of cells, also known as cell biology. Over a century later, many debates about cells began amongst scientists. Most of these debates involved the nature of cellular regeneration, and the idea of cells as a fundamental unit of life. Cell theory was eventually formulated in 1838. This is usually credited to Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann. However, many other scientists like Rudolf Virchow contributed to the theory. Cell theory has become the foundation of biology and is the most widely accepted explanation of the function of cells.The three tenets to the cell theory are as described below: All living organisms are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the most basic unit of life. All cells arise from pre-existing, living cells, by biogenesis.