Levels of Organization - Flipped Out Science with Mrs. Thomas!
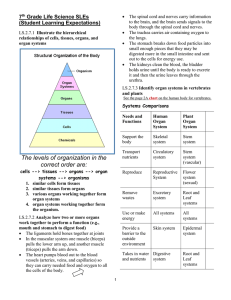
... Within multi-cellular organisms there is division of labor. Division of labor means that the work (labor) of keeping the organism alive is divided (division) among the different parts of the body. Each part has a job to do and as each part does its special job, it works in harmony with all the other ...
... Within multi-cellular organisms there is division of labor. Division of labor means that the work (labor) of keeping the organism alive is divided (division) among the different parts of the body. Each part has a job to do and as each part does its special job, it works in harmony with all the other ...
Photosynthesis and respiration Photosynthesis is the conversion of
... transport materials through the cell. It contains enzymes and produces and digests lipids (fats) and membrane proteins; smooth ER buds off from rough ER, moving the newly-made proteins and lipids to the Golgi body and membranes stroma - part of the chloroplasts in plant cells, located within the inn ...
... transport materials through the cell. It contains enzymes and produces and digests lipids (fats) and membrane proteins; smooth ER buds off from rough ER, moving the newly-made proteins and lipids to the Golgi body and membranes stroma - part of the chloroplasts in plant cells, located within the inn ...
Biology 2nd Semester Exam Review 1. What is the benefit of having
... 12. What is the reason that most male animals are larger than females of the same species? Males compete with each other for females ...
... 12. What is the reason that most male animals are larger than females of the same species? Males compete with each other for females ...
Outline 3
... Single-celled glands – ______________ cells are shaped somewhat like a wineglass, and are found in the epithelia of many mucous membranes Multicellular glands – include all other glands in which multiple cells work together to produce secretions Exocrine glands are glands that convey their sec ...
... Single-celled glands – ______________ cells are shaped somewhat like a wineglass, and are found in the epithelia of many mucous membranes Multicellular glands – include all other glands in which multiple cells work together to produce secretions Exocrine glands are glands that convey their sec ...
Sponges and Cnidarians
... and free-swimming larvae are then released via the osculum. This is the only time that sponges exhibit one of the hallmarks of the animal kingdom, motility. The larvae then attach to a substrate and spend their adult lives in the same spot. ...
... and free-swimming larvae are then released via the osculum. This is the only time that sponges exhibit one of the hallmarks of the animal kingdom, motility. The larvae then attach to a substrate and spend their adult lives in the same spot. ...
2401_ch4.pdf
... Hemidesmosomes – bind bottom-most cells to the basement layer in high stress areas Gap Junction – small protein channel (pore) that allows ions and small molecules to flow between cells (communication) Tight Junction – barrier to permeability. Large molecules can not pass except through transport pr ...
... Hemidesmosomes – bind bottom-most cells to the basement layer in high stress areas Gap Junction – small protein channel (pore) that allows ions and small molecules to flow between cells (communication) Tight Junction – barrier to permeability. Large molecules can not pass except through transport pr ...
The Five Kingdoms
... Fish – live in water, breathe through gills, are covered by scales, and are cold-blooded ...
... Fish – live in water, breathe through gills, are covered by scales, and are cold-blooded ...
Glossary
... between two variables on a graph where the line of best fit goes through 0,0 disc-diffusion technique used to test effectiveness of antibiotics or disinfectants on plates of cultured bacteria using paper discs soaked in the test substance and measuring the size of clear area around the discs disease ...
... between two variables on a graph where the line of best fit goes through 0,0 disc-diffusion technique used to test effectiveness of antibiotics or disinfectants on plates of cultured bacteria using paper discs soaked in the test substance and measuring the size of clear area around the discs disease ...
Immunity Power Point
... The reaction of the body to “nonself” cells is called the immune response. This involves destroying or neutralizing foreign cells or molecules with white blood cells and lymphatic tissue. ...
... The reaction of the body to “nonself” cells is called the immune response. This involves destroying or neutralizing foreign cells or molecules with white blood cells and lymphatic tissue. ...
A change in ocean current causes the climate on an island to
... 42. The REPRODUCTIVE System: allows for the production of offspring and the continuation of life. Reproduction is a characteristic of all living thing; because no individual lives forever, reproduction is essential to the continuation of every species. o Testes: Male reproductive organ that produce ...
... 42. The REPRODUCTIVE System: allows for the production of offspring and the continuation of life. Reproduction is a characteristic of all living thing; because no individual lives forever, reproduction is essential to the continuation of every species. o Testes: Male reproductive organ that produce ...
What is a Cell?
... the stage. Don’t say it looks bigger…look closely! What happened? Why do you think this happened? 3. Looking through the EYEPIECE, move the slide to the upper right area of the stage. What direction does the image move through the eyepiece? 4. How does the ink appear under the microscope compared to ...
... the stage. Don’t say it looks bigger…look closely! What happened? Why do you think this happened? 3. Looking through the EYEPIECE, move the slide to the upper right area of the stage. What direction does the image move through the eyepiece? 4. How does the ink appear under the microscope compared to ...
p² + 2pq+ q² = 1
... Molecular Genetics What explains why it’s common for bacteria to have mutations? ...
... Molecular Genetics What explains why it’s common for bacteria to have mutations? ...
EOCT REVIEW
... synthesis, aka condensation) new molecules. • Enzymes are used over & over (recyclable) but are very SPECIFIC in the reactions they participate in. • Enzymes can be denatured by changes in temperature, pH or salinity (salt) ...
... synthesis, aka condensation) new molecules. • Enzymes are used over & over (recyclable) but are very SPECIFIC in the reactions they participate in. • Enzymes can be denatured by changes in temperature, pH or salinity (salt) ...
Tissues and Integument
... 1. Science that studies the structure of an organism is anatomy a. Anas = to cut b. Tomos = apart 2. Science that studies how a particular structure functions is physiology 3. Levels of structural organization a. Atoms b. Molecules c. Organic macromolecules 1) Carbohydrates 2) Lipids 3) Proteins 4) ...
... 1. Science that studies the structure of an organism is anatomy a. Anas = to cut b. Tomos = apart 2. Science that studies how a particular structure functions is physiology 3. Levels of structural organization a. Atoms b. Molecules c. Organic macromolecules 1) Carbohydrates 2) Lipids 3) Proteins 4) ...
Biology Frameworks
... 1.1 Recognize that biological organisms are composed primarily of very few elements. The six most common are C, H, N, O, P, and S. 1.2 Describe the basic molecular structures and primary functions of the four major categories of organic molecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids). 1.3 ...
... 1.1 Recognize that biological organisms are composed primarily of very few elements. The six most common are C, H, N, O, P, and S. 1.2 Describe the basic molecular structures and primary functions of the four major categories of organic molecules (carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids). 1.3 ...
Textbook of Medical Physiology, 11 th Edition
... level of 100 to 160 mm Hg. If at another time the same volume of blood is infused into the same person when the baroreceptor system is functioning and the arterial pressure increases from the normal level from 100 mm Hg to 120 mm Hg, calculate the gain of the baroreceptor system in this person. a. ...
... level of 100 to 160 mm Hg. If at another time the same volume of blood is infused into the same person when the baroreceptor system is functioning and the arterial pressure increases from the normal level from 100 mm Hg to 120 mm Hg, calculate the gain of the baroreceptor system in this person. a. ...
Document
... and multiplies to form a complete organism The human female sex cell (egg) contains 23 chromosomes The human male sex cell (sperm) contains 23 chromosomes The fertilized egg, therefore contains the 23 from each parent making a total of 46 chromosomes with genetic material from both parents. ...
... and multiplies to form a complete organism The human female sex cell (egg) contains 23 chromosomes The human male sex cell (sperm) contains 23 chromosomes The fertilized egg, therefore contains the 23 from each parent making a total of 46 chromosomes with genetic material from both parents. ...
Study Questions for Test # 2
... What are the four major categories of macromolecules and what are the components from which these are constructed? What is a condensation reaction? A hydrolysis reaction? Which of these is involved with the formation of macromolecules? Which is responsible for the digestion/breakdown of macromolecul ...
... What are the four major categories of macromolecules and what are the components from which these are constructed? What is a condensation reaction? A hydrolysis reaction? Which of these is involved with the formation of macromolecules? Which is responsible for the digestion/breakdown of macromolecul ...
Answer Key - Teach Engineering
... Blood Cell Basics Activity – Blood Cells Under a Microscope Vocabulary Worksheet – Answer Key You have looked at a drop of blood under a microscope. You could see some odd shaped cells floating around in a liquid called plasma. These are the white blood cells. White blood cells are soldiers that fig ...
... Blood Cell Basics Activity – Blood Cells Under a Microscope Vocabulary Worksheet – Answer Key You have looked at a drop of blood under a microscope. You could see some odd shaped cells floating around in a liquid called plasma. These are the white blood cells. White blood cells are soldiers that fig ...
I. Introduction
... A. A zygote is formed when a sperm cell and an egg unite. B. Growth refers to an increase in size. C. Development is the continuous process by which an individual changes from one life phase to another. D. The two life phases are prenatal and postnatal. E. The prenatal phase extends from fertilizati ...
... A. A zygote is formed when a sperm cell and an egg unite. B. Growth refers to an increase in size. C. Development is the continuous process by which an individual changes from one life phase to another. D. The two life phases are prenatal and postnatal. E. The prenatal phase extends from fertilizati ...
The Necessities of Life
... • Proteins are made up of smaller molecules called amino acids. • Enzymes are proteins that speed up chemical reactions • Proteins are needed to build and repair body structures and to regulate processes in the body. • Hemoglobin is a protein found in red blood cells that attaches to oxygen • Spider ...
... • Proteins are made up of smaller molecules called amino acids. • Enzymes are proteins that speed up chemical reactions • Proteins are needed to build and repair body structures and to regulate processes in the body. • Hemoglobin is a protein found in red blood cells that attaches to oxygen • Spider ...
Life Science: Chapter 7 Study Guide
... 8. ____________________ are groups of protozoa that are parasites. 9. Ciliates are a group of protozoan that move by waving tiny hair-like ____________________. 10. A(n) ___________________________________ is used to help control the amount of water inside an organism and pump out excess water. 11. ...
... 8. ____________________ are groups of protozoa that are parasites. 9. Ciliates are a group of protozoan that move by waving tiny hair-like ____________________. 10. A(n) ___________________________________ is used to help control the amount of water inside an organism and pump out excess water. 11. ...
i. cardiovascular system
... provide motion and maintain posture B. Voluntary muscle-person can control 1. Skeletal-attached to bone C. Involuntary-functions without persons control 1. Smooth muscle-found in many internal organs 2. Cardiac-specialized tissue found only in the heart ...
... provide motion and maintain posture B. Voluntary muscle-person can control 1. Skeletal-attached to bone C. Involuntary-functions without persons control 1. Smooth muscle-found in many internal organs 2. Cardiac-specialized tissue found only in the heart ...
Additional Biology B2 Core Knowledge
... Worries that eating GM organisms may harm people (no evidence of this) Expensive to buy Do not produce fertile seed so new plants need to be brought ...
... Worries that eating GM organisms may harm people (no evidence of this) Expensive to buy Do not produce fertile seed so new plants need to be brought ...
Cell theory

In biology, cell theory is a scientific theory which describes the properties of cells. These cells are the basic unit of structure in all organisms and also the basic unit of reproduction. With continual improvements made to microscopes over time, magnification technology advanced enough to discover cells in the 17th century. This discovery is largely attributed to Robert Hooke, and began the scientific study of cells, also known as cell biology. Over a century later, many debates about cells began amongst scientists. Most of these debates involved the nature of cellular regeneration, and the idea of cells as a fundamental unit of life. Cell theory was eventually formulated in 1838. This is usually credited to Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann. However, many other scientists like Rudolf Virchow contributed to the theory. Cell theory has become the foundation of biology and is the most widely accepted explanation of the function of cells.The three tenets to the cell theory are as described below: All living organisms are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the most basic unit of life. All cells arise from pre-existing, living cells, by biogenesis.