Biology - Fall Semester Final Exam 2013-2014
... The enzymes that catalyze cellular reactions are macromolecules called proteins. Which of the following elements most often compose proteins? A ...
... The enzymes that catalyze cellular reactions are macromolecules called proteins. Which of the following elements most often compose proteins? A ...
7th Grade Fall Semester Review 2011
... 1. Organisms vary and these variations (genes) are inherited by their offspring. 2. Organisms produce more offspring than can possibly survive in nature. ...
... 1. Organisms vary and these variations (genes) are inherited by their offspring. 2. Organisms produce more offspring than can possibly survive in nature. ...
High - eduBuzz.org
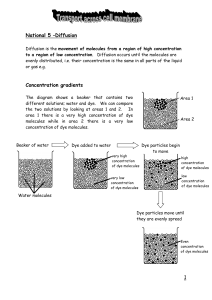
... a. The cell membrane consists of lipids and proteins and is selectively permeable. b. Passive transport is along a concentration gradient and does not require energy. c. Diffusion in cells as the movement of molecules down a concentration gradient. d. Osmosis as the movement of water molecules acros ...
... a. The cell membrane consists of lipids and proteins and is selectively permeable. b. Passive transport is along a concentration gradient and does not require energy. c. Diffusion in cells as the movement of molecules down a concentration gradient. d. Osmosis as the movement of water molecules acros ...
Homeostasis and Transport 1. Technology Enhanced Questions are
... the cell through osmosis and diffusion. The cell membrane also separates the cell's internal environment from the external world. 22. -23. Small molecules, such as molecules of oxygen and carbon dioxide gas, can move passively through a cell membrane as a result of concentration gradients. That is, ...
... the cell through osmosis and diffusion. The cell membrane also separates the cell's internal environment from the external world. 22. -23. Small molecules, such as molecules of oxygen and carbon dioxide gas, can move passively through a cell membrane as a result of concentration gradients. That is, ...
Tissues of human body
... Tissues are group of cells organized to perform specific function Tissues of human body Human body composed of 4 basic tissue types, which are: 1. Epithelial tissue = epithelium it covers the body surfaces and lines cavities and lumen and formed glands. There are: a) Surface epithelium b) Glandular ...
... Tissues are group of cells organized to perform specific function Tissues of human body Human body composed of 4 basic tissue types, which are: 1. Epithelial tissue = epithelium it covers the body surfaces and lines cavities and lumen and formed glands. There are: a) Surface epithelium b) Glandular ...
Review 3 - Sinoe Medical Association
... plasma membranes. Given this information, which one of the following statements is most likely true about a cell bathed in a solution that contains Procaine? a. There will be no osmosis across the cell’s plasma membrane. b. Na + will diffuse directly across the lipid bilayer. c. Na + will be ...
... plasma membranes. Given this information, which one of the following statements is most likely true about a cell bathed in a solution that contains Procaine? a. There will be no osmosis across the cell’s plasma membrane. b. Na + will diffuse directly across the lipid bilayer. c. Na + will be ...
Trainer 1 File
... Platyhelminthes branched off from the rest of the animals before the evolution of the coelom. However, some genetic studies have led some researchers to argue that flatworms descended from an ancestor that had a coelom, and later lost the coelom. Gastrovascular cavity: The digestive tract has only o ...
... Platyhelminthes branched off from the rest of the animals before the evolution of the coelom. However, some genetic studies have led some researchers to argue that flatworms descended from an ancestor that had a coelom, and later lost the coelom. Gastrovascular cavity: The digestive tract has only o ...
Word - LangdonBiology.org
... Hormones: prostaglandins are short range; steroids turn on/off genes producing new proteins; protein hormones turn on/off existing proteins Negative feedback: hormone levels vary inversely with their stimulus (as body temperature goes up, thyroxin levels go down) Sensory neuron: sense environment. I ...
... Hormones: prostaglandins are short range; steroids turn on/off genes producing new proteins; protein hormones turn on/off existing proteins Negative feedback: hormone levels vary inversely with their stimulus (as body temperature goes up, thyroxin levels go down) Sensory neuron: sense environment. I ...
Blood - Lancaster High School
... – Thrombin + Ca++ converts fibrinogen to fibrin -> forms a mesh that adheres to tissue & traps blood cells and platelets ...
... – Thrombin + Ca++ converts fibrinogen to fibrin -> forms a mesh that adheres to tissue & traps blood cells and platelets ...
5th Grade EOG Review - Structures and Functions of Living
... Which best describes how bacteria carry out the processes necessary for survival? A. Bacteria borrow cells from the host to carry out life ...
... Which best describes how bacteria carry out the processes necessary for survival? A. Bacteria borrow cells from the host to carry out life ...
Chapter 23: Pregnancy, Growth, and Development
... 4. Hardening of the zona pellucida after fertilization reduces the chance that other sperm cells will penetrate the secondary oocyte. 5. Once a sperm cell enters the oocyte’s cytoplasm, the secondary oocyte divides unequally to form a large cell (ovum) and a tiny second polar body. 6. Each sex cell ...
... 4. Hardening of the zona pellucida after fertilization reduces the chance that other sperm cells will penetrate the secondary oocyte. 5. Once a sperm cell enters the oocyte’s cytoplasm, the secondary oocyte divides unequally to form a large cell (ovum) and a tiny second polar body. 6. Each sex cell ...
Unit 3 Lesson 1: From Cells to Organ Word Parts/meaning of word, if
... and skeleton system? Skeletal System: 1. Provides shape and support 2. Enables you to move 3. Protects your internal organs 4. Produces blood cells 5. Stores certain material until your body needs them Muscular System: 1. Muscles are connected to your Skeletal System 2. Help you move your body parts ...
... and skeleton system? Skeletal System: 1. Provides shape and support 2. Enables you to move 3. Protects your internal organs 4. Produces blood cells 5. Stores certain material until your body needs them Muscular System: 1. Muscles are connected to your Skeletal System 2. Help you move your body parts ...
Nicole`s teacher asked her to make a diagram of a good chain for a
... A population of mice, some with light-colored fur and some with dark-colored fur, is introduced into a field with dark soil. A few generations later, the majority of the mice have dark-colored fur. Which of the following best explains this change? ...
... A population of mice, some with light-colored fur and some with dark-colored fur, is introduced into a field with dark soil. A few generations later, the majority of the mice have dark-colored fur. Which of the following best explains this change? ...
Science8__Unit1_Notes
... -electron micrographs: images made by electron microscopes -microscope is used by scientists to observe very small unicellular and multicellular living things -early microscopes were built in late 1600’s -Anton van Leeuwenhoek was one of first people to build a microscope -magnify up to 250x; used i ...
... -electron micrographs: images made by electron microscopes -microscope is used by scientists to observe very small unicellular and multicellular living things -early microscopes were built in late 1600’s -Anton van Leeuwenhoek was one of first people to build a microscope -magnify up to 250x; used i ...
animal cells and tissues
... plasma membrane. Most of the cell is occupied by striated, thread-like myofibrils. Within each myofibril there are dense Z lines. A sarcomere (or muscle functional unit) extends from Z line to Z line. Each sarcomere has thick and thin filaments. The thick filaments are made of myosin and occupy the ...
... plasma membrane. Most of the cell is occupied by striated, thread-like myofibrils. Within each myofibril there are dense Z lines. A sarcomere (or muscle functional unit) extends from Z line to Z line. Each sarcomere has thick and thin filaments. The thick filaments are made of myosin and occupy the ...
“Fight or flight” responses are a coordinated set of physiological
... Muscle contractions are produced by the interaction of actin and myosin filaments in response to the neurotransmitter acetylcholine (ACh). The nervous system regulates muscle contraction by controlling which motor units are stimulated as well as the rate at which the muscles are stimulated. If the m ...
... Muscle contractions are produced by the interaction of actin and myosin filaments in response to the neurotransmitter acetylcholine (ACh). The nervous system regulates muscle contraction by controlling which motor units are stimulated as well as the rate at which the muscles are stimulated. If the m ...
Cells - SignatureIBBiology
... organisms have one region of cytoplasm surrounded by a cell membrane. The protoctista cell is unusual in that it performs all functions. Such cells are usually much larger than other cells such that some biologist consider them 'acellular', that is, non-cellular. This is an image of an amoeba. A sin ...
... organisms have one region of cytoplasm surrounded by a cell membrane. The protoctista cell is unusual in that it performs all functions. Such cells are usually much larger than other cells such that some biologist consider them 'acellular', that is, non-cellular. This is an image of an amoeba. A sin ...
Unit 1 – Cell Biology
... concentration (more water) is said to be hypotonic. The solution with the lower water concentration (less water) is described as being hypertonic. ...
... concentration (more water) is said to be hypotonic. The solution with the lower water concentration (less water) is described as being hypertonic. ...
Lecture 3
... 3-Tertiary structure 4-Quaternary structure Primary structure Primary structure: sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide -The correct amino acid sequence is determined by the cell’s genetic ...
... 3-Tertiary structure 4-Quaternary structure Primary structure Primary structure: sequence of amino acids in a polypeptide -The correct amino acid sequence is determined by the cell’s genetic ...
Zoology First Semester Review Multiple Choice Questions Chapter
... 15. The most distinctive feature of nemerteans is a long proboscis held in a sheath called a rhynchocoel. 16. Nemerteans are microscopic, aquatic animals with a complete digestive tract and an unusual proboscis. 17. The monogenetic flukes (class Monogenea) are mostly external parasites of fishes 18. ...
... 15. The most distinctive feature of nemerteans is a long proboscis held in a sheath called a rhynchocoel. 16. Nemerteans are microscopic, aquatic animals with a complete digestive tract and an unusual proboscis. 17. The monogenetic flukes (class Monogenea) are mostly external parasites of fishes 18. ...
Gas Exchange in Plants
... mean that a direct exchange of gases across the cell membrane is sufficient to meet the organisms’ metabolic needs. You also saw that as animal organisms became larger and more complex, different kinds of respiratory systems evolved to increase the respiratory surface area and facilitate the exchang ...
... mean that a direct exchange of gases across the cell membrane is sufficient to meet the organisms’ metabolic needs. You also saw that as animal organisms became larger and more complex, different kinds of respiratory systems evolved to increase the respiratory surface area and facilitate the exchang ...
Big Idea 14 : Organization and Development of Living Organisms
... 1. Why is a cell compared to a city? 2. What are two differences between an animal and a plant cell? 3. What is the smallest building block of matter? 4. What is the smallest building block of life? ...
... 1. Why is a cell compared to a city? 2. What are two differences between an animal and a plant cell? 3. What is the smallest building block of matter? 4. What is the smallest building block of life? ...
Introduction to Animals
... Introduction to Animals Characteristics All multicellular (metazoans) & eukaryotic Cells lack cell walls & come in a variety of shapes Ingestive heterotrophs (take in food & internally digest it) Store food reserves temporarily as glycogen in the liver May be sessile (attached & non-moving ...
... Introduction to Animals Characteristics All multicellular (metazoans) & eukaryotic Cells lack cell walls & come in a variety of shapes Ingestive heterotrophs (take in food & internally digest it) Store food reserves temporarily as glycogen in the liver May be sessile (attached & non-moving ...
Cell theory

In biology, cell theory is a scientific theory which describes the properties of cells. These cells are the basic unit of structure in all organisms and also the basic unit of reproduction. With continual improvements made to microscopes over time, magnification technology advanced enough to discover cells in the 17th century. This discovery is largely attributed to Robert Hooke, and began the scientific study of cells, also known as cell biology. Over a century later, many debates about cells began amongst scientists. Most of these debates involved the nature of cellular regeneration, and the idea of cells as a fundamental unit of life. Cell theory was eventually formulated in 1838. This is usually credited to Matthias Schleiden and Theodor Schwann. However, many other scientists like Rudolf Virchow contributed to the theory. Cell theory has become the foundation of biology and is the most widely accepted explanation of the function of cells.The three tenets to the cell theory are as described below: All living organisms are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the most basic unit of life. All cells arise from pre-existing, living cells, by biogenesis.