Chapter 09 - Center of Mass and Linear Momentum
... are still balanced. Thus, during the collision, the net external impulse on the bullet–block system is zero. Therefore, the system is isolated and its total linear momentum is conserved. (2) The collision is one-dimensional in the sense that the direction of the bullet and block just after the colli ...
... are still balanced. Thus, during the collision, the net external impulse on the bullet–block system is zero. Therefore, the system is isolated and its total linear momentum is conserved. (2) The collision is one-dimensional in the sense that the direction of the bullet and block just after the colli ...
Chapter 16
... orbit around the center became globular clusters. 3. The initial cloud had some rotation, and as it contracted it spun faster. The rotating matter formed into a disk. 4. Density waves formed in the Galaxy’s disk, creating the spiral arms where star formation continues today. 5. In an alternative mod ...
... orbit around the center became globular clusters. 3. The initial cloud had some rotation, and as it contracted it spun faster. The rotating matter formed into a disk. 4. Density waves formed in the Galaxy’s disk, creating the spiral arms where star formation continues today. 5. In an alternative mod ...
the star
... of the Milky Way Galaxy because of the presence of dust. Only the 1500 most luminous of these stars are plotted. Most of these are visible to the unaided eye. Note the presence of the Hyades cluster. ...
... of the Milky Way Galaxy because of the presence of dust. Only the 1500 most luminous of these stars are plotted. Most of these are visible to the unaided eye. Note the presence of the Hyades cluster. ...
2003 - The Physics Teacher
... (i) Describe with the aid of a diagram how the student obtained this data. See diagram. Note the pressure of the gas from the pressure-gauge and the volume from the graduated scale. Turn the screw to decrease the volume and increase the pressure. Note the new readings and repeat to get about seven r ...
... (i) Describe with the aid of a diagram how the student obtained this data. See diagram. Note the pressure of the gas from the pressure-gauge and the volume from the graduated scale. Turn the screw to decrease the volume and increase the pressure. Note the new readings and repeat to get about seven r ...
Newton`s Second Law
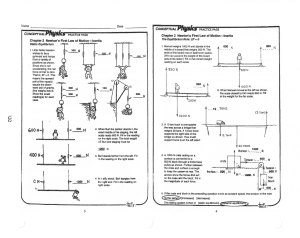
... The figure below shows an object of mass m moving on a frictionless inclined plane which makes an angle θ with the horizontal. a) Find the acceleration of the block in terms of the constants g and θ. b) If the block started from rest and travelled a distance d, find the final speed of the block and ...
... The figure below shows an object of mass m moving on a frictionless inclined plane which makes an angle θ with the horizontal. a) Find the acceleration of the block in terms of the constants g and θ. b) If the block started from rest and travelled a distance d, find the final speed of the block and ...
Tension is a reaction force applied by a stretched string (rope or a
... A good example of where we use freebody diagrams is friction. Friction: A force that resists motion when two objects are in contact (floor and object you are dragging). Friction always acts in the opposite direction of motion. Friction is NOT a conservative force. This means the energy used during t ...
... A good example of where we use freebody diagrams is friction. Friction: A force that resists motion when two objects are in contact (floor and object you are dragging). Friction always acts in the opposite direction of motion. Friction is NOT a conservative force. This means the energy used during t ...
Research proposal uploaded for ESO fellowship
... Currently, toy models are used to treat supernova feedback, which are parametrized to reproduce the faint-end of the luminosity function (Cole et al. 2000; Guo et al. 2010). These toy models do not take into account key physical conditions, such as the density of the ISM of galaxies or how much ener ...
... Currently, toy models are used to treat supernova feedback, which are parametrized to reproduce the faint-end of the luminosity function (Cole et al. 2000; Guo et al. 2010). These toy models do not take into account key physical conditions, such as the density of the ISM of galaxies or how much ener ...
Ch 9 HW Day : p 296 – 308, #`s 1, 3, 5, 7, 8, 9, 11, 13, 14, 15, 16, 17
... Picture the Problem The three forces acting on the basketball are the weight of the ball, the normal force, and the force of friction. Because the weight can be assumed to be acting at the center of mass, and the normal force acts through the center of mass, the only force which exerts a torque abou ...
... Picture the Problem The three forces acting on the basketball are the weight of the ball, the normal force, and the force of friction. Because the weight can be assumed to be acting at the center of mass, and the normal force acts through the center of mass, the only force which exerts a torque abou ...
ASTRO-114--Lecture 11-
... Acceleration — what is an acceleration? It’s a change of velocity. The first law mentions objects having a tendency to keep moving, to keep the same velocity. If you have a force, you change the velocity, you have an acceleration. So forces cause accelerations. The acceleration, how much it’s accele ...
... Acceleration — what is an acceleration? It’s a change of velocity. The first law mentions objects having a tendency to keep moving, to keep the same velocity. If you have a force, you change the velocity, you have an acceleration. So forces cause accelerations. The acceleration, how much it’s accele ...
Unit 3 Multiple Choice Answers
... 46. A car initially travels north and then turns to the left along a circular curve. This causes a package on the seat of the car to slide toward the right side of the car. Which of the following is true of the net force on the package while it is sliding? (A) The force is directed away from the cen ...
... 46. A car initially travels north and then turns to the left along a circular curve. This causes a package on the seat of the car to slide toward the right side of the car. Which of the following is true of the net force on the package while it is sliding? (A) The force is directed away from the cen ...
General Relativity and the Accelerated Expansion of the Universe
... one could choose a coordinate system such that everywhere the metric tensor is just the Minkowski metric tensor. But GR states that energy and momentum associated with matter warp the space-time geometry, entailing that in general it is not possible to choose inertial coordinates everywhere so that ...
... one could choose a coordinate system such that everywhere the metric tensor is just the Minkowski metric tensor. But GR states that energy and momentum associated with matter warp the space-time geometry, entailing that in general it is not possible to choose inertial coordinates everywhere so that ...
centripetal force - Worth County Schools
... which remains above the same point on the earth. Such a satellite orbits the earth in 24 hours, thus matching the earth's rotation. How high must a geosynchronous satellite be above the surface? (Mearth = 5.98x1024 kg, Rearth = 6.37 x 106 m) ...
... which remains above the same point on the earth. Such a satellite orbits the earth in 24 hours, thus matching the earth's rotation. How high must a geosynchronous satellite be above the surface? (Mearth = 5.98x1024 kg, Rearth = 6.37 x 106 m) ...
Linear Kinetics - Weber State University
... • Define impulse and momentum and explain the relationship between them • Explain what factors govern the outcome of a collision between two bodies • Discuss the interrelationship among mechanical work, power, and energy • Solve quantitative problems related to kinetic concepts ...
... • Define impulse and momentum and explain the relationship between them • Explain what factors govern the outcome of a collision between two bodies • Discuss the interrelationship among mechanical work, power, and energy • Solve quantitative problems related to kinetic concepts ...
File - Carroll`s Cave of Knowledge
... Newton’s First Law is also called the Law of Inertia: “An object at rest will stay at rest, and a moving object will maintain the same velocity (vector), if and only if the net force acting on it is zero.” Or, “Thing keep moving as they are until an unbalanced force acts ...
... Newton’s First Law is also called the Law of Inertia: “An object at rest will stay at rest, and a moving object will maintain the same velocity (vector), if and only if the net force acting on it is zero.” Or, “Thing keep moving as they are until an unbalanced force acts ...
Slide 1 - Phy 2048-0002
... 1) The speed of the interacting bodies are a fraction of the speed of light Einstein’s special theory of relativity. 2) The interacting bodies are on the scale of the atomic structure Quantum mechanics I. Newton’s first law: If no net force acts on a body, then the body’s velocity cannot change; ...
... 1) The speed of the interacting bodies are a fraction of the speed of light Einstein’s special theory of relativity. 2) The interacting bodies are on the scale of the atomic structure Quantum mechanics I. Newton’s first law: If no net force acts on a body, then the body’s velocity cannot change; ...
1 - CSUN.edu
... The action and reaction pairs are equal in magnitude. The ranking is then Ffloor on 1 > F1/2 > F2/3 There is no contact force between block 3 and 1 so F1/3 =0 B)Elevator moving upward with increasing speed (accelerating upward) There will be a term proportional to the acceleration on the RHS of the ...
... The action and reaction pairs are equal in magnitude. The ranking is then Ffloor on 1 > F1/2 > F2/3 There is no contact force between block 3 and 1 so F1/3 =0 B)Elevator moving upward with increasing speed (accelerating upward) There will be a term proportional to the acceleration on the RHS of the ...
Exploring The Universe
... strong radio signal. This object was called a quasar. • quasar quasi-stellar radio sources; very luminous objects that produce energy at a high rate and that are thought to be the most distant objects in the universe • Each quasar has a huge central black hole and a large disk of gas and dust around ...
... strong radio signal. This object was called a quasar. • quasar quasi-stellar radio sources; very luminous objects that produce energy at a high rate and that are thought to be the most distant objects in the universe • Each quasar has a huge central black hole and a large disk of gas and dust around ...
Physics 100A Homework 4
... C) A block of mass 2 kg is acted upon by two forces: 3N (directed to the left) and 4N (directed to the right). What can you say about the block's motion? The net force is point to the right, so the object could - be moving to the right and accelerating to the right (speeding up) - be moving to the l ...
... C) A block of mass 2 kg is acted upon by two forces: 3N (directed to the left) and 4N (directed to the right). What can you say about the block's motion? The net force is point to the right, so the object could - be moving to the right and accelerating to the right (speeding up) - be moving to the l ...
Modified Newtonian dynamics

In physics, modified Newtonian dynamics (MOND) is a theory that proposes a modification of Newton's laws to account for observed properties of galaxies. Created in 1983 by Israeli physicist Mordehai Milgrom, the theory's original motivation was to explain the fact that the velocities of stars in galaxies were observed to be larger than expected based on Newtonian mechanics. Milgrom noted that this discrepancy could be resolved if the gravitational force experienced by a star in the outer regions of a galaxy was proportional to the square of its centripetal acceleration (as opposed to the centripetal acceleration itself, as in Newton's Second Law), or alternatively if gravitational force came to vary inversely with radius (as opposed to the inverse square of the radius, as in Newton's Law of Gravity). In MOND, violation of Newton's Laws occurs at extremely small accelerations, characteristic of galaxies yet far below anything typically encountered in the Solar System or on Earth.MOND is an example of a class of theories known as modified gravity, and is an alternative to the hypothesis that the dynamics of galaxies are determined by massive, invisible dark matter halos. Since Milgrom's original proposal, MOND has successfully predicted a variety of galactic phenomena that are difficult to understand from a dark matter perspective. However, MOND and its generalisations do not adequately account for observed properties of galaxy clusters, and no satisfactory cosmological model has been constructed from the theory.