Chapter 5 Center of Mass and Linear Momentum
... potential energy is zero, too. As the mechanical energy is conserved, the least initial mechanical energy required at launch is zero. 4 (12) Zero, a hypothetical planet, has a mass of 5.0 1023 kg , a radius of 3.0 106 m , and no atmosphere. A 10kg space probe is to be launched vertically from its ...
... potential energy is zero, too. As the mechanical energy is conserved, the least initial mechanical energy required at launch is zero. 4 (12) Zero, a hypothetical planet, has a mass of 5.0 1023 kg , a radius of 3.0 106 m , and no atmosphere. A 10kg space probe is to be launched vertically from its ...
19 The Milky Way Galaxy
... 2. Observe objects at radio and infrared wavelengths to circumvent the problem of optical obscuration, and catalog their directions and distances. 3. Trace the orbital velocities of objects in different directions relative to our position. ...
... 2. Observe objects at radio and infrared wavelengths to circumvent the problem of optical obscuration, and catalog their directions and distances. 3. Trace the orbital velocities of objects in different directions relative to our position. ...
PPT - Modeling & Simulation Lab.
... Numbers of the form a+ib+jc, where a,b,c are real numbers and i2=j2=-1. He never succeeded in making this generalization. It has later been proven that the set of three-dimensional numbers is not closed under multiplication. Four numbers are needed to describe a rotation followed by a scaling. ...
... Numbers of the form a+ib+jc, where a,b,c are real numbers and i2=j2=-1. He never succeeded in making this generalization. It has later been proven that the set of three-dimensional numbers is not closed under multiplication. Four numbers are needed to describe a rotation followed by a scaling. ...
A Study of the Spiral Galaxy M101 Elizabeth City State University
... filters isolated select wavelengths of light to allow one to examine the galaxy in detail and look for regions of high and low ionization, including HII regions. Table 3 describes the observing site. The Image Reduction and Analysis Facility (IRAF) is the software that was used for the image reducti ...
... filters isolated select wavelengths of light to allow one to examine the galaxy in detail and look for regions of high and low ionization, including HII regions. Table 3 describes the observing site. The Image Reduction and Analysis Facility (IRAF) is the software that was used for the image reducti ...
A force is a push or pull on an object. In this lesson, you will be
... apple to accelerate towards the ground. The apple initially in the tree having a velocity of zero experiences an increase in downward velocity as it falls from the tree. This force is the force of gravity. Objects accelerate downward due to the force of gravity. Newton’s hypothesis has been tested a ...
... apple to accelerate towards the ground. The apple initially in the tree having a velocity of zero experiences an increase in downward velocity as it falls from the tree. This force is the force of gravity. Objects accelerate downward due to the force of gravity. Newton’s hypothesis has been tested a ...
PHY430 - Lecture 4 - Newton`s Laws
... mass 10.0 kg with a mystery surprise inside. The box is resting on the smooth (frictionless) horizontal surface of a table. (a) Determine the weight of the box and the normal force exerted on it by the table. (b) Now your friend pushes down on the box with a force of 40.0 N. Again determine the norm ...
... mass 10.0 kg with a mystery surprise inside. The box is resting on the smooth (frictionless) horizontal surface of a table. (a) Determine the weight of the box and the normal force exerted on it by the table. (b) Now your friend pushes down on the box with a force of 40.0 N. Again determine the norm ...
7.3 Uniform Circular Motion and Centripetal
... • Using mathematical representations of Newton’s Law of Gravitation and Kepler’s law , SWBAT to describe the motion of a satellite and apply the concepts of angular momentum and torque. • Using mathematical or computational representations , SWBAT to predict the motion of orbiting objects in the so ...
... • Using mathematical representations of Newton’s Law of Gravitation and Kepler’s law , SWBAT to describe the motion of a satellite and apply the concepts of angular momentum and torque. • Using mathematical or computational representations , SWBAT to predict the motion of orbiting objects in the so ...
Circular Motion Web Quest
... 17. Does the sensation of being thrown outward from the center of a circle mean that there was definitely an outward force? ...
... 17. Does the sensation of being thrown outward from the center of a circle mean that there was definitely an outward force? ...
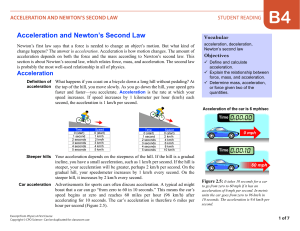
Acceleration and Newton`s Second Law
... a. What is the acceleration of a 1,500-kilogram car if a net force of 1,000 N is exerted on it? Answer: 1.5 m/sec2 b. As you coast down the hill on your bicycle, you accelerate at 0.5 m/sec2. If the total mass of your body and the bicycle is 80 kg, with what force is gravity pulling you down the hil ...
... a. What is the acceleration of a 1,500-kilogram car if a net force of 1,000 N is exerted on it? Answer: 1.5 m/sec2 b. As you coast down the hill on your bicycle, you accelerate at 0.5 m/sec2. If the total mass of your body and the bicycle is 80 kg, with what force is gravity pulling you down the hil ...
Chapter 9 Rotational Dynamics
... 9.4 Newton’s Second Law for Rotational Motion About a Fixed Axis 2nd law for linear motion of crate ...
... 9.4 Newton’s Second Law for Rotational Motion About a Fixed Axis 2nd law for linear motion of crate ...
Chapter 4 Dynamics: Newton`s Laws of Motion
... mass 10.0 kg with a mystery surprise inside. The box is resting on the smooth (frictionless) horizontal surface of a table. (a) Determine the weight of the box and the normal force exerted on it by the table. (b) Now your friend pushes down on the box with a force of 40.0 N. Again determine the norm ...
... mass 10.0 kg with a mystery surprise inside. The box is resting on the smooth (frictionless) horizontal surface of a table. (a) Determine the weight of the box and the normal force exerted on it by the table. (b) Now your friend pushes down on the box with a force of 40.0 N. Again determine the norm ...
Springs Virtual Lab
... The force that pulls it back and attempts to restore the spring to equilibrium is called the restoring force. It magnitude can be written as Restoring Force = (force constant)(displacement form equilibrium) or F = - ky This relationship is known as Hooke’s Law. The force constant is a measure of th ...
... The force that pulls it back and attempts to restore the spring to equilibrium is called the restoring force. It magnitude can be written as Restoring Force = (force constant)(displacement form equilibrium) or F = - ky This relationship is known as Hooke’s Law. The force constant is a measure of th ...
Chapter 5 - UCF College of Sciences
... of the speed of light Einstein’s special theory of relativity. ...
... of the speed of light Einstein’s special theory of relativity. ...
Black Holes - University of Oregon
... solar mass. This is an important point – to an external observer a black hole is merely a point with mass. As long as you are a long way from that point, you will not notice anything strange – it’s only when you get near the black hole, that strange things start to happen – some of which are detaile ...
... solar mass. This is an important point – to an external observer a black hole is merely a point with mass. As long as you are a long way from that point, you will not notice anything strange – it’s only when you get near the black hole, that strange things start to happen – some of which are detaile ...
File
... The net force is zero on an object with constant velocity. If velocity stays constant, then the acceleration is zero—so the net force must also be zero. ...
... The net force is zero on an object with constant velocity. If velocity stays constant, then the acceleration is zero—so the net force must also be zero. ...
Modified Newtonian dynamics

In physics, modified Newtonian dynamics (MOND) is a theory that proposes a modification of Newton's laws to account for observed properties of galaxies. Created in 1983 by Israeli physicist Mordehai Milgrom, the theory's original motivation was to explain the fact that the velocities of stars in galaxies were observed to be larger than expected based on Newtonian mechanics. Milgrom noted that this discrepancy could be resolved if the gravitational force experienced by a star in the outer regions of a galaxy was proportional to the square of its centripetal acceleration (as opposed to the centripetal acceleration itself, as in Newton's Second Law), or alternatively if gravitational force came to vary inversely with radius (as opposed to the inverse square of the radius, as in Newton's Law of Gravity). In MOND, violation of Newton's Laws occurs at extremely small accelerations, characteristic of galaxies yet far below anything typically encountered in the Solar System or on Earth.MOND is an example of a class of theories known as modified gravity, and is an alternative to the hypothesis that the dynamics of galaxies are determined by massive, invisible dark matter halos. Since Milgrom's original proposal, MOND has successfully predicted a variety of galactic phenomena that are difficult to understand from a dark matter perspective. However, MOND and its generalisations do not adequately account for observed properties of galaxy clusters, and no satisfactory cosmological model has been constructed from the theory.