Small Wonders: Canes Venatici
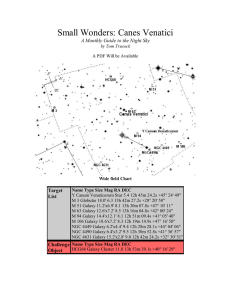
... on by both Ursa Major and Bootes, Canes is located in a somewhat barren section of the night sky. Canes (whose name means The Hunting Dogs) has been seen as Bootes pets for at least several hundred years, but the constellation may not have been "stand alone" until sometime in the late 17th century w ...
... on by both Ursa Major and Bootes, Canes is located in a somewhat barren section of the night sky. Canes (whose name means The Hunting Dogs) has been seen as Bootes pets for at least several hundred years, but the constellation may not have been "stand alone" until sometime in the late 17th century w ...
0708 - Astronomy
... - it shows that no matter where you draw the origin (i.e., no matter your location), you will always observe that all points are moving away from YOU ...
... - it shows that no matter where you draw the origin (i.e., no matter your location), you will always observe that all points are moving away from YOU ...
RevfinQ2010AnsFa06
... Answer: The little calculator. The momenta of the two objects were identical before slowing, and p = mv, so the little calculator must have been going really fast to have the same momentum as the big physics text. Since the two objects slowed to a stop in the same time, the distance traveled is grea ...
... Answer: The little calculator. The momenta of the two objects were identical before slowing, and p = mv, so the little calculator must have been going really fast to have the same momentum as the big physics text. Since the two objects slowed to a stop in the same time, the distance traveled is grea ...
Final Exam Review
... This is a problem with constant acceleration, so we can use the constant acceleration formulas. A: True B: False False: As they get closer, the force of gravity increases and so does the acceleration 13. An unhappy student works out his aggression by attempting to knock down a large wooden bowling p ...
... This is a problem with constant acceleration, so we can use the constant acceleration formulas. A: True B: False False: As they get closer, the force of gravity increases and so does the acceleration 13. An unhappy student works out his aggression by attempting to knock down a large wooden bowling p ...
Physics 11 Course Review – Sample questions and additional practice
... Which of the following statements concerning gravitational fields is true? a. Only very massive objects have gravitational fields. b. The gravitational field strength of an object is one-quarter as great at twice the distance from the object's centre. c. The strength of an object's gravitational fie ...
... Which of the following statements concerning gravitational fields is true? a. Only very massive objects have gravitational fields. b. The gravitational field strength of an object is one-quarter as great at twice the distance from the object's centre. c. The strength of an object's gravitational fie ...
Document
... ● Friction – Keep in mind that the coefficients of friction for given surfaces are listed on the reference table. If a problem does not specify frictionless, you must assume that there is friction. ● Incline Problems – Rotate the axis so the x direction is aligned parallel with surface. After drawin ...
... ● Friction – Keep in mind that the coefficients of friction for given surfaces are listed on the reference table. If a problem does not specify frictionless, you must assume that there is friction. ● Incline Problems – Rotate the axis so the x direction is aligned parallel with surface. After drawin ...
PH607lec11-4gal2
... The Tully-Fisher relation for spiral galaxies (and the FaberJackson relation for ellipticals), follow from the dynamics if we assume constant mass-to-light ratio and surface brightness. Plot the maximum circular velocity of spiral galaxies against their luminosity in a given band: ….to find that L a ...
... The Tully-Fisher relation for spiral galaxies (and the FaberJackson relation for ellipticals), follow from the dynamics if we assume constant mass-to-light ratio and surface brightness. Plot the maximum circular velocity of spiral galaxies against their luminosity in a given band: ….to find that L a ...
Physics S1 ideas overview
... 24. Understand the 2 components of a projectile and how they are related (and how component vectors relate to other measurements as well). 25. Understand the relationship between component vectors and Ɵ (also used for many other measurements). 26. At the very top of the trajectory, describe an objec ...
... 24. Understand the 2 components of a projectile and how they are related (and how component vectors relate to other measurements as well). 25. Understand the relationship between component vectors and Ɵ (also used for many other measurements). 26. At the very top of the trajectory, describe an objec ...
Document
... formulated a completely new theory of mechanics that forms the basis of modern science. In this new theory, observations and experiments play a very important role as they are used to verify or reject a physical theory. At the turn of the twentieth century it was found that Newton’s laws of motion d ...
... formulated a completely new theory of mechanics that forms the basis of modern science. In this new theory, observations and experiments play a very important role as they are used to verify or reject a physical theory. At the turn of the twentieth century it was found that Newton’s laws of motion d ...
HS 10 course outline and benchmarks File
... of an object in terms of position, time, velocity, and acceleration. Benchmark 1: Describe the motion of an object in terms of position, time, and velocity. a. Calculate the average velocity of a moving object using data obtained from measurements of position of the object at two or more times. b. D ...
... of an object in terms of position, time, velocity, and acceleration. Benchmark 1: Describe the motion of an object in terms of position, time, and velocity. a. Calculate the average velocity of a moving object using data obtained from measurements of position of the object at two or more times. b. D ...
Chapter5-Matter in Motion
... therefore changing its _____________, and thus ________________ is occurring. This circular acceleration is called __________________ __________________. ...
... therefore changing its _____________, and thus ________________ is occurring. This circular acceleration is called __________________ __________________. ...
gravitational and electric
... Permittivity The strength of the electric field will also depend upon what material is between the two charges. This is known as the permittivity, ε. ...
... Permittivity The strength of the electric field will also depend upon what material is between the two charges. This is known as the permittivity, ε. ...
PDF format
... b) An object orbiting the Sun and affected only by the Sun's gravity spirals into the Sun. c) One ball hits a second ball and stops moving while the second ball starts moving in the same direction. d) An object speeds up as it approaches the Sun and turns around it, and then slows down as it move ...
... b) An object orbiting the Sun and affected only by the Sun's gravity spirals into the Sun. c) One ball hits a second ball and stops moving while the second ball starts moving in the same direction. d) An object speeds up as it approaches the Sun and turns around it, and then slows down as it move ...
Forces and Newton`s Laws of Motion
... the “effect” of those forces that are different. The larger object has a smaller acceleration, and therefore, a small CHANGE in its motion after the force is applied. ...
... the “effect” of those forces that are different. The larger object has a smaller acceleration, and therefore, a small CHANGE in its motion after the force is applied. ...
Modified Newtonian dynamics

In physics, modified Newtonian dynamics (MOND) is a theory that proposes a modification of Newton's laws to account for observed properties of galaxies. Created in 1983 by Israeli physicist Mordehai Milgrom, the theory's original motivation was to explain the fact that the velocities of stars in galaxies were observed to be larger than expected based on Newtonian mechanics. Milgrom noted that this discrepancy could be resolved if the gravitational force experienced by a star in the outer regions of a galaxy was proportional to the square of its centripetal acceleration (as opposed to the centripetal acceleration itself, as in Newton's Second Law), or alternatively if gravitational force came to vary inversely with radius (as opposed to the inverse square of the radius, as in Newton's Law of Gravity). In MOND, violation of Newton's Laws occurs at extremely small accelerations, characteristic of galaxies yet far below anything typically encountered in the Solar System or on Earth.MOND is an example of a class of theories known as modified gravity, and is an alternative to the hypothesis that the dynamics of galaxies are determined by massive, invisible dark matter halos. Since Milgrom's original proposal, MOND has successfully predicted a variety of galactic phenomena that are difficult to understand from a dark matter perspective. However, MOND and its generalisations do not adequately account for observed properties of galaxy clusters, and no satisfactory cosmological model has been constructed from the theory.























