Chapter 8 Rotational Dynamics continued
... Example: A Satellite in an Elliptical Orbit An artificial satellite is placed in an elliptical orbit about the earth. Its point of closest approach is 8.37x106 m from the center of the earth, and its point of greatest distance is 25.1x106 m from the center of the earth.The speed of the satellite at ...
... Example: A Satellite in an Elliptical Orbit An artificial satellite is placed in an elliptical orbit about the earth. Its point of closest approach is 8.37x106 m from the center of the earth, and its point of greatest distance is 25.1x106 m from the center of the earth.The speed of the satellite at ...
Chapter 4 Forces and Newton’s Laws of Motion continued
... 4.3 Applications Newton’s Laws (Normal Forces) A block with a weight of 15 N sits on a table. It is pushed down with a force of 11 N or pulled up with a force of 11 N. Calculate the normal force in each ...
... 4.3 Applications Newton’s Laws (Normal Forces) A block with a weight of 15 N sits on a table. It is pushed down with a force of 11 N or pulled up with a force of 11 N. Calculate the normal force in each ...
Example 2.1. on pg 30
... Find the average force exerted on the car during the collision. F = (1500kg)(0m/s-15m/s)/.3sec = -75000N The negative sign means the force is in the opposite direction of the car’s velocity. Go over example 6.2. on page 153. 6.2. Conservation of Momentum If two particles of masses M1 and M2 form an ...
... Find the average force exerted on the car during the collision. F = (1500kg)(0m/s-15m/s)/.3sec = -75000N The negative sign means the force is in the opposite direction of the car’s velocity. Go over example 6.2. on page 153. 6.2. Conservation of Momentum If two particles of masses M1 and M2 form an ...
Lecture24
... The CMB was already visible in the data taken by Dunham and Adams of the properties of CN in the interstellar medium …back in 1937 The saw that CN was excited as if it was immersed in a thermal bath of radiation of temperature ...
... The CMB was already visible in the data taken by Dunham and Adams of the properties of CN in the interstellar medium …back in 1937 The saw that CN was excited as if it was immersed in a thermal bath of radiation of temperature ...
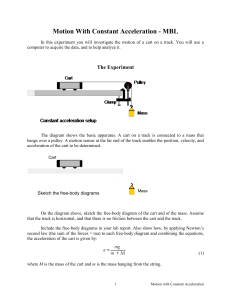
Motion With Constant Acceleration
... Record a set of data where you start with the cart near the pulley, and you give it a quick push so it moves away from the pulley. From one of the graphs, determine the acceleration for the motion when the cart is moving away from the pulley. Compare this with the acceleration you measure for the ca ...
... Record a set of data where you start with the cart near the pulley, and you give it a quick push so it moves away from the pulley. From one of the graphs, determine the acceleration for the motion when the cart is moving away from the pulley. Compare this with the acceleration you measure for the ca ...
laws of motion
... s, x( t) = A sin4p t for 0 < t <(1/4) s (A > o), and x = 0 for t >(1/4) s. Which of the following statements is true? (a) The force at t = (1/8) s on the particle is –16π2 A m. (b) The particle is acted upon by on impulse of magnitude 4 π2 A m at t = 0 s and t = (1/4) s. (c) The particle is not acte ...
... s, x( t) = A sin4p t for 0 < t <(1/4) s (A > o), and x = 0 for t >(1/4) s. Which of the following statements is true? (a) The force at t = (1/8) s on the particle is –16π2 A m. (b) The particle is acted upon by on impulse of magnitude 4 π2 A m at t = 0 s and t = (1/4) s. (c) The particle is not acte ...
MASSACHUSETTS INSTITUTE OF TECHNOLOGY
... A uniform cylinder of outer radius R and mass M with moment of inertia about the center of mass I cm (1/ 2) M R 2 starts from rest and moves down an incline tilted at an angle from the horizontal. The center of mass of the cylinder has dropped a vertical distance h when it reaches the bottom of ...
... A uniform cylinder of outer radius R and mass M with moment of inertia about the center of mass I cm (1/ 2) M R 2 starts from rest and moves down an incline tilted at an angle from the horizontal. The center of mass of the cylinder has dropped a vertical distance h when it reaches the bottom of ...
AH Physics SpaceandTimeTeachersNotes Mary
... Obviously the drawings above are not to scale and the actual bending would be very small. The important point here is the fact that a gravitational field will bend light. Inertial and gravitational effects are the same. An astronaut in deep space, far from any other gravitating matter, will feel wei ...
... Obviously the drawings above are not to scale and the actual bending would be very small. The important point here is the fact that a gravitational field will bend light. Inertial and gravitational effects are the same. An astronaut in deep space, far from any other gravitating matter, will feel wei ...
File
... gained lots of “momentum” and was very tough to beat. 5. What is the relationship between momentum and impulse? Change in momentum = impulse 6. What is the momentum of a 12 kg object traveling at a constant speed of 2 m/s? 12kg ∙2 m/s = 24 kg∙m/s 7. Which has more momentum: a. A 1100 kg car moving 1 ...
... gained lots of “momentum” and was very tough to beat. 5. What is the relationship between momentum and impulse? Change in momentum = impulse 6. What is the momentum of a 12 kg object traveling at a constant speed of 2 m/s? 12kg ∙2 m/s = 24 kg∙m/s 7. Which has more momentum: a. A 1100 kg car moving 1 ...
Overview - RI
... 5. Another way to apply a force to a charged atom is to pass it through a magnetic field. If the field is oriented properly you will apply a force that is perpendicular to the motion of the atom, causing the atom to deflect from its previously straight line path. The amount of force depends on the c ...
... 5. Another way to apply a force to a charged atom is to pass it through a magnetic field. If the field is oriented properly you will apply a force that is perpendicular to the motion of the atom, causing the atom to deflect from its previously straight line path. The amount of force depends on the c ...
Cosmology Handouts
... Rainbows reveal that white light is a combination of all the colours. In 1666, Isaac Newton showed that white light could be separated into its component colours using glass prisms. Soon scientists were using this new tool to analyze the light coming from several different light sources. Some scient ...
... Rainbows reveal that white light is a combination of all the colours. In 1666, Isaac Newton showed that white light could be separated into its component colours using glass prisms. Soon scientists were using this new tool to analyze the light coming from several different light sources. Some scient ...
Ellipticity, Its Origin and Progression in Comoving Galaxies
... That which cannot be predicted cannot be understood, and therefore, cannot be explained. –apodictic assertion Without any doubt, there can be no plausible explanation for elliptical galaxies —no explanation for their characteristic features, no explanation for their evolution— within an expanding-ty ...
... That which cannot be predicted cannot be understood, and therefore, cannot be explained. –apodictic assertion Without any doubt, there can be no plausible explanation for elliptical galaxies —no explanation for their characteristic features, no explanation for their evolution— within an expanding-ty ...
Lab 2 Force and Acceleration
... 2. Plug in the smart pulley into digital channels 1 and 2. 3. Drag the digital plug icon over digital channel 1 and select smart pulley (linear). Double click on the smart pulley to calibrate it. Enter the average of 0.0155 as the average radius of the pulley. 4. Plug the force sensor into analog ch ...
... 2. Plug in the smart pulley into digital channels 1 and 2. 3. Drag the digital plug icon over digital channel 1 and select smart pulley (linear). Double click on the smart pulley to calibrate it. Enter the average of 0.0155 as the average radius of the pulley. 4. Plug the force sensor into analog ch ...
Physics Exam – Circular Motion – Place all answers on the test
... Another simple homemade accelerometer involves a lit candle centered vertically in the middle of an open-air glass. If the glass is held level and at rest (such that there is no acceleration), then the candle flame extends in an upward direction. However, if you hold the glass-candle system with an ...
... Another simple homemade accelerometer involves a lit candle centered vertically in the middle of an open-air glass. If the glass is held level and at rest (such that there is no acceleration), then the candle flame extends in an upward direction. However, if you hold the glass-candle system with an ...
3.5 Notes – Special Case 2: Circular Motion Q: What determines
... vector, look at two velocity vectors, and consider their resultant ∆v. a. The sum of the interior angles for ANY triangle is 1800. b. Because the triangles are isosceles, the base angles are equal. c. As ∆t → 0, ∆θ also → 0. This means you are “pulling the triangle out of existence,” and the two bas ...
... vector, look at two velocity vectors, and consider their resultant ∆v. a. The sum of the interior angles for ANY triangle is 1800. b. Because the triangles are isosceles, the base angles are equal. c. As ∆t → 0, ∆θ also → 0. This means you are “pulling the triangle out of existence,” and the two bas ...
Question 1
... b) The rotation of the bulge and disk components c) The Sun’s age and age of the globular cluster stars d) The motion of spiral arms and the mass of the central black hole e) The orbital period and distance from the Galactic center of objects near the edge of the Galaxy Explanation: Use the modified ...
... b) The rotation of the bulge and disk components c) The Sun’s age and age of the globular cluster stars d) The motion of spiral arms and the mass of the central black hole e) The orbital period and distance from the Galactic center of objects near the edge of the Galaxy Explanation: Use the modified ...
Review - prettygoodphysics
... Arguably the greatest scientific genius ever. Came up with 3 Laws of Motion to explain the observations and analyses of Galileo and Johannes Kepler. Discovered that white light was composed of many colors all mixed together. Invented new mathematical techniques such as calculus and binomial expansio ...
... Arguably the greatest scientific genius ever. Came up with 3 Laws of Motion to explain the observations and analyses of Galileo and Johannes Kepler. Discovered that white light was composed of many colors all mixed together. Invented new mathematical techniques such as calculus and binomial expansio ...
Modified Newtonian dynamics

In physics, modified Newtonian dynamics (MOND) is a theory that proposes a modification of Newton's laws to account for observed properties of galaxies. Created in 1983 by Israeli physicist Mordehai Milgrom, the theory's original motivation was to explain the fact that the velocities of stars in galaxies were observed to be larger than expected based on Newtonian mechanics. Milgrom noted that this discrepancy could be resolved if the gravitational force experienced by a star in the outer regions of a galaxy was proportional to the square of its centripetal acceleration (as opposed to the centripetal acceleration itself, as in Newton's Second Law), or alternatively if gravitational force came to vary inversely with radius (as opposed to the inverse square of the radius, as in Newton's Law of Gravity). In MOND, violation of Newton's Laws occurs at extremely small accelerations, characteristic of galaxies yet far below anything typically encountered in the Solar System or on Earth.MOND is an example of a class of theories known as modified gravity, and is an alternative to the hypothesis that the dynamics of galaxies are determined by massive, invisible dark matter halos. Since Milgrom's original proposal, MOND has successfully predicted a variety of galactic phenomena that are difficult to understand from a dark matter perspective. However, MOND and its generalisations do not adequately account for observed properties of galaxy clusters, and no satisfactory cosmological model has been constructed from the theory.