1 Complex Numbers in Quantum Mechanics
... of a coin toss is random, if we were willing to undertake the enormous task of solving the equations of motion taking account of all possible forces and carefully specifying the initial conditions, the outcome of a coin toss is predictable. In the same way, so-called hidden variable theories of quan ...
... of a coin toss is random, if we were willing to undertake the enormous task of solving the equations of motion taking account of all possible forces and carefully specifying the initial conditions, the outcome of a coin toss is predictable. In the same way, so-called hidden variable theories of quan ...
Consciousness and Quantum Theory: Strange Bedfellows Barry Loewer
... The nature of consciousness and the interpretation of quantum mechanics are two subjects that excite great interest. Even more exciting then is the idea percolating through certain quarters that there are deep and significant connections between the two. Among those who have advocated a quantum mech ...
... The nature of consciousness and the interpretation of quantum mechanics are two subjects that excite great interest. Even more exciting then is the idea percolating through certain quarters that there are deep and significant connections between the two. Among those who have advocated a quantum mech ...
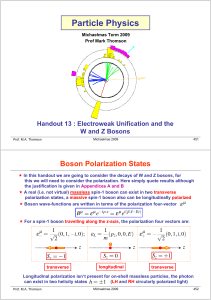
Desperately Seeking SUSY h (University of Cambridge) Please ask questions while I’m talking
... gluinos and squarks that have not yet been ruled out by searches. Same-sign dilepton searches without huge E 6 T cut will be interesting. It covers almost all possible cases of RPV operator. In case of Ui Dj Dk operators, current searches ⇒ mg̃ > 550 GeV. Anomalous AF B measurements can also be expl ...
... gluinos and squarks that have not yet been ruled out by searches. Same-sign dilepton searches without huge E 6 T cut will be interesting. It covers almost all possible cases of RPV operator. In case of Ui Dj Dk operators, current searches ⇒ mg̃ > 550 GeV. Anomalous AF B measurements can also be expl ...
Conclusive Exclusion of Quantum States
... chosen at random from a finite set of k known states. In the quantum state discrimination problem, we would attempt to identify the state that has been prepared. It is a well known result [1] that this can be done with certainty if and only if all of the states in the set of preparations are orthogo ...
... chosen at random from a finite set of k known states. In the quantum state discrimination problem, we would attempt to identify the state that has been prepared. It is a well known result [1] that this can be done with certainty if and only if all of the states in the set of preparations are orthogo ...
LECTURE 13 QUARKS PHY492 Nuclear and Elementary Particle Physics
... They also interact by the weak and electromagnetic interactions, although such effects can often be neglected compared to the strong interaction. February 7, 2014 ...
... They also interact by the weak and electromagnetic interactions, although such effects can often be neglected compared to the strong interaction. February 7, 2014 ...
Relation between the psychological and thermodynamic arrows of
... fread (r(t)), that we slightly alter the state of the particles (but not the rotor) at ti . We alter the coordinates and momenta of the particles by a small amount, but such that no particle changes position from one side of the barrier to the other, or, more precisely, so that the coarse-grained va ...
... fread (r(t)), that we slightly alter the state of the particles (but not the rotor) at ti . We alter the coordinates and momenta of the particles by a small amount, but such that no particle changes position from one side of the barrier to the other, or, more precisely, so that the coarse-grained va ...
Experimental determination of size distributions: Analyzing proper
... deviation equal to 20% of the mean value, thus representing a possible outcome of an experiment (Case 1). The shape of the distribution is usually unknown, but in this case we assume a priori a realistic shape, according to the bubble size measurement experiments of (Laakkonen et al 2006). Figure 1 ...
... deviation equal to 20% of the mean value, thus representing a possible outcome of an experiment (Case 1). The shape of the distribution is usually unknown, but in this case we assume a priori a realistic shape, according to the bubble size measurement experiments of (Laakkonen et al 2006). Figure 1 ...