Honors Chemistry
... Noble gases - 8 valence electrons - least reactive of all elements kernel - part of the atom exclusive of valence electrons (includes the nucleus) ...
... Noble gases - 8 valence electrons - least reactive of all elements kernel - part of the atom exclusive of valence electrons (includes the nucleus) ...
3.2 Bohr`s Model of the Atom
... The movement of an electron from one energy level to another is called a transition The ground state is the lowest energy state for an atom When an atom gains energy it moves into an excited state The transition from a lower energy level to a higher energy level requires a quantized amount of energy ...
... The movement of an electron from one energy level to another is called a transition The ground state is the lowest energy state for an atom When an atom gains energy it moves into an excited state The transition from a lower energy level to a higher energy level requires a quantized amount of energy ...
Chapter 4 Section 2
... Neils Bohr--Planetary model—electrons arranged in circular paths (orbits) around the nucleus Answered Rutherford’s ?—electrons in a particular path have a fixed energy, they do NOT lose energy and fall into the nucleus Energy level—region around nucleus where it is likely to be moving, similar to ru ...
... Neils Bohr--Planetary model—electrons arranged in circular paths (orbits) around the nucleus Answered Rutherford’s ?—electrons in a particular path have a fixed energy, they do NOT lose energy and fall into the nucleus Energy level—region around nucleus where it is likely to be moving, similar to ru ...
Slide 1 - s3.amazonaws.com
... Physicists were both mystified and intrigued by Bohr’s theory. They questioned why the energies of hydrogen electron are quantized, or, why is the electron in a Bohr atom restricted or orbiting the nucleus at certain fixed distance? For a decade there is no logical explanation. In 1924, Louis de Bro ...
... Physicists were both mystified and intrigued by Bohr’s theory. They questioned why the energies of hydrogen electron are quantized, or, why is the electron in a Bohr atom restricted or orbiting the nucleus at certain fixed distance? For a decade there is no logical explanation. In 1924, Louis de Bro ...
Atomic Spectra
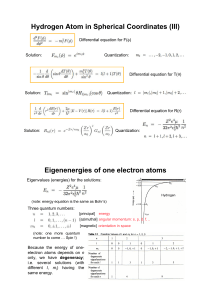
... one-electron situation such as He+, Li+2, Be+3) can be found from the equation: ...
... one-electron situation such as He+, Li+2, Be+3) can be found from the equation: ...
“solar system” model of the atom
... Periodic Table The Pauli exclusion principle states that only one electron may be in each quantum state: Only one electron at a time may have a particular set of quantum numbers, n, l, ml, and ms. Once a particular state is occupied, other electrons are excluded from that state. Therefore, if electr ...
... Periodic Table The Pauli exclusion principle states that only one electron may be in each quantum state: Only one electron at a time may have a particular set of quantum numbers, n, l, ml, and ms. Once a particular state is occupied, other electrons are excluded from that state. Therefore, if electr ...
schoa - Schieck
... ) may not cause ionization of an atom whereas, ultraviolet light (f=10 16 Hz) does. III. The Bohr Model of the Atom & Spectra N: Read p. 174-179: 7. Describe the electron in an atom as Bohr understood it. In the equation: E = -R/n2 a)What does E represent? b) What does n represent? describe any rest ...
... ) may not cause ionization of an atom whereas, ultraviolet light (f=10 16 Hz) does. III. The Bohr Model of the Atom & Spectra N: Read p. 174-179: 7. Describe the electron in an atom as Bohr understood it. In the equation: E = -R/n2 a)What does E represent? b) What does n represent? describe any rest ...
Handout
... ∂x2 is the kinetic energy and V is the potential energy, and therefore H is the total energy in the system. The phase of the wave function oscillates at a frequency fixed by the energy, ω = E/~. ...
... ∂x2 is the kinetic energy and V is the potential energy, and therefore H is the total energy in the system. The phase of the wave function oscillates at a frequency fixed by the energy, ω = E/~. ...
Helium Atom
... Lecture 11 Title : Helium Atom Page-1 In this lecture we will extend the problem to more than one electron atoms. We will start with the simple one such as He atom. The quantum mechanical calculations of the energy levels in different approximations are discussed. From the ionization energy i.e the ...
... Lecture 11 Title : Helium Atom Page-1 In this lecture we will extend the problem to more than one electron atoms. We will start with the simple one such as He atom. The quantum mechanical calculations of the energy levels in different approximations are discussed. From the ionization energy i.e the ...
+l - My CCSD
... This image shows a ring of 76 iron atoms on a copper (111) surface. Electrons on this surface form a two-dimensional electron gas and scatter from the iron atoms but are confined by boundary or "corral." The wave pattern in the interior is due to the density distribution of the trapped electrons. Th ...
... This image shows a ring of 76 iron atoms on a copper (111) surface. Electrons on this surface form a two-dimensional electron gas and scatter from the iron atoms but are confined by boundary or "corral." The wave pattern in the interior is due to the density distribution of the trapped electrons. Th ...
File
... (4) Use the periodic table to determine the number of protons, electrons, neutrons, and atomic mass for a given element. (5) Define isotope and state how the atomic structure for isotopes of the same element are similar and different. (6) Calculate the average atomic mass from the relative abundance ...
... (4) Use the periodic table to determine the number of protons, electrons, neutrons, and atomic mass for a given element. (5) Define isotope and state how the atomic structure for isotopes of the same element are similar and different. (6) Calculate the average atomic mass from the relative abundance ...
Chapter 5 Review “Electrons in Atoms”
... What is the next atomic orbital in the series: 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p? In Bohr’s model of the atom, where are the electrons and protons located? What is the basis for exceptions to the aufbau diagram? How does the energy of an electron change when the electron moves closer to the nucleus? ...
... What is the next atomic orbital in the series: 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p? In Bohr’s model of the atom, where are the electrons and protons located? What is the basis for exceptions to the aufbau diagram? How does the energy of an electron change when the electron moves closer to the nucleus? ...
Chapter 5 Review “Electrons in Atoms”
... What is the next atomic orbital in the series: 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p? In Bohr’s model of the atom, where are the electrons and protons located? What is the basis for exceptions to the aufbau diagram? How does the energy of an electron change when the electron moves closer to the nucleus? ...
... What is the next atomic orbital in the series: 1s, 2s, 2p, 3s, 3p? In Bohr’s model of the atom, where are the electrons and protons located? What is the basis for exceptions to the aufbau diagram? How does the energy of an electron change when the electron moves closer to the nucleus? ...
Prelab notes
... • Atomic Orbitals: – A region around the nucleus of an atom where an electron with a given energy is likely to be found. ...
... • Atomic Orbitals: – A region around the nucleus of an atom where an electron with a given energy is likely to be found. ...
Electron Configuration
... • Atomic Orbitals: – A region around the nucleus of an atom where an electron with a given energy is likely to be found. ...
... • Atomic Orbitals: – A region around the nucleus of an atom where an electron with a given energy is likely to be found. ...