Advanced Cooling for Power Electronics
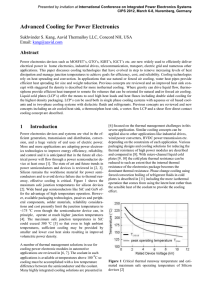
... air heats up. In this way, the base of the heat sink can be kept more isothermal so that power modules mounted at different distances from the edge where the air enters can be cooled to similar temperatures. Furthermore, the total pressure drop through the heat sink and the total mass is reduced bec ...
... air heats up. In this way, the base of the heat sink can be kept more isothermal so that power modules mounted at different distances from the edge where the air enters can be cooled to similar temperatures. Furthermore, the total pressure drop through the heat sink and the total mass is reduced bec ...
Experiment 1 - 8. Form of Energy
... In this experiment, we measure the internal energy changes, understand the way to vary the internal energy, measure the mechanical equivalent of heat and measure the specific heat of an object. ...
... In this experiment, we measure the internal energy changes, understand the way to vary the internal energy, measure the mechanical equivalent of heat and measure the specific heat of an object. ...
Manual(Exp.1)
... In the system where the internal energy can be changed by the heat and the work, its mechanical energy might not be conserved. It could be emitted in the form of heat, or the influx of heat could make the system work. Even in the internal system alone, there could be the energy exchanges between hea ...
... In the system where the internal energy can be changed by the heat and the work, its mechanical energy might not be conserved. It could be emitted in the form of heat, or the influx of heat could make the system work. Even in the internal system alone, there could be the energy exchanges between hea ...
Heat of Reaction
... produced by combusting 3.79 liter (1 gallon) of ETOH ? H = -1368 KJ/mol, p = 0.789 g/mL. CH3CH2OH + 3O2 ...
... produced by combusting 3.79 liter (1 gallon) of ETOH ? H = -1368 KJ/mol, p = 0.789 g/mL. CH3CH2OH + 3O2 ...
Apparatus to measure high-temperature thermal conductivity and
... details of instrument fabrication, the method of calibration, and typical measurements on test samples are described. The apparatus can also be used to measure the Seebeck coefficient in the same temperature range. As an example we report the thermal properties of CrSi2, which is a potential candida ...
... details of instrument fabrication, the method of calibration, and typical measurements on test samples are described. The apparatus can also be used to measure the Seebeck coefficient in the same temperature range. As an example we report the thermal properties of CrSi2, which is a potential candida ...
Procedure
... 1. To use calorimetry to measure the heat of neutralization of the reaction of aqueous NH3 with aqueous HCl to form aqueous ammonium chloride. 2. To use calorimetry to measure the heat of solution of ammonium chloride. 3. To calculate the heat of formation of solid ammonium chloride using these data ...
... 1. To use calorimetry to measure the heat of neutralization of the reaction of aqueous NH3 with aqueous HCl to form aqueous ammonium chloride. 2. To use calorimetry to measure the heat of solution of ammonium chloride. 3. To calculate the heat of formation of solid ammonium chloride using these data ...
Thermochem
... Calorimeter – insulated device used to measure heat changes. If the specific heat capacity is a characteristic property of a substance, it can be used to determine the identity of an unknown metal. ...
... Calorimeter – insulated device used to measure heat changes. If the specific heat capacity is a characteristic property of a substance, it can be used to determine the identity of an unknown metal. ...
Heat demand for a building
... losses in heat distribution losses in heat emitters (e.g. under floor heating) losses in control systems ...
... losses in heat distribution losses in heat emitters (e.g. under floor heating) losses in control systems ...
Binnie Thermochemistry Practice ANSWERS - binnie
... A) The specific heat capacity of steel is higher than the specific heat capacity of wood. B) The specific heat capacity of steel is lower than the specific heat capacity of wood. C) Steel has the ability to resist a temperature change better than wood. D) The mass of steel is less than wood so it lo ...
... A) The specific heat capacity of steel is higher than the specific heat capacity of wood. B) The specific heat capacity of steel is lower than the specific heat capacity of wood. C) Steel has the ability to resist a temperature change better than wood. D) The mass of steel is less than wood so it lo ...
JIF 314 Thermodynamics
... by the amount |QH| from HTR, turning part of this heat into work |W|, and the balance of heat, |QL| =|QH| -|W|, is rejected into the LTR. After the rejection of |QL|, the heat engine’s state will resume to the initial state i. ...
... by the amount |QH| from HTR, turning part of this heat into work |W|, and the balance of heat, |QL| =|QH| -|W|, is rejected into the LTR. After the rejection of |QL|, the heat engine’s state will resume to the initial state i. ...
Temperature & Heat
... touching the outside of the cylinder that, Heat was generated; … at 2 hours and 30 minutes it (the water) ACTUALLY BOILED…without any fire.” • The generation of heat was related to the kinetic energy of truing the cannon barrel. ...
... touching the outside of the cylinder that, Heat was generated; … at 2 hours and 30 minutes it (the water) ACTUALLY BOILED…without any fire.” • The generation of heat was related to the kinetic energy of truing the cannon barrel. ...
The Second Law of Thermodynamics: Entropy and Maxwell`s Demon
... theory to the explanation of various properties of gases, and to show that, besides accounting for the relations of pressure, density, and temperature in a single gas, it affords a mechanical explanation of the known chemical relation between the density of a gas and its equivalent weight, commonly ...
... theory to the explanation of various properties of gases, and to show that, besides accounting for the relations of pressure, density, and temperature in a single gas, it affords a mechanical explanation of the known chemical relation between the density of a gas and its equivalent weight, commonly ...
JIF 314 Thermodynamics
... by the amount |QH| from HTR, turning part of this heat into work |W|, and the balance of heat, |QL| =|QH| -|W|, is rejected into the LTR. After the rejection of |QL|, the heat engine’s state will resume to the initial state i. ...
... by the amount |QH| from HTR, turning part of this heat into work |W|, and the balance of heat, |QL| =|QH| -|W|, is rejected into the LTR. After the rejection of |QL|, the heat engine’s state will resume to the initial state i. ...
Heat sink

A heat sink is a passive heat exchanger that transfers the heat generated by an electronic or a mechanical device into a coolant fluid in motion. Then-transferred heat leaves the device with the fluid in motion, therefore allowing the regulation of the device temperature at physically feasible levels. In computers, heat sinks are used to cool central processing units or graphics processors. Heat sinks are used with high-power semiconductor devices such as power transistors and optoelectronics such as lasers and light emitting diodes (LEDs), where the heat dissipation ability of the basic device is insufficient to moderate its temperature.A heat sink is designed to maximize its surface area in contact with the cooling medium surrounding it, such as the air. Air velocity, choice of material, protrusion design and surface treatment are factors that affect the performance of a heat sink. Heat sink attachment methods and thermal interface materials also affect the die temperature of the integrated circuit. Thermal adhesive or thermal grease improve the heat sink's performance by filling air gaps between the heat sink and the heat spreader on the device.