Fundamentals of the Heat Transfer Theory
... q = −λ gradT where q is the heat flux density determined as the amount of heat transferred per unit time from unit surface; gradT = dT dn is the rate of threshold temperature variation to an isothermal surface at a given body point and at a given time moment; λ is the thermal conductivity of substan ...
... q = −λ gradT where q is the heat flux density determined as the amount of heat transferred per unit time from unit surface; gradT = dT dn is the rate of threshold temperature variation to an isothermal surface at a given body point and at a given time moment; λ is the thermal conductivity of substan ...
latest developments in indirectly heated electric resistance
... supervision or data management has been done by strip chart recorders or data loggers. This separation of function requires communication among the logic controllers, loop controllers and data acquisition equipment. Finally supervision computer to handle such factors such as scheduling, parts purcha ...
... supervision or data management has been done by strip chart recorders or data loggers. This separation of function requires communication among the logic controllers, loop controllers and data acquisition equipment. Finally supervision computer to handle such factors such as scheduling, parts purcha ...
3 - College of Arts and Sciences
... How are Moles determined from Molarity? Moles of Solute = Molarity x (Volume in Liters) ------------------------------------Calculate the number of moles of HCl in 50.0 mL of 2.00 M HCl(aq) ...
... How are Moles determined from Molarity? Moles of Solute = Molarity x (Volume in Liters) ------------------------------------Calculate the number of moles of HCl in 50.0 mL of 2.00 M HCl(aq) ...
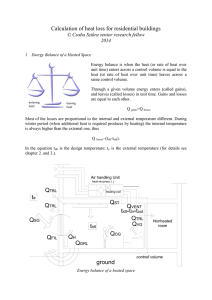
Calculation of heat loss for buildings
... External gain is or solar gain (also known as solar heat gain or passive solar gain) which refers to the increase in temperature in a space, object or structure that results from solar radiation. The amount of solar gain increases with the strength of the sun, and with the ability of any intervening ...
... External gain is or solar gain (also known as solar heat gain or passive solar gain) which refers to the increase in temperature in a space, object or structure that results from solar radiation. The amount of solar gain increases with the strength of the sun, and with the ability of any intervening ...
The Second Law: Definition of Entropy
... The cycle just described could be the cycle for a piston in a steam engine or in an internal combustion engine. The hot gas that expands following combustion of a small quantity of fossil fuel drives the cycle. If you think about the fact that the piston is connected to the crankshaft you pressure o ...
... The cycle just described could be the cycle for a piston in a steam engine or in an internal combustion engine. The hot gas that expands following combustion of a small quantity of fossil fuel drives the cycle. If you think about the fact that the piston is connected to the crankshaft you pressure o ...
Heat
... between two surfaces is a complicated matter since it depends on • the properties of the surfaces • their orientation relative to each other • the interaction of the medium between the surfaces with radiation Radiation is usually significant relative to conduction or natural convection, but negligib ...
... between two surfaces is a complicated matter since it depends on • the properties of the surfaces • their orientation relative to each other • the interaction of the medium between the surfaces with radiation Radiation is usually significant relative to conduction or natural convection, but negligib ...
heat transfer (for d..
... closer its atoms are together. That means the transfer of energy of one atom to the next is more effective. Thus, gases insulate better than liquids, which in turn insulate better than solids. An interesting fact is that poor conductors of electricity are also poor heat conductors. Wood is a much be ...
... closer its atoms are together. That means the transfer of energy of one atom to the next is more effective. Thus, gases insulate better than liquids, which in turn insulate better than solids. An interesting fact is that poor conductors of electricity are also poor heat conductors. Wood is a much be ...
Heat gains utilisation and system efficiency influence to the heat
... The heat demand for heating of buildings on Lithuanian climate conditions usually is a major part of the overall building energy balance. Therefore, the exact and correct estimation of heat demand is very important both for the design of new, and especially for the analysis of existing, renovated bu ...
... The heat demand for heating of buildings on Lithuanian climate conditions usually is a major part of the overall building energy balance. Therefore, the exact and correct estimation of heat demand is very important both for the design of new, and especially for the analysis of existing, renovated bu ...
Heat sink

A heat sink is a passive heat exchanger that transfers the heat generated by an electronic or a mechanical device into a coolant fluid in motion. Then-transferred heat leaves the device with the fluid in motion, therefore allowing the regulation of the device temperature at physically feasible levels. In computers, heat sinks are used to cool central processing units or graphics processors. Heat sinks are used with high-power semiconductor devices such as power transistors and optoelectronics such as lasers and light emitting diodes (LEDs), where the heat dissipation ability of the basic device is insufficient to moderate its temperature.A heat sink is designed to maximize its surface area in contact with the cooling medium surrounding it, such as the air. Air velocity, choice of material, protrusion design and surface treatment are factors that affect the performance of a heat sink. Heat sink attachment methods and thermal interface materials also affect the die temperature of the integrated circuit. Thermal adhesive or thermal grease improve the heat sink's performance by filling air gaps between the heat sink and the heat spreader on the device.