Historical Geology
... • Geologists use two different frames of reference – when discussing geologic time – Relative dating involves placing geologic events • in a sequential order as determined • from their position in the geologic record ...
... • Geologists use two different frames of reference – when discussing geologic time – Relative dating involves placing geologic events • in a sequential order as determined • from their position in the geologic record ...
Plate Tectonic Quiz Review
... • Heat transfers by movement of currents in liquids and gasses. This is caused by differences in temperature and density. An example of this type of heat transfer occurs when mantle rock moves from near the core, towards the crust, and back again. A. Radiation B. Conduction C. Convection ...
... • Heat transfers by movement of currents in liquids and gasses. This is caused by differences in temperature and density. An example of this type of heat transfer occurs when mantle rock moves from near the core, towards the crust, and back again. A. Radiation B. Conduction C. Convection ...
Geology Power Hour Powerpoint Geology Power Hour
... between convergent, divergent, and transform plate boundaries. 5. I can list and describe the three types of volcanoes. 6. I can use evidence such as layers of fossils and sediments, current landforms, and tectonic movements as evidence of geologic processes that have changed the Earth’s surface. ...
... between convergent, divergent, and transform plate boundaries. 5. I can list and describe the three types of volcanoes. 6. I can use evidence such as layers of fossils and sediments, current landforms, and tectonic movements as evidence of geologic processes that have changed the Earth’s surface. ...
Continental Drift Theory and Plate Tectonics
... Support For Continental Drift Theory • The Shapes Match • The continents look as if they were pieces of a giant jigsaw puzzle • The Plants and Animals Match • Identical fossil species along the coastal parts of Africa and South America. • Rocks Match - These broad belts match when the end of the co ...
... Support For Continental Drift Theory • The Shapes Match • The continents look as if they were pieces of a giant jigsaw puzzle • The Plants and Animals Match • Identical fossil species along the coastal parts of Africa and South America. • Rocks Match - These broad belts match when the end of the co ...
Plate Tectonics, Tectonic Plates Information, Facts, News, Photos
... There are a few handfuls of major plates and dozens of smaller, or minor, plates. Six of the majors are named for the continents embedded within them, such as the North American, African, and Antarctic plates. Though smaller in size, the minors are no less important when it comes to shaping the Eart ...
... There are a few handfuls of major plates and dozens of smaller, or minor, plates. Six of the majors are named for the continents embedded within them, such as the North American, African, and Antarctic plates. Though smaller in size, the minors are no less important when it comes to shaping the Eart ...
Chapter 7 Earth: Our Home in Space
... Earth’s Geologic History • Gravitational condensation from the solar nebula of gases to solid particles about 4.5 billion years ago. • Rapid accretion of particles to planetesimals about half the size of the current planet. • Slower accretion from largest planetesimals. Complete melting of surface. ...
... Earth’s Geologic History • Gravitational condensation from the solar nebula of gases to solid particles about 4.5 billion years ago. • Rapid accretion of particles to planetesimals about half the size of the current planet. • Slower accretion from largest planetesimals. Complete melting of surface. ...
Continental Drift Notes
... Wegener’s idea was ridiculed by geologists This is because while Wegener could provide evidence, he couldn’t ...
... Wegener’s idea was ridiculed by geologists This is because while Wegener could provide evidence, he couldn’t ...
FOURTH QUARTER - New Haven Science
... 4. How does the silica content of magma affect the type of landform that is formed? 5. How do volcanic belts form along plate boundaries? d. Essential Concepts 1. Energy from an earthquake travels in waves. The waves can produce severe movement in the Earth’s crust and surface. 2. Scientists use lev ...
... 4. How does the silica content of magma affect the type of landform that is formed? 5. How do volcanic belts form along plate boundaries? d. Essential Concepts 1. Energy from an earthquake travels in waves. The waves can produce severe movement in the Earth’s crust and surface. 2. Scientists use lev ...
Unit 5_Lesson 109_Review
... -Evaporation: liquid water is heated up by the Sun and becomes vapor. -Condensation: vapor in the air cools down and turns into a liquid. This forms clouds. -Precipitation: water falls from clouds as rain, sleet, hail, or snow. -Runoff: water flows downhill and eventually reaches the ocean or sinks ...
... -Evaporation: liquid water is heated up by the Sun and becomes vapor. -Condensation: vapor in the air cools down and turns into a liquid. This forms clouds. -Precipitation: water falls from clouds as rain, sleet, hail, or snow. -Runoff: water flows downhill and eventually reaches the ocean or sinks ...
Dynamic Ocean Floor
... Outer section of this layer is liquid, this allows the lithosphere to move. • Convection currents play an important role. ...
... Outer section of this layer is liquid, this allows the lithosphere to move. • Convection currents play an important role. ...
How*s Earth*s Plates Move
... Earth’s Structure D6 9/27 Earth’s Layers 1. crust: Earth’s outermost layer 2. mantle: layer directly beneath ...
... Earth’s Structure D6 9/27 Earth’s Layers 1. crust: Earth’s outermost layer 2. mantle: layer directly beneath ...
Eclipses & Features of the Moon
... • The revolution of the moon not only causes the phases of the moon but also is the cause of eclipses. • The moon's orbit is not in the same plane as the Earth's orbit around the sun so eclipses only happen a few times a year. ...
... • The revolution of the moon not only causes the phases of the moon but also is the cause of eclipses. • The moon's orbit is not in the same plane as the Earth's orbit around the sun so eclipses only happen a few times a year. ...
Plate Tectonics Lesson Plan
... Standard ES-3: Students will demonstrate an understanding of the internal and external dynamics of solid Earth. ES-3.2 Explain the differentiation of the structure of Earth’s layers into a core, mantle, and crust based on the production of internal heat from the decay of isotopes and the role of gra ...
... Standard ES-3: Students will demonstrate an understanding of the internal and external dynamics of solid Earth. ES-3.2 Explain the differentiation of the structure of Earth’s layers into a core, mantle, and crust based on the production of internal heat from the decay of isotopes and the role of gra ...
Exam Block #5
... km – not even through the crust! (Earth’s diameter is 6371 km). Most of our knowledge of Earth’s interior comes from the study of earthquake waves. ...
... km – not even through the crust! (Earth’s diameter is 6371 km). Most of our knowledge of Earth’s interior comes from the study of earthquake waves. ...
File
... A cross section of Earth showing the following layers: (1) crust (2) mantle (3a) outer core (3b) inner core (4) lithosphere (5) asthenosphere (6) outer core (7) inner core. Core, mantle, and crust are divisions based on composition: 1. The crust is less than 1% of Earth by mass. The two types are oc ...
... A cross section of Earth showing the following layers: (1) crust (2) mantle (3a) outer core (3b) inner core (4) lithosphere (5) asthenosphere (6) outer core (7) inner core. Core, mantle, and crust are divisions based on composition: 1. The crust is less than 1% of Earth by mass. The two types are oc ...
Lecture 5 - Plate Tectonics and Rocks
... Intermediate (chemically) igneous rocks are commonly formed at convergent boundaries Partial melting of basaltic oceanic crust produces intermediate magmas ...
... Intermediate (chemically) igneous rocks are commonly formed at convergent boundaries Partial melting of basaltic oceanic crust produces intermediate magmas ...
lithosphere, mid-ocean ridge
... b. the home of all life on Earth c. the thickest layer of hot rock d. the thinnest and hottest layer 8. Tectonic plates make up Earth’s a. lower mantle b. lithosphere c. asthenosphere d. inner core 9. Why did many scientists regent Wegner’s continental drift hypothesis? a. He could not explain how t ...
... b. the home of all life on Earth c. the thickest layer of hot rock d. the thinnest and hottest layer 8. Tectonic plates make up Earth’s a. lower mantle b. lithosphere c. asthenosphere d. inner core 9. Why did many scientists regent Wegner’s continental drift hypothesis? a. He could not explain how t ...
1 Eons, Eras, Periods and Epochs Dating by radioactive isotopes
... view of a new solar system 1500 l-y away in the Orion Nebula ...
... view of a new solar system 1500 l-y away in the Orion Nebula ...
6TH GRADE ADVANCED EARTH SCIENCE LEOCE STUDY GUIDE
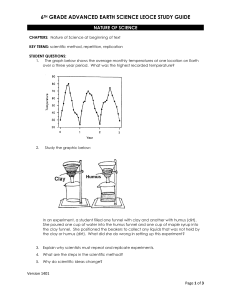
... radiation, global winds, evaporation, water cycle, weather, ozone layer, condensation, transpiration, precipitation, salinity, radiation, conduction, and convection, land breeze, sea breeze STUDENT QUESTIONS: 6. Explain the Sun’s role in the water cycle. 7. Explain the effects of ocean currents on c ...
... radiation, global winds, evaporation, water cycle, weather, ozone layer, condensation, transpiration, precipitation, salinity, radiation, conduction, and convection, land breeze, sea breeze STUDENT QUESTIONS: 6. Explain the Sun’s role in the water cycle. 7. Explain the effects of ocean currents on c ...
Geophysics

Geophysics /dʒiːoʊfɪzɪks/ is a subject of natural science concerned with the physical processes and physical properties of the Earth and its surrounding space environment, and the use of quantitative methods for their analysis. The term geophysics sometimes refers only to the geological applications: Earth's shape; its gravitational and magnetic fields; its internal structure and composition; its dynamics and their surface expression in plate tectonics, the generation of magmas, volcanism and rock formation. However, modern geophysics organizations use a broader definition that includes the water cycle including snow and ice; fluid dynamics of the oceans and the atmosphere; electricity and magnetism in the ionosphere and magnetosphere and solar-terrestrial relations; and analogous problems associated with the Moon and other planets.Although geophysics was only recognized as a separate discipline in the 19th century, its origins go back to ancient times. The first magnetic compasses were made from lodestones, while more modern magnetic compasses played an important role in the history of navigation. The first seismic instrument was built in 132 BC. Isaac Newton applied his theory of mechanics to the tides and the precession of the equinox; and instruments were developed to measure the Earth's shape, density and gravity field, as well as the components of the water cycle. In the 20th century, geophysical methods were developed for remote exploration of the solid Earth and the ocean, and geophysics played an essential role in the development of the theory of plate tectonics.Geophysics is applied to societal needs, such as mineral resources, mitigation of natural hazards and environmental protection. Geophysical survey data are used to analyze potential petroleum reservoirs and mineral deposits, locate groundwater, find archaeological relics, determine the thickness of glaciers and soils, and assess sites for environmental remediation.