Module 19 Hearing Module Preview In the sense of hearing, sound
... energy. The visible outer ear channels the sound waves through the auditory canal to the eardrum, a tight membrane that vibrates with the waves. Transmitted via the bones of the middle ear (the hammer, anvil, and stirrup) to the fluid-filled cochlea in the inner ear, these vibrations cause the oval ...
... energy. The visible outer ear channels the sound waves through the auditory canal to the eardrum, a tight membrane that vibrates with the waves. Transmitted via the bones of the middle ear (the hammer, anvil, and stirrup) to the fluid-filled cochlea in the inner ear, these vibrations cause the oval ...
Sensory system - WordPress.com
... o Tympanic membrane o Ear bones (ossicles): responsible for the transmission Malleus (hammer) Incus ( anvil) Stapes (stirrup) ...
... o Tympanic membrane o Ear bones (ossicles): responsible for the transmission Malleus (hammer) Incus ( anvil) Stapes (stirrup) ...
Influence of hearing sounds Materials:
... 4. Marco Polo: Have one person sit in the middle with eyes closed and play “marco polo” and have them point to the direction of the sound. 5. 2 better than 1: To show the importance of two ears, measure out distances from a seat 5ft, 10ft, 15ft. have the subject close their eyes and you go stand on ...
... 4. Marco Polo: Have one person sit in the middle with eyes closed and play “marco polo” and have them point to the direction of the sound. 5. 2 better than 1: To show the importance of two ears, measure out distances from a seat 5ft, 10ft, 15ft. have the subject close their eyes and you go stand on ...
Lecture 11- ear final
... Define the contents of the tympanic cavity: I. Ear ossicles,: (malleus, incus and stapes) II. Muscles, (tensor tympani and stapedius). III. Nerves (branches of facial and glossopharyngeal). List the parts of the inner ear, bony part filled with perilymph (Cochlea, vestibule and semicircular canals), ...
... Define the contents of the tympanic cavity: I. Ear ossicles,: (malleus, incus and stapes) II. Muscles, (tensor tympani and stapedius). III. Nerves (branches of facial and glossopharyngeal). List the parts of the inner ear, bony part filled with perilymph (Cochlea, vestibule and semicircular canals), ...
EXAMINATION OF THE EAR
... your right hand, handle pointing forwards For left ear, hold in your left hand, handle pointing forwards Pull the pinna up and back to straighten EAM ...
... your right hand, handle pointing forwards For left ear, hold in your left hand, handle pointing forwards Pull the pinna up and back to straighten EAM ...
The Nonvisual senses
... inner ear; sound waves traveling through the cochlear fluid trigger neural impulses The motion of these impulses causes ripples in ...
... inner ear; sound waves traveling through the cochlear fluid trigger neural impulses The motion of these impulses causes ripples in ...
The external ear
... It measures about 20-mm length & consists of 2-parts; the membranous labyrinth located within the 2nd part the bony labyrinth, which is a bony cavity, the membranous part consist of a delicate sacs & canals filled with fluid called: endolymph, while the space between the bony & membranous labyrinth ...
... It measures about 20-mm length & consists of 2-parts; the membranous labyrinth located within the 2nd part the bony labyrinth, which is a bony cavity, the membranous part consist of a delicate sacs & canals filled with fluid called: endolymph, while the space between the bony & membranous labyrinth ...
The External Ear
... known as the annulus. The fibrous annulus in turn fits into a slot in the tympanic bone called the sulcus. Landmarks of the ear drum The tympanic membrane has a pearly grey colour with a triangular bright area, the cone of light, extending from the centre (umbo) downwards and forwards. The most pro ...
... known as the annulus. The fibrous annulus in turn fits into a slot in the tympanic bone called the sulcus. Landmarks of the ear drum The tympanic membrane has a pearly grey colour with a triangular bright area, the cone of light, extending from the centre (umbo) downwards and forwards. The most pro ...
Ear Anatomy Auricle Anatomy: – Elastic cartilage that is covered with
... the stapes in the oval window. This will tighten the anular ligament and reduce the osscilatory range. • This muscle is innervated by the facial nerve (CN VII) Clinical Applications: – Paralysis of the Stapedius Muscle: • Usually caused by a lesion or mass to the facial nerve • Results in the patien ...
... the stapes in the oval window. This will tighten the anular ligament and reduce the osscilatory range. • This muscle is innervated by the facial nerve (CN VII) Clinical Applications: – Paralysis of the Stapedius Muscle: • Usually caused by a lesion or mass to the facial nerve • Results in the patien ...
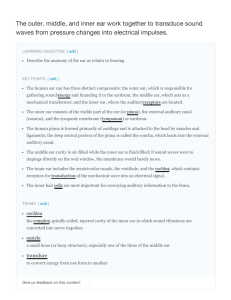
The outer, middle, and inner ear work together to
... waves strike the tympanum, causing it to vibrate. The mechanical energy from the moving tympanum transmits the vibrations to the three bones of the middle ear. The stapes transmits the vibrations to a thin diaphragm called the oval window, which is the outermost structure of the inner ear. Why must ...
... waves strike the tympanum, causing it to vibrate. The mechanical energy from the moving tympanum transmits the vibrations to the three bones of the middle ear. The stapes transmits the vibrations to a thin diaphragm called the oval window, which is the outermost structure of the inner ear. Why must ...
Psychoacoustics - University of Limerick
... The basilar membrane response to sound • Movement of the stapes sets the oval window in motion – causes the BM to move. • Response of BM to sinusoidal stimulation – travelling wave, which moves from base to apex. • The position of the peak in the vibration pattern on the BM depends on the frequen ...
... The basilar membrane response to sound • Movement of the stapes sets the oval window in motion – causes the BM to move. • Response of BM to sinusoidal stimulation – travelling wave, which moves from base to apex. • The position of the peak in the vibration pattern on the BM depends on the frequen ...
otolaryngology
... The purpose of the middle ear and ossicular chain is to overcome the impedance mismatch of going from an air filled outer ear to a fluid filled inner ear. ...
... The purpose of the middle ear and ossicular chain is to overcome the impedance mismatch of going from an air filled outer ear to a fluid filled inner ear. ...
The sense of hearing - Lightweight OCW University of Palestine
... There are two middle ear muscles: 1. The tensor tympani muscle: inserts on the malleus. Action: dampens down vibrations of tympanic membrane. 2. The stapedius muscle: inserts on the neck of stapes. Action: dampens down vibrations of stapes. Function: 1. They regulate the range of movement in the tym ...
... There are two middle ear muscles: 1. The tensor tympani muscle: inserts on the malleus. Action: dampens down vibrations of tympanic membrane. 2. The stapedius muscle: inserts on the neck of stapes. Action: dampens down vibrations of stapes. Function: 1. They regulate the range of movement in the tym ...
Show It
... The scala tympani terminates at the round window The scalas tympani and vestibuli: Are filled with perilymph Are continuous with each other via the helicotrema The scala media is filled with endolymph ...
... The scala tympani terminates at the round window The scalas tympani and vestibuli: Are filled with perilymph Are continuous with each other via the helicotrema The scala media is filled with endolymph ...
PSY 342: Review for Exam 3 Chapter 11: Sound and the Auditory
... Human hearing range is 20-20,000 Hertz Ear structures (outer, middle and inner ear) Outer ear: pinna and auditory canal (protects tympanic membrane or ear drum) Middle ear: tympanic membrane and three ossicles (malleus, incus, stapes) amplify vibrations Inner ear: Cochlea which contains the Organ of ...
... Human hearing range is 20-20,000 Hertz Ear structures (outer, middle and inner ear) Outer ear: pinna and auditory canal (protects tympanic membrane or ear drum) Middle ear: tympanic membrane and three ossicles (malleus, incus, stapes) amplify vibrations Inner ear: Cochlea which contains the Organ of ...
Ear
The ear is the organ that detects sound. It not only receives sound, but also aids in balance and body position. The ear is part of the auditory system.Often the entire organ is considered the ear, though it may also be considered just the visible portion. In most mammals, the visible ear is a flap of tissue that is also called the pinna (or auricle in humans) and is the first of many steps in hearing. Vertebrates have a pair of ears placed somewhat symmetrically on opposite sides of the head. This arrangement aids in the ability to localize sound sources.