Mechanics 1 Revision Notes
... Always state which direction (up or down) you are taking as positive. A ball is thrown vertically upwards from O with a speed of 14 m s-1. ...
... Always state which direction (up or down) you are taking as positive. A ball is thrown vertically upwards from O with a speed of 14 m s-1. ...
ƒ A S ƒ ƒ B
... the shape of the path is always a parabola. We usually choose the origin to be at the initial position of the projectile. (See Examples 3.5–3.10.) Uniform and nonuniform circular motion: When a particle moves in a circular path of radius R with constant speed v S (uniform circular motion), its accel ...
... the shape of the path is always a parabola. We usually choose the origin to be at the initial position of the projectile. (See Examples 3.5–3.10.) Uniform and nonuniform circular motion: When a particle moves in a circular path of radius R with constant speed v S (uniform circular motion), its accel ...
Relativity made relatively easy
... 16.3.2 Particle and antiparticle solutions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 439 16.3.3 Low velocity limit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 442 16.4 Exercises ...
... 16.3.2 Particle and antiparticle solutions . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 439 16.3.3 Low velocity limit . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 442 16.4 Exercises ...
Example
... Example: The figure shows a student seated on a stool that can rotate freely about a vertical axis. The student, who has been set into rotation at an initial angular speed i , holds two dumbbells in his outstretched hands. His angular momentum vector L lies along the rotation axis, pointing upward ...
... Example: The figure shows a student seated on a stool that can rotate freely about a vertical axis. The student, who has been set into rotation at an initial angular speed i , holds two dumbbells in his outstretched hands. His angular momentum vector L lies along the rotation axis, pointing upward ...
Newton`s Third Law 1.0
... force Fmax and the interaction time t. The force Fmax occurs when the carts are closest to each other with their magnets repelling most strongly. As always, t is the time interval during which one cart feels the force due to the other cart. The average value of the time-dependent force (over the t ...
... force Fmax and the interaction time t. The force Fmax occurs when the carts are closest to each other with their magnets repelling most strongly. As always, t is the time interval during which one cart feels the force due to the other cart. The average value of the time-dependent force (over the t ...
jeopardy final physics review
... car’s final velocity was 90 miles/hr, what was the car’s initial velocity? A: What is 84 mph ? S2C06 Jeopardy Review ...
... car’s final velocity was 90 miles/hr, what was the car’s initial velocity? A: What is 84 mph ? S2C06 Jeopardy Review ...
Acceleration - Solon City Schools
... A. Speed is more complex while velocity is less complex. B. Velocity is time divided by distance and speed is distance divided by time. C. Velocity requires a direction while speed does not. D. Speed and velocity are ...
... A. Speed is more complex while velocity is less complex. B. Velocity is time divided by distance and speed is distance divided by time. C. Velocity requires a direction while speed does not. D. Speed and velocity are ...
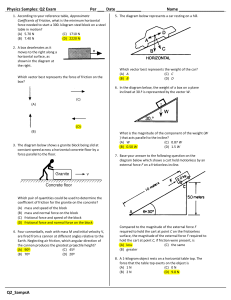
Exam 1 Solutions Kinematics and Newton’s laws of motion
... A) The car travels westward at constant speed. B) The car travels eastward and speeds up. C) The car travels westward and slows down. D) The car travels eastward and slows down. E) The car starts from rest and moves toward the east. In C) What if you choose west as negative? ...
... A) The car travels westward at constant speed. B) The car travels eastward and speeds up. C) The car travels westward and slows down. D) The car travels eastward and slows down. E) The car starts from rest and moves toward the east. In C) What if you choose west as negative? ...
module p1: energy for the home
... reduces the forces required to act, reduces the injury Explain that momentum is a property that is always conserved and use that to explain: explosions, recoil, rocket ...
... reduces the forces required to act, reduces the injury Explain that momentum is a property that is always conserved and use that to explain: explosions, recoil, rocket ...
CONCEPT OF EQUILIBRIUM AND ROTATIONAL INERTIA
... En Pointe is a position in ballet that is presented on the tips of the toes. En Pointe can be of different varieties in ballet, but their specific focus is based on grace and particular technique. The structural concept behind the technique of En Pointe is that of equilibrium. A body or physical sys ...
... En Pointe is a position in ballet that is presented on the tips of the toes. En Pointe can be of different varieties in ballet, but their specific focus is based on grace and particular technique. The structural concept behind the technique of En Pointe is that of equilibrium. A body or physical sys ...
Ezio Fornero, Space and Motion as Problems of
... theory laws of Physics are invariant with respect to all the possible different systems of reference, so special frames of references are not needed. This is an optimum method to discover the real, universal physical laws and leads to General Relativity. Let’s follow for now Classical Dynamics. Whil ...
... theory laws of Physics are invariant with respect to all the possible different systems of reference, so special frames of references are not needed. This is an optimum method to discover the real, universal physical laws and leads to General Relativity. Let’s follow for now Classical Dynamics. Whil ...
Planar kinematics of a rigid body: Review
... 1.2.2 Classification of kinematic mechanisms (see Figure 1.21) Type 1: All joints are a revolute pair. Type 2: There is a sliding pair but its sliding axis is fixed with respect to the ground. Type 3: There is a high pair with the bar body fixed with respect to the ground. Type 4: There is a high pa ...
... 1.2.2 Classification of kinematic mechanisms (see Figure 1.21) Type 1: All joints are a revolute pair. Type 2: There is a sliding pair but its sliding axis is fixed with respect to the ground. Type 3: There is a high pair with the bar body fixed with respect to the ground. Type 4: There is a high pa ...
Motion and Speed Classwork Name
... 1. A change in position relative to a reference frame. 2. You are seeing the ground at rest because you are moving at the same speed as the ground. Someone in space sees you moving in a circle because they are in a different reference frame relative to you. 3. Speed is change in total distance trave ...
... 1. A change in position relative to a reference frame. 2. You are seeing the ground at rest because you are moving at the same speed as the ground. Someone in space sees you moving in a circle because they are in a different reference frame relative to you. 3. Speed is change in total distance trave ...