Chapter 13: Periodic Motion
... • In real world dissipative forces such as friction between a block and a table exist. Such a dissipative force will decrease the amplitude of an oscillation – damped oscillation. The friction reduces the mechanical energy of the system as time passes, and the motion is said to be damped. ...
... • In real world dissipative forces such as friction between a block and a table exist. Such a dissipative force will decrease the amplitude of an oscillation – damped oscillation. The friction reduces the mechanical energy of the system as time passes, and the motion is said to be damped. ...
doc - atmo.arizona.edu
... larger, raindrop scales, the drag force is due to combined eddy viscosity and stagnation pressure. The transition between the two types of behavior occurs near a droplet radius of 200 microns. For typical cloud droplet sizes of ~10 microns or less the terminal velocity is quite small, 1 cm/s or less ...
... larger, raindrop scales, the drag force is due to combined eddy viscosity and stagnation pressure. The transition between the two types of behavior occurs near a droplet radius of 200 microns. For typical cloud droplet sizes of ~10 microns or less the terminal velocity is quite small, 1 cm/s or less ...
PRACExam-00
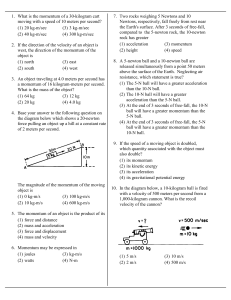
... 77. Tarzan can swim at a speed of 5.00 km/hr in still water. How long will it take him to swim 8.00 km upstream if the R current against him is 2.00 km/hr? A a. 1.14 hours b. .375 hours c. 2.67 hours d. 24 hours 78. If you constantly exert a horizontal force of 200 N to slide a crate across a factor ...
... 77. Tarzan can swim at a speed of 5.00 km/hr in still water. How long will it take him to swim 8.00 km upstream if the R current against him is 2.00 km/hr? A a. 1.14 hours b. .375 hours c. 2.67 hours d. 24 hours 78. If you constantly exert a horizontal force of 200 N to slide a crate across a factor ...
Ch# 9 - KFUPM Faculty List
... Q12. A 3.0 kg mass is positioned at (0, 8.0) m, and a 1.0 kg mass is positioned at (12, 0) m. What are the coordinates of a 4.0 kg mass which will result in the center of mass of the system of three masses being located at the origin (0, 0)? (Ans: (-3.0, -6.0) m ) T052: Q#9: The location of two thin ...
... Q12. A 3.0 kg mass is positioned at (0, 8.0) m, and a 1.0 kg mass is positioned at (12, 0) m. What are the coordinates of a 4.0 kg mass which will result in the center of mass of the system of three masses being located at the origin (0, 0)? (Ans: (-3.0, -6.0) m ) T052: Q#9: The location of two thin ...
Lecture 1: Rotation of Rigid Body
... unexpected speedup called a glitch. One explanation is that a glitch occurs when the crust of the neutron star settles slightly, decreasing the moment of inertia about the rotation axis. A neutron star with angular speed 0=70.4 rad/s underwent such a glitch in October 1975 that increased its angula ...
... unexpected speedup called a glitch. One explanation is that a glitch occurs when the crust of the neutron star settles slightly, decreasing the moment of inertia about the rotation axis. A neutron star with angular speed 0=70.4 rad/s underwent such a glitch in October 1975 that increased its angula ...
Powerpoint for Today
... dive, his body moves at high speed along a segment of an upward-bending, approximately circular path. While his body moves up, his blood tends to move straight ahead (tangent to the circle) and begins to fill the easily expandable veins in his legs. This can deprive his brain of blood and cause a bl ...
... dive, his body moves at high speed along a segment of an upward-bending, approximately circular path. While his body moves up, his blood tends to move straight ahead (tangent to the circle) and begins to fill the easily expandable veins in his legs. This can deprive his brain of blood and cause a bl ...
t = 0
... t=0 . The projection of P on the x axis point Q, moves back and forth along a line parallel to the diameter of the circle, between the limits .We see that the x coordinate of p and Q is given by x A cos(t ) ...
... t=0 . The projection of P on the x axis point Q, moves back and forth along a line parallel to the diameter of the circle, between the limits .We see that the x coordinate of p and Q is given by x A cos(t ) ...
Physics - Study in Pakistan
... disturbance because of the human activities in the ecological balance, thus taking care of the environment; ...
... disturbance because of the human activities in the ecological balance, thus taking care of the environment; ...
physics5 - Ingvar Johansson: Philosophy Home Page
... instance, in ‘(force) =def (mass) x (length) x (time)-2’, and ‘(energy) =def (mass) x (length)2 x (time)-2 ’. Every base quantity is also ascribed a conventional base unit; length has meter, mass has kilogram, time second, and temperature kelvin. The metaphysically relevant question is whether it is ...
... instance, in ‘(force) =def (mass) x (length) x (time)-2’, and ‘(energy) =def (mass) x (length)2 x (time)-2 ’. Every base quantity is also ascribed a conventional base unit; length has meter, mass has kilogram, time second, and temperature kelvin. The metaphysically relevant question is whether it is ...
Chapter 9 Clickers
... summer camp. The canoe happens to be oriented with the front of the canoe pointing due north. One of the girls is at the front of the canoe and the other is at the back of the canoe. The girl at the front walks to sit next to her friend at the back and sits down. What effect does this event have on ...
... summer camp. The canoe happens to be oriented with the front of the canoe pointing due north. One of the girls is at the front of the canoe and the other is at the back of the canoe. The girl at the front walks to sit next to her friend at the back and sits down. What effect does this event have on ...