Document
... So, B is understood to represent a vector quantity, having magnitude and direction, while B is understood to be a scalar quantity, having magnitude but no direction. When handwriting a vector, place an arrow over the letter to represent a vector. ...
... So, B is understood to represent a vector quantity, having magnitude and direction, while B is understood to be a scalar quantity, having magnitude but no direction. When handwriting a vector, place an arrow over the letter to represent a vector. ...
Force and Motion -
... physics through the process. Additional references should be sought to further understand the topics like vectors, elementary calculus, etc., most of which can be found in relevant F6-7 ...
... physics through the process. Additional references should be sought to further understand the topics like vectors, elementary calculus, etc., most of which can be found in relevant F6-7 ...
Torque
... A weight attached to a spring undergoes simple harmonic motion. A marking pen attached to the bob traces a sine curve on a sheet of paper that is moving horizontally at constant speed. A sine curve is a pictorial representation of a wave. A sine curve is a pictorial representation of a SHM. ...
... A weight attached to a spring undergoes simple harmonic motion. A marking pen attached to the bob traces a sine curve on a sheet of paper that is moving horizontally at constant speed. A sine curve is a pictorial representation of a wave. A sine curve is a pictorial representation of a SHM. ...
rate of change
... The Lagrangian term dt is the rate of change experienced by a given tagged water parcel. The Eulerian term t is the local rate of change at a fixed point. du ...
... The Lagrangian term dt is the rate of change experienced by a given tagged water parcel. The Eulerian term t is the local rate of change at a fixed point. du ...
ME 242 Chapter 13
... (B) vA,y = v0*cot() (C) vA,y = v0*cos() (D)vA,y = 2*v0 (E) vA,y = v0/cos() ...
... (B) vA,y = v0*cot() (C) vA,y = v0*cos() (D)vA,y = 2*v0 (E) vA,y = v0/cos() ...
01-4-momentum-with
... • change in momentum is in same direction as net force • applies to each component of momentum • net force is due to interactions of the system with the surroundings • time interval is the duration of the interaction • product of net force times the time interval is called impulse • if no interactio ...
... • change in momentum is in same direction as net force • applies to each component of momentum • net force is due to interactions of the system with the surroundings • time interval is the duration of the interaction • product of net force times the time interval is called impulse • if no interactio ...
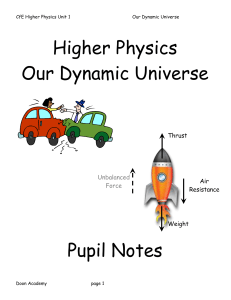
Our Dynamic Universe notes
... Albert Einstein was the first person to fully consider that travelling at the speed of light can alter space time – this was fully discussed in his Special Theory of Relativity. The theory states that, in reality, nothing of mass would be able to travel at the speed of light as the mass of the objec ...
... Albert Einstein was the first person to fully consider that travelling at the speed of light can alter space time – this was fully discussed in his Special Theory of Relativity. The theory states that, in reality, nothing of mass would be able to travel at the speed of light as the mass of the objec ...
Solutions - UCSB C.L.A.S.
... compressing it. The spring then unloads, sending the box back in the opposite direction. ...
... compressing it. The spring then unloads, sending the box back in the opposite direction. ...
Ch13-2 Simple Harmonic Motion
... B. Conservation of energy. C. Conservation of momentum. D. The work-kinetic energy theorem. ...
... B. Conservation of energy. C. Conservation of momentum. D. The work-kinetic energy theorem. ...




![Fall Semester Review - Physics [Regular]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001475483_1-821ba0594b36cdf9728de3eb9fea5ec6-300x300.png)