Moments & Levers
... In order to understand Mechanisms better, we need to understand pivots, moments and equilibrium. ...
... In order to understand Mechanisms better, we need to understand pivots, moments and equilibrium. ...
Dynamics Pupil Notes Name
... Be able to perform calculations using the a = (v-u)/t formula. Be able to draw a velocity time graph and describe the motion of an object from its velocity time graph. Be able to calculate acceleration and displacement from a velocity time graph. ...
... Be able to perform calculations using the a = (v-u)/t formula. Be able to draw a velocity time graph and describe the motion of an object from its velocity time graph. Be able to calculate acceleration and displacement from a velocity time graph. ...
Mechanisms Levers Class 1 levers:
... gear ratio, and can be calculated using the number of teeth. The formula is: Gear ratio = number or teeth on driven gear ÷ number of teeth on the driver gear So the gear ratio for the simple gear train above, if the smaller gear is the driver gear, is: Gear ratio = 60 ÷ 15 = 4. In other words, the d ...
... gear ratio, and can be calculated using the number of teeth. The formula is: Gear ratio = number or teeth on driven gear ÷ number of teeth on the driver gear So the gear ratio for the simple gear train above, if the smaller gear is the driver gear, is: Gear ratio = 60 ÷ 15 = 4. In other words, the d ...
1 - CSUN.edu
... 1.Choose an object that you will use to test your hypotheses. Calculate kinetic friction of the object you will be using for table B. 2.Decide on three NET forces you will be testing. For example you can test the net forces of 2N, 4N, and 6N. Write these net forces in time table B. 3. Draw the three ...
... 1.Choose an object that you will use to test your hypotheses. Calculate kinetic friction of the object you will be using for table B. 2.Decide on three NET forces you will be testing. For example you can test the net forces of 2N, 4N, and 6N. Write these net forces in time table B. 3. Draw the three ...
Rotational Kinematics and Dynamics - Personal.psu.edu
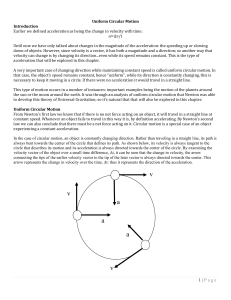
... It is important to notice that circular motion connects the concepts of linear and rotational motion. For any object that is rotating, a particular point on that object is moving in a circle. One of the goals of this lab activity is to explore and understand this connection. The translational motion ...
... It is important to notice that circular motion connects the concepts of linear and rotational motion. For any object that is rotating, a particular point on that object is moving in a circle. One of the goals of this lab activity is to explore and understand this connection. The translational motion ...
Momentum PPT
... Forces applied over time periods create impulses. An impulse is equal to the net force on the object times the time period over which this force is applied. Below, impulse is derived from the equation F = ma, which comes from Newton's second law of motion. The first line is our familiar equation F = ...
... Forces applied over time periods create impulses. An impulse is equal to the net force on the object times the time period over which this force is applied. Below, impulse is derived from the equation F = ma, which comes from Newton's second law of motion. The first line is our familiar equation F = ...
Slide 1
... Forces applied over time periods create impulses. An impulse is equal to the net force on the object times the time period over which this force is applied. Below, impulse is derived from the equation F = ma, which comes from Newton's second law of motion. The first line is our familiar equation F = ...
... Forces applied over time periods create impulses. An impulse is equal to the net force on the object times the time period over which this force is applied. Below, impulse is derived from the equation F = ma, which comes from Newton's second law of motion. The first line is our familiar equation F = ...
Slide 1
... • The force needed to slow a person from 50 km/h to zero in 0.1 s is equal to 14 times the force that gravity exerts on the person. • The belt loosens a little as it restrains the person, increasing the time it takes to slow the person down. ...
... • The force needed to slow a person from 50 km/h to zero in 0.1 s is equal to 14 times the force that gravity exerts on the person. • The belt loosens a little as it restrains the person, increasing the time it takes to slow the person down. ...
05 - UTSC
... velocity, then the object will experience an appreciable frictional force that depends in a non-obvious way on its velocity relative to the medium. If the velocity is low then the frictional force is observed to be directly proportional to the velocity. If the velocity is high then the force is obse ...
... velocity, then the object will experience an appreciable frictional force that depends in a non-obvious way on its velocity relative to the medium. If the velocity is low then the frictional force is observed to be directly proportional to the velocity. If the velocity is high then the force is obse ...
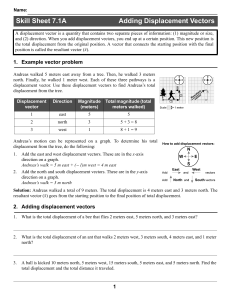
Lesson 1: Vectors - Fundamentals and Operations
... A person walks 150. meters due east and then walks 30. meters due west. The entire trip takes the person 10. minutes. Determine the magnitude and the direction of the person’s total displacement. 2. A dog walks 8.0 meters due north and then 6.0 meters due east. a. Determine the magnitude of the dog’ ...
... A person walks 150. meters due east and then walks 30. meters due west. The entire trip takes the person 10. minutes. Determine the magnitude and the direction of the person’s total displacement. 2. A dog walks 8.0 meters due north and then 6.0 meters due east. a. Determine the magnitude of the dog’ ...