Vectors: Motion and Forces in Two Dimensions
... force required to produce equilibrium 1. decreases 2. increases 3. remains the same ...
... force required to produce equilibrium 1. decreases 2. increases 3. remains the same ...
Chapter 5 - Southern Local Schools
... You might think that the motion of an object is easy to detect—you just observe the object. But you actually must observe the object in relation to another object that appears to stay in place. The object that appears to stay in place is a reference point. When an object changes positions over time ...
... You might think that the motion of an object is easy to detect—you just observe the object. But you actually must observe the object in relation to another object that appears to stay in place. The object that appears to stay in place is a reference point. When an object changes positions over time ...
ω = ag/
... ( eθ is a unit vector in the direction of increasing θ ) (a) Write the Lagrangian and Hamiltonian functions . (b) Show that there are three constants of the motion .Write them down , and discuss the kinds of motion which can occur . (c) Assuming that an electron leaves the inner wire with zero initi ...
... ( eθ is a unit vector in the direction of increasing θ ) (a) Write the Lagrangian and Hamiltonian functions . (b) Show that there are three constants of the motion .Write them down , and discuss the kinds of motion which can occur . (c) Assuming that an electron leaves the inner wire with zero initi ...
AS90183_NBC_1a
... Significant figures are important in physics and we need to understand what role 0 plays in this. Consider the following: ...
... Significant figures are important in physics and we need to understand what role 0 plays in this. Consider the following: ...
Preface 1 PDF
... The kinematics of a particle, the curvilinear and normal coordinates, and kinematic pairs and chains constitute the focus of Chap. 4. In Sect. 4.1, the motion of a particle and trajectory (path) of motion are defined including its velocity and acceleration. Section 4.2 deals with selected problems o ...
... The kinematics of a particle, the curvilinear and normal coordinates, and kinematic pairs and chains constitute the focus of Chap. 4. In Sect. 4.1, the motion of a particle and trajectory (path) of motion are defined including its velocity and acceleration. Section 4.2 deals with selected problems o ...
Curriculum Map - Weld RE
... Free fall and air resistance NEWTONS 3RD LAW Action forces Reaction forces ...
... Free fall and air resistance NEWTONS 3RD LAW Action forces Reaction forces ...
Linear Momentum
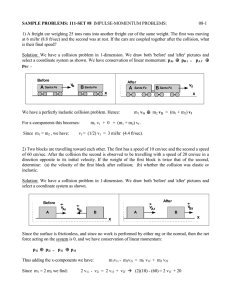
... For any kind of collision however, linear momentum must be preserved. This is because in a closed, isolated system, the total linear moment cannot change without the presence of an external force (and the forces involved in a collision are internal to the system – not external). This does not mean t ...
... For any kind of collision however, linear momentum must be preserved. This is because in a closed, isolated system, the total linear moment cannot change without the presence of an external force (and the forces involved in a collision are internal to the system – not external). This does not mean t ...
Laws of Motion - physics teacher
... Force and inertia, first law of motion, momentum, second law of rtion, impulse, some kinds offerees in nature. Third law of motion, nervation of momentum, rocket propulsion. Equilibrium of conrrent forces. Static and kinetic friction. Laws of friction, rolling Xion-lubrication. Inertial and non iner ...
... Force and inertia, first law of motion, momentum, second law of rtion, impulse, some kinds offerees in nature. Third law of motion, nervation of momentum, rocket propulsion. Equilibrium of conrrent forces. Static and kinetic friction. Laws of friction, rolling Xion-lubrication. Inertial and non iner ...
Momentum Conservation
... The force on the cannonball inside the cannon barrel is equal and opposite to the force causing the cannon to recoil. The action and reaction forces are internal to the system so they don’t change the momentum of the cannon-cannonball system. • Before the firing, the momentum is zero. • After the fi ...
... The force on the cannonball inside the cannon barrel is equal and opposite to the force causing the cannon to recoil. The action and reaction forces are internal to the system so they don’t change the momentum of the cannon-cannonball system. • Before the firing, the momentum is zero. • After the fi ...
Newtons` Second Law
... • There is a force acting in the vertical direction – force of gravity! – Vertical velocity changes the same as if the projectile had been thrown straight up (or dropped) – Time in air determined by vertical travel ...
... • There is a force acting in the vertical direction – force of gravity! – Vertical velocity changes the same as if the projectile had been thrown straight up (or dropped) – Time in air determined by vertical travel ...
Circular Motion
... • If you were to put a bubble in a bag of water on the international space station and spin in in a circle…which way would the bubble travel? (inward, outward, stay random throughout ...
... • If you were to put a bubble in a bag of water on the international space station and spin in in a circle…which way would the bubble travel? (inward, outward, stay random throughout ...
Physics 206a
... x̂ strikes another ball. The second ball is at rest, initially. The second impact is perfectly elastic. The collision is “head on,” i.e., this is a one-dimensional problem. Find the velocity of the both balls after the collision if: a. The mass of the second ball is 250 grams. b. The mass of the sec ...
... x̂ strikes another ball. The second ball is at rest, initially. The second impact is perfectly elastic. The collision is “head on,” i.e., this is a one-dimensional problem. Find the velocity of the both balls after the collision if: a. The mass of the second ball is 250 grams. b. The mass of the sec ...
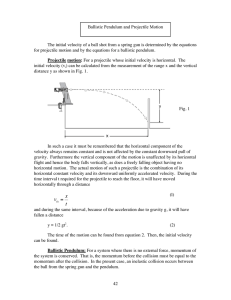
Physics 20 Lesson 13 Projectile Motion
... gravity. The result is that the object follows a parabolic path or trajectory. A parabolic path results because the projectile is falling due to the attraction of gravity and, at the same time, it is moving horizontally. In the stroboscopic picture note that the projected ball falls at the same rate ...
... gravity. The result is that the object follows a parabolic path or trajectory. A parabolic path results because the projectile is falling due to the attraction of gravity and, at the same time, it is moving horizontally. In the stroboscopic picture note that the projected ball falls at the same rate ...