Forces and the Laws of Motion
... _____ 1. An action exerted on an object which may change the object’s state of rest or motion defines a. acceleration. b. force. c. mass. d. velocity. _____ 2. Units that measure weight are units of a. acceleration. b. force. c. mass. d. velocity. _____ 3. Which of the following statements are true ...
... _____ 1. An action exerted on an object which may change the object’s state of rest or motion defines a. acceleration. b. force. c. mass. d. velocity. _____ 2. Units that measure weight are units of a. acceleration. b. force. c. mass. d. velocity. _____ 3. Which of the following statements are true ...
File
... Elastic collision -- One in which the total kinetic energy of the system after the collision is equal to the total kinetic energy before the collision. Inelastic collision -- One in which the total kinetic energy of the system after the collision is not equal to the total kinetic energy before the c ...
... Elastic collision -- One in which the total kinetic energy of the system after the collision is equal to the total kinetic energy before the collision. Inelastic collision -- One in which the total kinetic energy of the system after the collision is not equal to the total kinetic energy before the c ...
Powerpoint
... Draw a system schema: • Draw a diagram where you write down the name of each object in the system and then draw a solid circle drawn around it. • Draw two sided arrows like this between the object circles of objects that interact (This illustrates all interactions between the objects in this diagram ...
... Draw a system schema: • Draw a diagram where you write down the name of each object in the system and then draw a solid circle drawn around it. • Draw two sided arrows like this between the object circles of objects that interact (This illustrates all interactions between the objects in this diagram ...
The real solutions of 6x2 = 7x + 3 are
... smooth ramp. If friction is ignored, which one is moving faster when it reaches the bottom? A) The block that went straight down. B) The block that went down the ramp. C) They both will have the same speed. D) Insufficient information to work the problem. 14) Two cars traveling in opposite direction ...
... smooth ramp. If friction is ignored, which one is moving faster when it reaches the bottom? A) The block that went straight down. B) The block that went down the ramp. C) They both will have the same speed. D) Insufficient information to work the problem. 14) Two cars traveling in opposite direction ...
Collisions
... speed means more impact • what has more impact -catching a tossed ball or line drive? ...
... speed means more impact • what has more impact -catching a tossed ball or line drive? ...
January 1998
... An insulated, uncharged, conducting, spherical shell of radius a is placed in a uniform electric field of magnitude E0 . Suppose the shell is cut into two hemispheres at its equator (in the plane perpendicular to the field). What force is required to keep the hemispheres from separating? ...
... An insulated, uncharged, conducting, spherical shell of radius a is placed in a uniform electric field of magnitude E0 . Suppose the shell is cut into two hemispheres at its equator (in the plane perpendicular to the field). What force is required to keep the hemispheres from separating? ...
Questions – Impulse and Momentum
... 7. Calculate the momentum of cart 1 – 2.00 kg cart moving at 30 m/s North. Calculate the momentum of cart 2 – 1.50 kg cart moving 40.0 m/s South. Can you say their momentums are equal? Why or why not? 8. A golf ball of mass 100 g, initially at rest, is struck by a club. After the impact, the ball mo ...
... 7. Calculate the momentum of cart 1 – 2.00 kg cart moving at 30 m/s North. Calculate the momentum of cart 2 – 1.50 kg cart moving 40.0 m/s South. Can you say their momentums are equal? Why or why not? 8. A golf ball of mass 100 g, initially at rest, is struck by a club. After the impact, the ball mo ...
Learning Outcomes
... b) why it reaches terminal velocity? 17. What is work done a measure of? 18. Can I carry out calculations involving the relationships between Work done, force and displacement (Ew = F s)? 19. What is weight an example of? 20. What does weight mean? 21. Do I know the difference between weight and mas ...
... b) why it reaches terminal velocity? 17. What is work done a measure of? 18. Can I carry out calculations involving the relationships between Work done, force and displacement (Ew = F s)? 19. What is weight an example of? 20. What does weight mean? 21. Do I know the difference between weight and mas ...
2a - Clinton Public Schools
... 2a. Identify patterns found in chemical symbols, formulas, reactions, and equations that apply to the law of conservation of mass. 1. Write balanced chemical equations for photosynthesis and cellular respiration. Label reactants & products. 2. Define the law of conservation of mass and explain how i ...
... 2a. Identify patterns found in chemical symbols, formulas, reactions, and equations that apply to the law of conservation of mass. 1. Write balanced chemical equations for photosynthesis and cellular respiration. Label reactants & products. 2. Define the law of conservation of mass and explain how i ...
The Wizard Test Maker
... Two sinusoidal waves are combined to obtain the result in the figure above. Which of the following can best be explained by this figure? (A) Doppler shift (D) beats (B) diffraction (E) refraction (C) polarization 63. If the critical angle of a material against air is 30°, what is the index of refrac ...
... Two sinusoidal waves are combined to obtain the result in the figure above. Which of the following can best be explained by this figure? (A) Doppler shift (D) beats (B) diffraction (E) refraction (C) polarization 63. If the critical angle of a material against air is 30°, what is the index of refrac ...
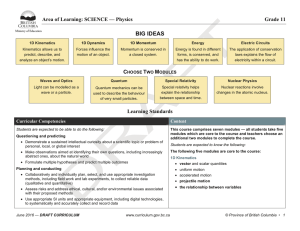
Sample Unit – Physics – Year 11
... work done in lifting a mass or accelerating an object and equate to the change in GPE. Students analyse the change in KE over set distances using trolleys and pulleys with masses and time the motion to determine the relationship between change in KE, work and power. Students use the same formulae fr ...
... work done in lifting a mass or accelerating an object and equate to the change in GPE. Students analyse the change in KE over set distances using trolleys and pulleys with masses and time the motion to determine the relationship between change in KE, work and power. Students use the same formulae fr ...
Regular Physics Mid-Term Review Packet
... 20. If you drop the above ball in the train where will it fall. Would your result be any different if the train were at rest ? ...
... 20. If you drop the above ball in the train where will it fall. Would your result be any different if the train were at rest ? ...
Mechanics 1 Revision Notes
... A particle moves through a point O with speed 13 ms-1 with acceleration -6 m s-2. Find the time(s) at which the particle is 12 m from O. ...
... A particle moves through a point O with speed 13 ms-1 with acceleration -6 m s-2. Find the time(s) at which the particle is 12 m from O. ...
hp1f2013_class15_rolling_motion_and_accelerating_frames
... Let's consider the time derivatives of a changing particle position in inertial and rotating (primed parameters) frames. Let the x,y,z and x',y',z' coordinates of the particle coincide at t=0. At a later time r (t t ) r (t ) r so r r (t t ) r (t ). Since observer' and observer(inerti ...
... Let's consider the time derivatives of a changing particle position in inertial and rotating (primed parameters) frames. Let the x,y,z and x',y',z' coordinates of the particle coincide at t=0. At a later time r (t t ) r (t ) r so r r (t t ) r (t ). Since observer' and observer(inerti ...























