Generalized Linear Acceleration and Linear Velocity for a Particle of
... interactions in nature through a force. Newton’s theory was successful in explaining the gravitation phenomena on the surface of the earth and experimental facts about the solar system and Einstein geometric theory of gravitation published in 1916 called General relativity. In his theory, he general ...
... interactions in nature through a force. Newton’s theory was successful in explaining the gravitation phenomena on the surface of the earth and experimental facts about the solar system and Einstein geometric theory of gravitation published in 1916 called General relativity. In his theory, he general ...
Newton`s Second Law I
... Inertia is a term used to measure the ability of an object to resist a change in its state of motion. An object with a lot of inertia takes a lot of force to start or stop; an object with a small amount of inertia requires a small amount of force to start or stop. The word “inertia” comes from the L ...
... Inertia is a term used to measure the ability of an object to resist a change in its state of motion. An object with a lot of inertia takes a lot of force to start or stop; an object with a small amount of inertia requires a small amount of force to start or stop. The word “inertia” comes from the L ...
Astronomy
... Define linear momentum. Explain the relationship between momentum and force. State Newton’s second law of motion in terms of momentum. Calculate momentum given mass and velocity. Bill Nye – Momentum 8.2. Impulse Define impulse. Describe effects of impulses in everyday life. Determine t ...
... Define linear momentum. Explain the relationship between momentum and force. State Newton’s second law of motion in terms of momentum. Calculate momentum given mass and velocity. Bill Nye – Momentum 8.2. Impulse Define impulse. Describe effects of impulses in everyday life. Determine t ...
Packet 3 - Work Energy Power
... 28. A 2000 kg car, initially at rest, is accelerated along a horizontal roadway at 3 m/s 2. What is the average power required to bring the car to a final speed of 20 m/s? (A) 6 × 103 W (B) 2 × 104 W (C) 3 × 104 W (D) 4 × l04 W (E) 6 × 104 W 22. When a block slides a certain distance down an incline ...
... 28. A 2000 kg car, initially at rest, is accelerated along a horizontal roadway at 3 m/s 2. What is the average power required to bring the car to a final speed of 20 m/s? (A) 6 × 103 W (B) 2 × 104 W (C) 3 × 104 W (D) 4 × l04 W (E) 6 × 104 W 22. When a block slides a certain distance down an incline ...
Physics Quiz II
... as they move past each other c. an attracting force that acts between any two masses d. the product of an object’s velocity and mass; an object with lots of this is difficult to stop e. a push or pull that acts on an object f. the speed and direction an object is moving g. fluid friction acting on a ...
... as they move past each other c. an attracting force that acts between any two masses d. the product of an object’s velocity and mass; an object with lots of this is difficult to stop e. a push or pull that acts on an object f. the speed and direction an object is moving g. fluid friction acting on a ...
Mechanics 2
... To build on the work in Mechanics 1 by extending the range of mechanics concepts which students are able to use in modelling situations. Students will be able to use the rigid body model in simple cases involving moments. Students will be expected to formulate models, using the mechanics within this ...
... To build on the work in Mechanics 1 by extending the range of mechanics concepts which students are able to use in modelling situations. Students will be able to use the rigid body model in simple cases involving moments. Students will be expected to formulate models, using the mechanics within this ...
Chapter 1 The Science of Physics
... a. the product of the mass of the object and the time interval. b. the net external force divided by the time interval. c. the time interval divided by the net external force. d. the product of the force applied to the object and the time interval. ...
... a. the product of the mass of the object and the time interval. b. the net external force divided by the time interval. c. the time interval divided by the net external force. d. the product of the force applied to the object and the time interval. ...
Momentum Notes
... m1v1 + m2v2 = mtotalvtotal m1=mass of 1st object (kg) v1=velocity of 1st object(m/s) m2= mass of 2nd object(kg) v2=velocity of 2nd object(m/s) ...
... m1v1 + m2v2 = mtotalvtotal m1=mass of 1st object (kg) v1=velocity of 1st object(m/s) m2= mass of 2nd object(kg) v2=velocity of 2nd object(m/s) ...
6.04 Laws and Forces - 94 Newmarket Air Cadet Squadron
... Newton’s First Law • Newton’s First Law – An object either is at rest or maintains uniform motion, unless acted upon by an unbalanced external force ...
... Newton’s First Law • Newton’s First Law – An object either is at rest or maintains uniform motion, unless acted upon by an unbalanced external force ...
6.04 Laws and Forces
... Newton’s First Law • Newton’s First Law – An object either is at rest or maintains uniform motion, unless acted upon by an unbalanced external force ...
... Newton’s First Law • Newton’s First Law – An object either is at rest or maintains uniform motion, unless acted upon by an unbalanced external force ...
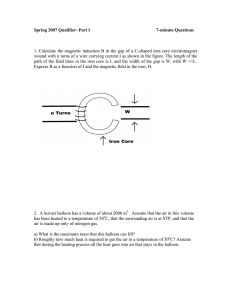
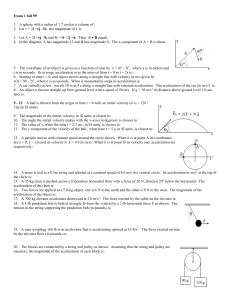
Spring 2007 Qualifier- Part I 7-minute Questions
... a) the equilibrium distribution function; b) the free energy; c) the equation of state. Hint: ...
... a) the equilibrium distribution function; b) the free energy; c) the equation of state. Hint: ...
Physics - 2007 - Maktaba – by TETEA
... Magnetic materials can be magnetized in three different methods namely A. stroking, burning and electrical methods. B. stroking, electrical and induction methods. C. burning, induction and hammering methods. D. hammering, burning and demagnetizing methods. ...
... Magnetic materials can be magnetized in three different methods namely A. stroking, burning and electrical methods. B. stroking, electrical and induction methods. C. burning, induction and hammering methods. D. hammering, burning and demagnetizing methods. ...
Document
... 15. A 25-kg chair is pushed across a frictionless horizontal floor with a force of 20 N, directed 20 0 below the horizontal. The acceleration of the chair is: 16. Two forces are applied to a 5.0-kg object: one is 6 N to the north and the other is 8 N to the west. The magnitude of the acceleration of ...
... 15. A 25-kg chair is pushed across a frictionless horizontal floor with a force of 20 N, directed 20 0 below the horizontal. The acceleration of the chair is: 16. Two forces are applied to a 5.0-kg object: one is 6 N to the north and the other is 8 N to the west. The magnitude of the acceleration of ...