Forces - U of M Physics
... Determine the length of string you should use to connect the block to the mass hanger holding masses (object A). Remember that you will want to take a video of the system while both objects are accelerating (before object A hits the floor). Decide on a position where you will release the block that ...
... Determine the length of string you should use to connect the block to the mass hanger holding masses (object A). Remember that you will want to take a video of the system while both objects are accelerating (before object A hits the floor). Decide on a position where you will release the block that ...
LEVERS
... Mechanical Advantage can either be equal to 1, less than 1 or greater than 1 depending upon the type of lever ...
... Mechanical Advantage can either be equal to 1, less than 1 or greater than 1 depending upon the type of lever ...
PHYJeopardy
... Momentum– 20 points • It is the definition of the law of conservation of momentum. • What is in any closed system, the total momentum before the collision is equal to the total momentum after the collision (or a paraphrase of this)? ...
... Momentum– 20 points • It is the definition of the law of conservation of momentum. • What is in any closed system, the total momentum before the collision is equal to the total momentum after the collision (or a paraphrase of this)? ...
The Electro Magnetic Cannon Saba Zargham, Hamid
... Figure 13: Velocity vs length of the ferromagnetic coil for various wires ...
... Figure 13: Velocity vs length of the ferromagnetic coil for various wires ...
AN INTRODUCTION TO PHYSICS
... plain nonsense even though you may have miraculously got the last six digits right. Physics is commonsense first, so use your intelligence before submitting any answer. 8. Always check your equations to see if they have the same dimensions on the left side as on the right. So, for example, from this ...
... plain nonsense even though you may have miraculously got the last six digits right. Physics is commonsense first, so use your intelligence before submitting any answer. 8. Always check your equations to see if they have the same dimensions on the left side as on the right. So, for example, from this ...
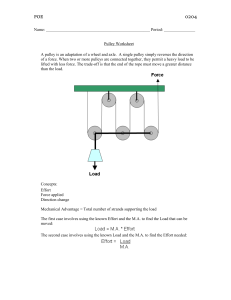
Pulley Worksheet
... A movable pulley splits the work in half. The effort needed to lift 180 pounds weight is 90 pounds. The mechanical advantage of a movable pulley is 2. Block and Tackle: The block and tackle is a system of three pulleys. It reverses the direction of the effort so that a downward pull can be used to l ...
... A movable pulley splits the work in half. The effort needed to lift 180 pounds weight is 90 pounds. The mechanical advantage of a movable pulley is 2. Block and Tackle: The block and tackle is a system of three pulleys. It reverses the direction of the effort so that a downward pull can be used to l ...
Electric Potential
... In what direction does the force on a negative charge at point A point? 1) left 2) right 3) up Physics 102: Lecture 3, Slide 4 ...
... In what direction does the force on a negative charge at point A point? 1) left 2) right 3) up Physics 102: Lecture 3, Slide 4 ...
Physical Science 1st Semester Exam Study Guide 2010 Introduction
... 44. A(An) ____________________ is a statement that summarizes a pattern found in nature. 45. A(An) _________________________ explains a pattern found in nature. 46. A scientific ____________________ describes a natural event but does not explain why the event happens. 47. 375 cm equals _____________ ...
... 44. A(An) ____________________ is a statement that summarizes a pattern found in nature. 45. A(An) _________________________ explains a pattern found in nature. 46. A scientific ____________________ describes a natural event but does not explain why the event happens. 47. 375 cm equals _____________ ...
Projectile Motion
... used. The other two equations are seldom (if ever) used. An application of projectile concepts to each of these equations would also lead one to conclude that any term with ax in it would cancel out of the equation since ax = 0 m/s/s. ...
... used. The other two equations are seldom (if ever) used. An application of projectile concepts to each of these equations would also lead one to conclude that any term with ax in it would cancel out of the equation since ax = 0 m/s/s. ...
Physical Science 1st Semester Exam Study Guide 2010 Introduction
... 44. A(An) ____________________ is a statement that summarizes a pattern found in nature. 45. A(An) _________________________ explains a pattern found in nature. 46. A scientific ____________________ describes a natural event but does not explain why the event happens. 47. 375 cm equals _____________ ...
... 44. A(An) ____________________ is a statement that summarizes a pattern found in nature. 45. A(An) _________________________ explains a pattern found in nature. 46. A scientific ____________________ describes a natural event but does not explain why the event happens. 47. 375 cm equals _____________ ...
weight - ParishPhysics
... 1. If you take a trip from Earth to the Moon, which statement below is correct? A. Your mass and weight both decrease. B. Your mass stays the same and your weight decreases. C. Your mass decreases and your weight stays the same. D. Your mass increases and your weight decreases. ...
... 1. If you take a trip from Earth to the Moon, which statement below is correct? A. Your mass and weight both decrease. B. Your mass stays the same and your weight decreases. C. Your mass decreases and your weight stays the same. D. Your mass increases and your weight decreases. ...
(Classical) Molecular Dynamics
... Is based on Trotter decomposition of Liouville operator formulation, also basis of Multiple time steps, and modern thermostats such as the ...
... Is based on Trotter decomposition of Liouville operator formulation, also basis of Multiple time steps, and modern thermostats such as the ...
Experiment P09: Acceleration of a Dynamics Cart I (Smart Pulley)
... For this activity, a Smart Pulley will measure the motion of a cart as it is pulled by a string that is attached to an object suspended over the pulley. The Science Workshop program calculates the changing speed of the cart as it moves. A graph of speed and time can give the acceleration of the cart ...
... For this activity, a Smart Pulley will measure the motion of a cart as it is pulled by a string that is attached to an object suspended over the pulley. The Science Workshop program calculates the changing speed of the cart as it moves. A graph of speed and time can give the acceleration of the cart ...
Classical central-force problem
In classical mechanics, the central-force problem is to determine the motion of a particle under the influence of a single central force. A central force is a force that points from the particle directly towards (or directly away from) a fixed point in space, the center, and whose magnitude only depends on the distance of the object to the center. In many important cases, the problem can be solved analytically, i.e., in terms of well-studied functions such as trigonometric functions.The solution of this problem is important to classical physics, since many naturally occurring forces are central. Examples include gravity and electromagnetism as described by Newton's law of universal gravitation and Coulomb's law, respectively. The problem is also important because some more complicated problems in classical physics (such as the two-body problem with forces along the line connecting the two bodies) can be reduced to a central-force problem. Finally, the solution to the central-force problem often makes a good initial approximation of the true motion, as in calculating the motion of the planets in the Solar System.