P2 02 Forces and Motion
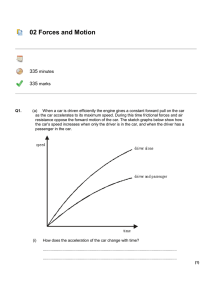
... Write down the equation which links acceleration, change in velocity and time taken. ...
... Write down the equation which links acceleration, change in velocity and time taken. ...
Plane Motion of Rigid Bodies: Forces and Accelerations
... of rigid bodies, i.e., to a motion in which each particle of the body remains at a constant distance from a fixed reference plane. (2) The rigid bodies considered will consist only of plane slabs and of bodies which are symmetrical with respect to the reference plane.† The study of the plane motion ...
... of rigid bodies, i.e., to a motion in which each particle of the body remains at a constant distance from a fixed reference plane. (2) The rigid bodies considered will consist only of plane slabs and of bodies which are symmetrical with respect to the reference plane.† The study of the plane motion ...
Centripetal Force Lab
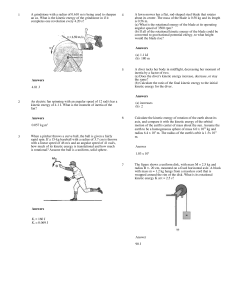
... 1. The radius of rotation and the mass of the brass object will be held constant for this part of the experiment. Weigh the brass object again and record its mass. Hang the brass object from the side post and connect the string from the spring to the object, as before. 2. Attach the clamp-on-pulley ...
... 1. The radius of rotation and the mass of the brass object will be held constant for this part of the experiment. Weigh the brass object again and record its mass. Hang the brass object from the side post and connect the string from the spring to the object, as before. 2. Attach the clamp-on-pulley ...
Ch_9
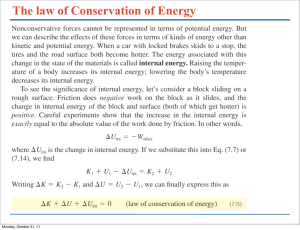
... simple case where N = 3. The system has a total momentum: Applying Newton’s second law for each individual particle, we find the rate of change of the total momentum of the system is: © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... simple case where N = 3. The system has a total momentum: Applying Newton’s second law for each individual particle, we find the rate of change of the total momentum of the system is: © 2013 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
3.5 Represent and Reason Consider the experiments from
... Read each of the scenarios below. For each scenario, identify two systems, one where the quantity is constant and one where the quantity is conserved. Represent each scenario with a conservation bar chart. Write a mathematical expression to show the conservation of this quantity. a) In the morning, ...
... Read each of the scenarios below. For each scenario, identify two systems, one where the quantity is constant and one where the quantity is conserved. Represent each scenario with a conservation bar chart. Write a mathematical expression to show the conservation of this quantity. a) In the morning, ...
3 Two-Dimensional Kinematics
... The fact that the straight-line distance (10.3 blocks) in Figure 3.5 is less than the total distance walked (14 blocks) is one example of a general characteristic of vectors. (Recall that vectors are quantities that have both magnitude and direction.) As for one-dimensional kinematics, we use arrows ...
... The fact that the straight-line distance (10.3 blocks) in Figure 3.5 is less than the total distance walked (14 blocks) is one example of a general characteristic of vectors. (Recall that vectors are quantities that have both magnitude and direction.) As for one-dimensional kinematics, we use arrows ...
Physics 106P: Lecture 6 Notes
... The Free Body Diagram The tools we have for making & solving problems: » Ropes & Pulleys (tension) » Hooke’s Law (springs) ...
... The Free Body Diagram The tools we have for making & solving problems: » Ropes & Pulleys (tension) » Hooke’s Law (springs) ...
Chapter 4 Gravity and Projectiles
... The Legend of the Falling Apple • Newton was not the first to discover gravity. Newton discovered that gravity is universal. • Legend—Newton, sitting under an apple tree, realized that the force between Earth and the apple is the same as that between moons and planets and everything else. ...
... The Legend of the Falling Apple • Newton was not the first to discover gravity. Newton discovered that gravity is universal. • Legend—Newton, sitting under an apple tree, realized that the force between Earth and the apple is the same as that between moons and planets and everything else. ...
Units and Dimensions - RIT
... A vector can be broken up into the sum of two vectors, one parallel to the x-axis, one parallel to the yaxis. The scalar lengths of the two vectors above are given from trigonometry, in equation 3-5 of text. These are called the components of the vector, and can be positive, negative, or zero. ...
... A vector can be broken up into the sum of two vectors, one parallel to the x-axis, one parallel to the yaxis. The scalar lengths of the two vectors above are given from trigonometry, in equation 3-5 of text. These are called the components of the vector, and can be positive, negative, or zero. ...
10-Momentum - Collège Mérici
... The force is negative because an axis in the direction of the velocity was used. A negative force means that the force is in the opposite direction to the velocity, so towards the rear of the car. Note that this force corresponds to nearly 20 times the weight of the person. This person thus experien ...
... The force is negative because an axis in the direction of the velocity was used. A negative force means that the force is in the opposite direction to the velocity, so towards the rear of the car. Note that this force corresponds to nearly 20 times the weight of the person. This person thus experien ...
The Law of Momentum Conservation
... In most collisions between two objects, one object slows down and loses momentum while the other object speeds up and gains momentum. If object 1 loses 75 units of momentum, then object 2 gains 75 units of momentum. Yet, the total momentum of the two objects (object 1 plus object 2) is the same befo ...
... In most collisions between two objects, one object slows down and loses momentum while the other object speeds up and gains momentum. If object 1 loses 75 units of momentum, then object 2 gains 75 units of momentum. Yet, the total momentum of the two objects (object 1 plus object 2) is the same befo ...
Physics OER
... understand the properties and applications of waves. Objective 1: Demonstrate an understanding of mechanical waves in terms of general wave properties. a) Differentiate between period, frequency, wavelength, and amplitude of waves. b) Investigate and compare reflection, refraction, and diffraction o ...
... understand the properties and applications of waves. Objective 1: Demonstrate an understanding of mechanical waves in terms of general wave properties. a) Differentiate between period, frequency, wavelength, and amplitude of waves. b) Investigate and compare reflection, refraction, and diffraction o ...
Impulse and Momentum - DCW Industries, Inc.
... Chapter Abstract. As discussed in Chapter 4, we can reduce the complexity of dynamics problems for which the change of a particle’s speed is known. We accomplish this through the Principle of Work and Energy by integrating Newton’s Second Law over a given particle’s trajectory, which relates the spa ...
... Chapter Abstract. As discussed in Chapter 4, we can reduce the complexity of dynamics problems for which the change of a particle’s speed is known. We accomplish this through the Principle of Work and Energy by integrating Newton’s Second Law over a given particle’s trajectory, which relates the spa ...
Unit 1 Practice Test
... b. when stepping from a curb d. all of the above ____ 26. The product of an object’s mass and velocity is its a. centripetal force. c. net force. b. momentum. d. weight. ____ 27. What is conserved when two objects collide in a closed system? a. acceleration c. speed b. momentum d. velocity Problem 2 ...
... b. when stepping from a curb d. all of the above ____ 26. The product of an object’s mass and velocity is its a. centripetal force. c. net force. b. momentum. d. weight. ____ 27. What is conserved when two objects collide in a closed system? a. acceleration c. speed b. momentum d. velocity Problem 2 ...
Newtonian Physics - UFDC Image Array 2
... We Americans assume that our economic system will always scamper to provide us with the products we want. Special orders don’t upset us! I want my MTV! The truth is more complicated, especially in our education system, which is paid for by the students but controlled by the professoriate. Witness th ...
... We Americans assume that our economic system will always scamper to provide us with the products we want. Special orders don’t upset us! I want my MTV! The truth is more complicated, especially in our education system, which is paid for by the students but controlled by the professoriate. Witness th ...
Classical central-force problem
In classical mechanics, the central-force problem is to determine the motion of a particle under the influence of a single central force. A central force is a force that points from the particle directly towards (or directly away from) a fixed point in space, the center, and whose magnitude only depends on the distance of the object to the center. In many important cases, the problem can be solved analytically, i.e., in terms of well-studied functions such as trigonometric functions.The solution of this problem is important to classical physics, since many naturally occurring forces are central. Examples include gravity and electromagnetism as described by Newton's law of universal gravitation and Coulomb's law, respectively. The problem is also important because some more complicated problems in classical physics (such as the two-body problem with forces along the line connecting the two bodies) can be reduced to a central-force problem. Finally, the solution to the central-force problem often makes a good initial approximation of the true motion, as in calculating the motion of the planets in the Solar System.