College Physics, 2e (Knight)
... provided by gravitational attraction. The net force experienced by an astronaut is 0, thus the astronaut is weightless. (The astronaut is in a continual state of free fall while in orbit.) Var: 1 10) Can a satellite be in an elliptical orbit under uniform circular motion? Answer: No. A satellite in ...
... provided by gravitational attraction. The net force experienced by an astronaut is 0, thus the astronaut is weightless. (The astronaut is in a continual state of free fall while in orbit.) Var: 1 10) Can a satellite be in an elliptical orbit under uniform circular motion? Answer: No. A satellite in ...
A
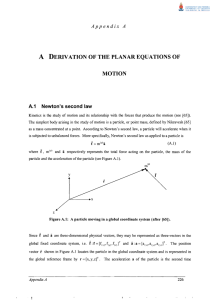
... The simplest body arising in the study of motion is a particle, or point mass, defined by Nikravesh [65] as a mass concentrated at a point. According to Newton's second law, a particle will accelerate when it is subjected to unbalanced forces. More specifically, Newton's second law as applied to a p ...
... The simplest body arising in the study of motion is a particle, or point mass, defined by Nikravesh [65] as a mass concentrated at a point. According to Newton's second law, a particle will accelerate when it is subjected to unbalanced forces. More specifically, Newton's second law as applied to a p ...
Ch 5
... The maximum static friction force is related to the normal force in a similar way as the kinetic friction force. The static friction force acts in response to a force trying to cause a stationary object to start moving. If there is no such force acting on an object, the static friction force is zero ...
... The maximum static friction force is related to the normal force in a similar way as the kinetic friction force. The static friction force acts in response to a force trying to cause a stationary object to start moving. If there is no such force acting on an object, the static friction force is zero ...
Dynamic Simulation of Non-penetrating Flexible Bodies
... flexible bodies that covers collisions and continuous contact as well as free motion. The model, which draws on the flexible-body model proposed by Witkin and Welch[9] and on the analytical contact force model for rigid bodies presented by Baraff[1,2], centers on the idea that flexible body simulati ...
... flexible bodies that covers collisions and continuous contact as well as free motion. The model, which draws on the flexible-body model proposed by Witkin and Welch[9] and on the analytical contact force model for rigid bodies presented by Baraff[1,2], centers on the idea that flexible body simulati ...
Lecture 14
... The train car on the left, mass m1, is moving with speed Vo when it collides with a stationary car of mass m2. The two stick together. 1. What is their speed after the collision? 2. Show that this is inelastic ...
... The train car on the left, mass m1, is moving with speed Vo when it collides with a stationary car of mass m2. The two stick together. 1. What is their speed after the collision? 2. Show that this is inelastic ...
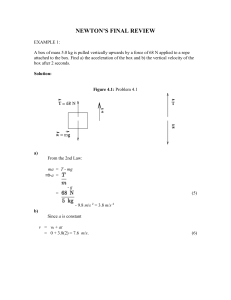
Final Newtons Review
... e. An object has an acceleration of 8 m/s/s. If the net force acting upon the object is increased by a factor of 2, then the new acceleration would be 10 m/s/s. f. An object has an acceleration of 8 m/s/s. If the net force acting upon the object is increased by a factor of 3, then the new accelerati ...
... e. An object has an acceleration of 8 m/s/s. If the net force acting upon the object is increased by a factor of 2, then the new acceleration would be 10 m/s/s. f. An object has an acceleration of 8 m/s/s. If the net force acting upon the object is increased by a factor of 3, then the new accelerati ...
AB_Activity_03
... above the floor where object A is released. Assign these quantities symbols so that you can use them in algebra. The unknown quantities are the velocity of the cart and of object A just before object A hits the floor. There are other unknowns as well. List them. What is the relationship between what ...
... above the floor where object A is released. Assign these quantities symbols so that you can use them in algebra. The unknown quantities are the velocity of the cart and of object A just before object A hits the floor. There are other unknowns as well. List them. What is the relationship between what ...
Kinematics Assignment Sheet - Honors
... problems will be addressed each week, and additional review will occur the day of a quiz. However, there will be a homework solution binder available in class to check your work at any time. 10% penalty per day for late homework. Do not make late homework a habit! QUIZZES are a way to check to see i ...
... problems will be addressed each week, and additional review will occur the day of a quiz. However, there will be a homework solution binder available in class to check your work at any time. 10% penalty per day for late homework. Do not make late homework a habit! QUIZZES are a way to check to see i ...
2.1.2 Forces and Motion SILVER QP
... A sports scientist investigated how the force exerted by a swimmer’s hands against the water affects the swimmer’s speed. The investigation involved 20 males and 20 females swimming a fixed distance. Sensors placed on each swimmer’s hands measured the force 85 times every second over the last 10 met ...
... A sports scientist investigated how the force exerted by a swimmer’s hands against the water affects the swimmer’s speed. The investigation involved 20 males and 20 females swimming a fixed distance. Sensors placed on each swimmer’s hands measured the force 85 times every second over the last 10 met ...
Lateral forces on nanoparticles near a surface under circularly
... force that acts simultaneously on several particles at different locations within a wide area (not requiring focusing of a light beam onto the individual objects), and, in addition, is directed laterally (parallel to the substrate and perpendicular to the illumination direction), would enable the ma ...
... force that acts simultaneously on several particles at different locations within a wide area (not requiring focusing of a light beam onto the individual objects), and, in addition, is directed laterally (parallel to the substrate and perpendicular to the illumination direction), would enable the ma ...
Chapter 9 - Collisions and Momentum
... Example 9-12: Billiard ball collision in 2-D. Billiard ball A moving with speed vA = 3.0 m/s in the +x direction strikes an equal-mass ball B initially at rest. The two balls are observed to move off at 45° to the x axis, ball A above the x axis and ball B below. That is, θA’ = 45° and θB’ = -45 °. ...
... Example 9-12: Billiard ball collision in 2-D. Billiard ball A moving with speed vA = 3.0 m/s in the +x direction strikes an equal-mass ball B initially at rest. The two balls are observed to move off at 45° to the x axis, ball A above the x axis and ball B below. That is, θA’ = 45° and θB’ = -45 °. ...
Section 6.3 Apparent Forces in Circular Motion
... Example 6.15 Locating a geostationary satellite Communication satellites appear to “hover” over one point on the earth’s equator. A satellite that appears to remain stationary as the earth rotates is said to be in a geostationary orbit. What is the radius of the orbit of such a satellite? For the s ...
... Example 6.15 Locating a geostationary satellite Communication satellites appear to “hover” over one point on the earth’s equator. A satellite that appears to remain stationary as the earth rotates is said to be in a geostationary orbit. What is the radius of the orbit of such a satellite? For the s ...
University of Northern British Columbia Physics 115 Laboratory Manual Fall 2014
... The experiment will be performed with the aid of a computer interface system which will allow you to use your computer to collect, display and analyze the data. ...
... The experiment will be performed with the aid of a computer interface system which will allow you to use your computer to collect, display and analyze the data. ...
05._UsingNewtonsLaws
... 5.1. Using Newton’s 2nd Law Example 5.1. Skiing A skier of mass m = 65 kg glides down a frictionless slope of angle = 32. ...
... 5.1. Using Newton’s 2nd Law Example 5.1. Skiing A skier of mass m = 65 kg glides down a frictionless slope of angle = 32. ...
Classical central-force problem
In classical mechanics, the central-force problem is to determine the motion of a particle under the influence of a single central force. A central force is a force that points from the particle directly towards (or directly away from) a fixed point in space, the center, and whose magnitude only depends on the distance of the object to the center. In many important cases, the problem can be solved analytically, i.e., in terms of well-studied functions such as trigonometric functions.The solution of this problem is important to classical physics, since many naturally occurring forces are central. Examples include gravity and electromagnetism as described by Newton's law of universal gravitation and Coulomb's law, respectively. The problem is also important because some more complicated problems in classical physics (such as the two-body problem with forces along the line connecting the two bodies) can be reduced to a central-force problem. Finally, the solution to the central-force problem often makes a good initial approximation of the true motion, as in calculating the motion of the planets in the Solar System.