Momentum and Collisions
... Example 6.2: Two identical 1500 kg cars are moving perpendicular to each other. One moves with a speed of 25.0 m/s due north and the other moves at 15.0 m/s due east. What is the total linear momentum of the system? ...
... Example 6.2: Two identical 1500 kg cars are moving perpendicular to each other. One moves with a speed of 25.0 m/s due north and the other moves at 15.0 m/s due east. What is the total linear momentum of the system? ...
Lecture 15 - USU Department of Physics
... What happens when a ball bounces? • Forces like this are difficult to analyze: • Strong forces that act for a very short time. • Forces that may change rapidly during the collision. • It will help to write Newton’s second law in terms of the total change in velocity over time, instead of accelerati ...
... What happens when a ball bounces? • Forces like this are difficult to analyze: • Strong forces that act for a very short time. • Forces that may change rapidly during the collision. • It will help to write Newton’s second law in terms of the total change in velocity over time, instead of accelerati ...
4 Newton`s First Law of Motion—Inertia
... Galileo stated that this tendency of a moving body to keep moving is natural and that every material object resists changes to its state of motion. The property of a body to resist changes to its state of motion is called inertia. ...
... Galileo stated that this tendency of a moving body to keep moving is natural and that every material object resists changes to its state of motion. The property of a body to resist changes to its state of motion is called inertia. ...
Ch33
... A 5.0 kg box slides down a 5.0 m high frictionless hill starting from rest. It slides across a 2-m long “rough” horizontal section with uk = 0.25. At the end of the horizontal section the box hits a horizontal spring with k = 500 N/m. a. How fast is the box going before reaching the rough surface? 9 ...
... A 5.0 kg box slides down a 5.0 m high frictionless hill starting from rest. It slides across a 2-m long “rough” horizontal section with uk = 0.25. At the end of the horizontal section the box hits a horizontal spring with k = 500 N/m. a. How fast is the box going before reaching the rough surface? 9 ...
Planetary Motion and Gravitation
... On Earth’s surface, the strength of the gravitational field is 9.80 N/kg, and its direction is toward Earth’s center. The field can be represented by a vector of length g pointing toward the center of the object producing the field. You can picture the gravitational field of Earth as a collection of ...
... On Earth’s surface, the strength of the gravitational field is 9.80 N/kg, and its direction is toward Earth’s center. The field can be represented by a vector of length g pointing toward the center of the object producing the field. You can picture the gravitational field of Earth as a collection of ...
ppt
... Summary of experimental result • Static friction increases with the logarithm of hold time. • True contact area increases with the logarithm of hold time. • True contact area increases proportionally to the normal load. • A sudden increase in the piston's velocity gives rise to a sudden increase in ...
... Summary of experimental result • Static friction increases with the logarithm of hold time. • True contact area increases with the logarithm of hold time. • True contact area increases proportionally to the normal load. • A sudden increase in the piston's velocity gives rise to a sudden increase in ...
Dynamics Problems - La Citadelle, Ontario, Canada
... A pumpkin of unknown mass is suspended by a cord attached to the ceiling and pushed away from vertical. When a 24.0 N force is applied to the pumpkin at an angle of 18.00 to horizontal, the pumpkin will remain in equilibrium when the cord makes an angle of 32.00 with the vertical. (A) What is the te ...
... A pumpkin of unknown mass is suspended by a cord attached to the ceiling and pushed away from vertical. When a 24.0 N force is applied to the pumpkin at an angle of 18.00 to horizontal, the pumpkin will remain in equilibrium when the cord makes an angle of 32.00 with the vertical. (A) What is the te ...
PowerPoint Presentation - Physics 121, Lecture 12.
... • We conclude that the motion of the center of mass is only determined by the external forces. Forces exerted by one part of the system on other parts of the system are called internal forces. According to Newton’s third law, the sum of all internal forces cancel out (for each interaction there are ...
... • We conclude that the motion of the center of mass is only determined by the external forces. Forces exerted by one part of the system on other parts of the system are called internal forces. According to Newton’s third law, the sum of all internal forces cancel out (for each interaction there are ...
1. Earth`s gravity attracts a person with a force of 120 lbs. The force
... The path of this asteroid will be a sinusoid. a parabola. → an ellipse. a straight line. Accessibility: Keyboard Navigation Difficulty: Easy Gradable: automatic Topic: Planetary Motion Multiple Choice Question Type: Conceptual MC An asteroid moving around the Sun happens to... Type: Definition 18. A ...
... The path of this asteroid will be a sinusoid. a parabola. → an ellipse. a straight line. Accessibility: Keyboard Navigation Difficulty: Easy Gradable: automatic Topic: Planetary Motion Multiple Choice Question Type: Conceptual MC An asteroid moving around the Sun happens to... Type: Definition 18. A ...
Chapter 09 Notes
... proportionality between stress and strain – For sufficiently small stresses, the stress is directly proportional to the strain – The constant of proportionality depends on the material being deformed and the nature of the ...
... proportionality between stress and strain – For sufficiently small stresses, the stress is directly proportional to the strain – The constant of proportionality depends on the material being deformed and the nature of the ...
Mechanical Systems - Rose
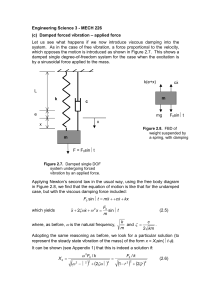
... showed phases like those of the moon, indicating that it must orbit the sun rather than the Earth. I’ll only mention a few of his ideas which strongly influenced dynamics. By 1604 he had determined the correct relationship for falling bodies (d ∝ t2) and had stated that bodies of different weights s ...
... showed phases like those of the moon, indicating that it must orbit the sun rather than the Earth. I’ll only mention a few of his ideas which strongly influenced dynamics. By 1604 he had determined the correct relationship for falling bodies (d ∝ t2) and had stated that bodies of different weights s ...
Moissis, A.A., and M. Zahn. Boundary Value Problems in Electrofluidized and Magnetically Stabilized Beds, Chemical Engineering Communications 67, 181-204, 1988
... magnetic or electric field collinear with the direction of the gas flow is applied to a bed of highly magnetizable or polarizable particles [2-10]. Unlike magnetic systems which only have magnetization forces, electric field systems can also have free charge forces described by Coulomb's law. Such s ...
... magnetic or electric field collinear with the direction of the gas flow is applied to a bed of highly magnetizable or polarizable particles [2-10]. Unlike magnetic systems which only have magnetization forces, electric field systems can also have free charge forces described by Coulomb's law. Such s ...
Vectors in Two Dimensions (cont.)
... • Frictional force depends on the materials that the surfaces are made of. • For example, there is more friction between skis and concrete than there is between skis and snow. • The normal force between the two objects also matters. The harder one object is pushed against the other, the greater the ...
... • Frictional force depends on the materials that the surfaces are made of. • For example, there is more friction between skis and concrete than there is between skis and snow. • The normal force between the two objects also matters. The harder one object is pushed against the other, the greater the ...
Unit 6 - PowerPoint
... unequal masses, and that the collision is elastic and occurs along a line (head-on). (a) Derive equations for vB’ and vA’ in terms of the initial velocity vA of mass mA and the masses mA and mB. (b) Determine the final velocities if the moving object is much more massive than the target (mA >> mB). ...
... unequal masses, and that the collision is elastic and occurs along a line (head-on). (a) Derive equations for vB’ and vA’ in terms of the initial velocity vA of mass mA and the masses mA and mB. (b) Determine the final velocities if the moving object is much more massive than the target (mA >> mB). ...
pdf file
... additional state properties for potentialities has failed? The answer on this question seems to be: yes and no. The answer is ‘yes’ in the sense that in the three possibilities considered there has not been found anything physically real in the state as a basis for a potentiality as a genuine state ...
... additional state properties for potentialities has failed? The answer on this question seems to be: yes and no. The answer is ‘yes’ in the sense that in the three possibilities considered there has not been found anything physically real in the state as a basis for a potentiality as a genuine state ...
Complete article - Scientific Reasoning Research Institute
... the solution to Eq. (1a)]. How the various constants in the general solution are related to the initial conditions is indicated in Fig. 3. A graphical representation of the solution for a particular set of parameters and initial conditions is provided in Fig. 4. The model predicts that the center o ...
... the solution to Eq. (1a)]. How the various constants in the general solution are related to the initial conditions is indicated in Fig. 3. A graphical representation of the solution for a particular set of parameters and initial conditions is provided in Fig. 4. The model predicts that the center o ...
Newton's Second Law
... the car goes from a state of being at rest to a state of motion, the car must be accelerated, since acceleration is a change in velocity (vi = 0; vf = v for an acceleration value a). The missing factor that relates the force to the acceleration can be deduced by considering that any one of us would ...
... the car goes from a state of being at rest to a state of motion, the car must be accelerated, since acceleration is a change in velocity (vi = 0; vf = v for an acceleration value a). The missing factor that relates the force to the acceleration can be deduced by considering that any one of us would ...
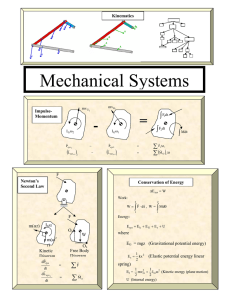
Chapter 8 Momentum and Its Conservation
... the motion of a single body, but rather the motion of two bodies. The two bodies are the system. Even though there is a force on ball 1 and ball 2, these forces are internal forces, and the internal forces can not exert a net force on the system, only an external force can do that. Whenever a system ...
... the motion of a single body, but rather the motion of two bodies. The two bodies are the system. Even though there is a force on ball 1 and ball 2, these forces are internal forces, and the internal forces can not exert a net force on the system, only an external force can do that. Whenever a system ...
Classical central-force problem
In classical mechanics, the central-force problem is to determine the motion of a particle under the influence of a single central force. A central force is a force that points from the particle directly towards (or directly away from) a fixed point in space, the center, and whose magnitude only depends on the distance of the object to the center. In many important cases, the problem can be solved analytically, i.e., in terms of well-studied functions such as trigonometric functions.The solution of this problem is important to classical physics, since many naturally occurring forces are central. Examples include gravity and electromagnetism as described by Newton's law of universal gravitation and Coulomb's law, respectively. The problem is also important because some more complicated problems in classical physics (such as the two-body problem with forces along the line connecting the two bodies) can be reduced to a central-force problem. Finally, the solution to the central-force problem often makes a good initial approximation of the true motion, as in calculating the motion of the planets in the Solar System.