work
... an object is positive, the kinetic energy of the object will increase. – When net work due to all forces acting upon an object is negative, the kinetic energy of the object will decrease. – When there is no net work acting upon an object, the kinetic energy of the object will be ...
... an object is positive, the kinetic energy of the object will increase. – When net work due to all forces acting upon an object is negative, the kinetic energy of the object will decrease. – When there is no net work acting upon an object, the kinetic energy of the object will be ...
Basic Mechanics
... 40. The orientation of the collagen fibers at the superficial tangential zone of an articular cartilage is _____ to the articular surface in order to withstand _____ stresses. a. parallel, shear b. oblique, twist c. vertical, compression d. random, any kind of 41. The strength of a bone is defined a ...
... 40. The orientation of the collagen fibers at the superficial tangential zone of an articular cartilage is _____ to the articular surface in order to withstand _____ stresses. a. parallel, shear b. oblique, twist c. vertical, compression d. random, any kind of 41. The strength of a bone is defined a ...
premedical course – physics
... speeding up, and turning provide a sufficient vocabulary for describing the motion of objects. In physics, we use these words and many more such as distance, displacement, speed, velocity, and acceleration. DISTANCE AND DISPLACEMENT The way - the points in which the body is moving under the given ti ...
... speeding up, and turning provide a sufficient vocabulary for describing the motion of objects. In physics, we use these words and many more such as distance, displacement, speed, velocity, and acceleration. DISTANCE AND DISPLACEMENT The way - the points in which the body is moving under the given ti ...
presentation source
... Because we are in the space strongly influenced by the Earth’s gravity, we call this the gravitational potential energy. Consider the force gravity exerts on the bucket as we move it from the ground to a height of 0.5 m at constant velocity. Fg = m g = (5 kg)(-10 m/s2) = -50 N W = Fs s = Fg (yf - ...
... Because we are in the space strongly influenced by the Earth’s gravity, we call this the gravitational potential energy. Consider the force gravity exerts on the bucket as we move it from the ground to a height of 0.5 m at constant velocity. Fg = m g = (5 kg)(-10 m/s2) = -50 N W = Fs s = Fg (yf - ...
fall04-term2-exercise
... 60. A mass of 2 kg is placed on an inclined plane (making an angle of 30ø with the horizontal) and connected to a spring fastened at the top of the plane. The spring has spring constant 50 N/m. The mass is released from rest with the spring initially unstretched. The block moves a distance 25 cm bef ...
... 60. A mass of 2 kg is placed on an inclined plane (making an angle of 30ø with the horizontal) and connected to a spring fastened at the top of the plane. The spring has spring constant 50 N/m. The mass is released from rest with the spring initially unstretched. The block moves a distance 25 cm bef ...
幻灯片 1
... The acceleration of the particle measured by an observer in one frame of reference is the same as that measured by any other observer moving with constant velocity relative to the ...
... The acceleration of the particle measured by an observer in one frame of reference is the same as that measured by any other observer moving with constant velocity relative to the ...
Chapter 7 Impulse and Momentum continued
... The mass of the block of wood is 2.50-kg and the mass of the bullet is 0.0100-kg. The block swings to a maximum height of 0.650 m above the initial position. Find the initial speed of the bullet. ...
... The mass of the block of wood is 2.50-kg and the mass of the bullet is 0.0100-kg. The block swings to a maximum height of 0.650 m above the initial position. Find the initial speed of the bullet. ...
Friction
... What happened? Describe the motion of the single filter and the stack of four filters (acceleration, velocity, and/or position as a function of time). ...
... What happened? Describe the motion of the single filter and the stack of four filters (acceleration, velocity, and/or position as a function of time). ...
Basic_MD
... situation might seem troubling, we should remember that at this point we have already introduced a much more severe approximation by using classical mechanics in lieu of the correct quantum treatment. Much more important than absolute accuracy of the trajectories is adherence of the whole system to ...
... situation might seem troubling, we should remember that at this point we have already introduced a much more severe approximation by using classical mechanics in lieu of the correct quantum treatment. Much more important than absolute accuracy of the trajectories is adherence of the whole system to ...
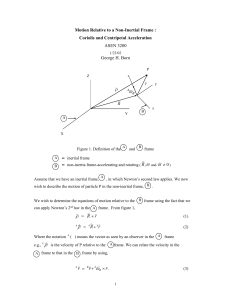
Motion Relative to a non-inertial frame
... In Eq. (19), we have moved the centripetal and Coriolis accelerations to the force side of the equation. In this situation they are referred to as the centripetal and Coriolis apparent forces per unit mass. Hence, the signs of the centripetal and Coriolis apparent forces per unit mass are opposite t ...
... In Eq. (19), we have moved the centripetal and Coriolis accelerations to the force side of the equation. In this situation they are referred to as the centripetal and Coriolis apparent forces per unit mass. Hence, the signs of the centripetal and Coriolis apparent forces per unit mass are opposite t ...
For an object travelling with “uniform circular motion,”
... 5. A rock is tied to the end of a 35 cm long string and whirled around in a circle that describes a vertical plane. The tension in the string becomes zero when the speed of the rock is a) 9.8 x 102 cm/s c) 19 cm/s b) 1.9 x 102 cm/s d) 9.8 cm/s e) 1.9 cm/s 6. A curve in the highway is banked at 15° a ...
... 5. A rock is tied to the end of a 35 cm long string and whirled around in a circle that describes a vertical plane. The tension in the string becomes zero when the speed of the rock is a) 9.8 x 102 cm/s c) 19 cm/s b) 1.9 x 102 cm/s d) 9.8 cm/s e) 1.9 cm/s 6. A curve in the highway is banked at 15° a ...
Powerpoint Slide
... This type of force is called a “restoring force” because it always acts to restore the system to equilibrium. If we pull on the spring-mass system and let it go it will oscillate back and forth. If we make a plot of the spring’s position vs time we get: ...
... This type of force is called a “restoring force” because it always acts to restore the system to equilibrium. If we pull on the spring-mass system and let it go it will oscillate back and forth. If we make a plot of the spring’s position vs time we get: ...
Classical central-force problem
In classical mechanics, the central-force problem is to determine the motion of a particle under the influence of a single central force. A central force is a force that points from the particle directly towards (or directly away from) a fixed point in space, the center, and whose magnitude only depends on the distance of the object to the center. In many important cases, the problem can be solved analytically, i.e., in terms of well-studied functions such as trigonometric functions.The solution of this problem is important to classical physics, since many naturally occurring forces are central. Examples include gravity and electromagnetism as described by Newton's law of universal gravitation and Coulomb's law, respectively. The problem is also important because some more complicated problems in classical physics (such as the two-body problem with forces along the line connecting the two bodies) can be reduced to a central-force problem. Finally, the solution to the central-force problem often makes a good initial approximation of the true motion, as in calculating the motion of the planets in the Solar System.