Powerpoint
... future. Objects only know what is acting directly on them right now Newton's 1st Law An object that is at rest will remain at rest and an object that is moving will continue to move in a straight line with constant speed, if and only if the sum of the forces acting on that object is zero. Newton's 3 ...
... future. Objects only know what is acting directly on them right now Newton's 1st Law An object that is at rest will remain at rest and an object that is moving will continue to move in a straight line with constant speed, if and only if the sum of the forces acting on that object is zero. Newton's 3 ...
45 Newton`s Laws Introduction
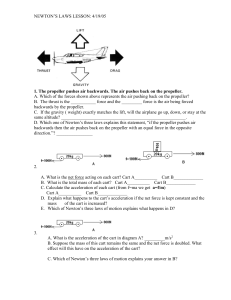
... B. The thrust is the ___________ force and the _________ force is the air being forced backwards by the propeller. C. If the gravity ( weight) exactly matches the lift, will the airplane go up, down, or stay at the same altitude? _______________________________________________________. D. Which one ...
... B. The thrust is the ___________ force and the _________ force is the air being forced backwards by the propeller. C. If the gravity ( weight) exactly matches the lift, will the airplane go up, down, or stay at the same altitude? _______________________________________________________. D. Which one ...
Mid-term Study Guide Answer Key
... 17.1 Mechanical waves – waves = traveling disturbances that carries E 121. You can make a wave in a rope by adding energy (shake) at one end of the rope. 122. Instead of crests and troughs, as in an ocean wave, a longitudinal wave has compressions and rarefactions. (compression=molecules of medium c ...
... 17.1 Mechanical waves – waves = traveling disturbances that carries E 121. You can make a wave in a rope by adding energy (shake) at one end of the rope. 122. Instead of crests and troughs, as in an ocean wave, a longitudinal wave has compressions and rarefactions. (compression=molecules of medium c ...
Newtons Law - Henry County Schools
... planets holds the planets in orbit around the sun. If that force of gravity suddenly disappeared, in what kind of path would the planets move? • Each planet would move in a straight line at constant speed. ...
... planets holds the planets in orbit around the sun. If that force of gravity suddenly disappeared, in what kind of path would the planets move? • Each planet would move in a straight line at constant speed. ...
Notes on Newton`s Laws of Motion
... Newton’s Second Law of Motion • “The acceleration of an object is equal to the net force acting on it divided by the object’s mass” • Acceleration = net force/mass, or a = F/m • Mass is the amount of matter in an object and stays constant • Weight is the force of gravity on an object and can change ...
... Newton’s Second Law of Motion • “The acceleration of an object is equal to the net force acting on it divided by the object’s mass” • Acceleration = net force/mass, or a = F/m • Mass is the amount of matter in an object and stays constant • Weight is the force of gravity on an object and can change ...
Download_2
... and motion software. The motion sensor acts like a stupid bat when hooked up with a computer-based laboratory system. It sends out a series of sound pulses that are too high frequency to hear. These pulses reflect from objects in the vicinity of the motion sensor and some of the sound energy returns ...
... and motion software. The motion sensor acts like a stupid bat when hooked up with a computer-based laboratory system. It sends out a series of sound pulses that are too high frequency to hear. These pulses reflect from objects in the vicinity of the motion sensor and some of the sound energy returns ...
Chapter 5
... speed of light Einstein’s special theory of relativity. 2) The interacting bodies are on the scale of the atomic structure Quantum mechanics I. Newton’s first law: If no net force acts on a body, then the body’s velocity cannot change; the body cannot accelerate v = constant in magnitude and di ...
... speed of light Einstein’s special theory of relativity. 2) The interacting bodies are on the scale of the atomic structure Quantum mechanics I. Newton’s first law: If no net force acts on a body, then the body’s velocity cannot change; the body cannot accelerate v = constant in magnitude and di ...
Newtons Laws ppt
... Only if there is friction! In the absence of any net external force, an object will keep moving at a constant speed in a straight line, or remain at rest. This is also known as the law of inertia. ...
... Only if there is friction! In the absence of any net external force, an object will keep moving at a constant speed in a straight line, or remain at rest. This is also known as the law of inertia. ...
Acceleration
... • Demonstrate your understanding of directions and signs for velocity, displacement, and acceleration. • Solve problems involving a free-falling body in a gravitational field. ...
... • Demonstrate your understanding of directions and signs for velocity, displacement, and acceleration. • Solve problems involving a free-falling body in a gravitational field. ...
Document
... distance of his slide is completely independent of how big he is, and we have a = g. (Note that the units work out since is dimensionless.) This is just the magnitude of a. If the forward direction is positive, his acceleration (which is always in the direction of the net force) must be ...
... distance of his slide is completely independent of how big he is, and we have a = g. (Note that the units work out since is dimensionless.) This is just the magnitude of a. If the forward direction is positive, his acceleration (which is always in the direction of the net force) must be ...
Classical central-force problem
In classical mechanics, the central-force problem is to determine the motion of a particle under the influence of a single central force. A central force is a force that points from the particle directly towards (or directly away from) a fixed point in space, the center, and whose magnitude only depends on the distance of the object to the center. In many important cases, the problem can be solved analytically, i.e., in terms of well-studied functions such as trigonometric functions.The solution of this problem is important to classical physics, since many naturally occurring forces are central. Examples include gravity and electromagnetism as described by Newton's law of universal gravitation and Coulomb's law, respectively. The problem is also important because some more complicated problems in classical physics (such as the two-body problem with forces along the line connecting the two bodies) can be reduced to a central-force problem. Finally, the solution to the central-force problem often makes a good initial approximation of the true motion, as in calculating the motion of the planets in the Solar System.