Review C: Work and Kinetic Energy
... decrease its speed. When the total work done is zero, the object will maintain a constant speed. In fact we have a more precise result, the total work done by all the applied forces on an object is equal to the change in kinetic energy of the object. ...
... decrease its speed. When the total work done is zero, the object will maintain a constant speed. In fact we have a more precise result, the total work done by all the applied forces on an object is equal to the change in kinetic energy of the object. ...
Chapter 5 Work and Energy
... The concept of forces acting on a mass (one object) is intimately related to the concept of ENERGY production or storage. • A mass accelerated to a non-zero speed carries energy (mechanical) • A mass raised up carries energy (gravitational) • The mass of an atom in a molecule carries energy (chemica ...
... The concept of forces acting on a mass (one object) is intimately related to the concept of ENERGY production or storage. • A mass accelerated to a non-zero speed carries energy (mechanical) • A mass raised up carries energy (gravitational) • The mass of an atom in a molecule carries energy (chemica ...
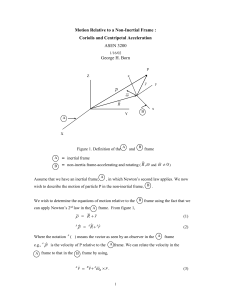
Motion Relative to a non-inertial frame
... In Eq. (19), we have moved the centripetal and Coriolis accelerations to the force side of the equation. In this situation they are referred to as the centripetal and Coriolis apparent forces per unit mass. Hence, the signs of the centripetal and Coriolis apparent forces per unit mass are opposite t ...
... In Eq. (19), we have moved the centripetal and Coriolis accelerations to the force side of the equation. In this situation they are referred to as the centripetal and Coriolis apparent forces per unit mass. Hence, the signs of the centripetal and Coriolis apparent forces per unit mass are opposite t ...
Unit 7 Vocabulary
... Velocity- the distance and direction an object is traveling Acceleration- a change in velocity (speed and/or direction) Motion- a change in position measured by distance and time Force- a push or a pull Unbalanced force- forces that cause a change in an objects motion Balanced force- forces that can ...
... Velocity- the distance and direction an object is traveling Acceleration- a change in velocity (speed and/or direction) Motion- a change in position measured by distance and time Force- a push or a pull Unbalanced force- forces that cause a change in an objects motion Balanced force- forces that can ...
WorkPowerEnergy
... • Identify several forms of energy • Calculate kinetic energy for an object • Apply in the work-kinetic energy theorem to solve problems • Distinguish between kinetic and potential energy • Classify different types of potential energy • Calculate the potential energy associated with an object’s posi ...
... • Identify several forms of energy • Calculate kinetic energy for an object • Apply in the work-kinetic energy theorem to solve problems • Distinguish between kinetic and potential energy • Classify different types of potential energy • Calculate the potential energy associated with an object’s posi ...
Sample Paper
... 20. One similarity of DNA and RNA is that they both contain a) Nucleotide b) ATP c) Thymine d) Deoxyribose sugar 21. One of the characteristics of all living things is that they a) Require oxygen for respiration b) Originate from preexisting life c) Carry on heterotrophic nutrition d) Carry on autot ...
... 20. One similarity of DNA and RNA is that they both contain a) Nucleotide b) ATP c) Thymine d) Deoxyribose sugar 21. One of the characteristics of all living things is that they a) Require oxygen for respiration b) Originate from preexisting life c) Carry on heterotrophic nutrition d) Carry on autot ...
Falling Chain Name: Date:
... 1. Set up lab as shown in diagram 2. Calibrate the force sensor 3. Take a paper clip and hook it on the force sensor and hook the bucket on the paperclip and open force sensor program 4. Find mass of bucket using force sensor program use formula (weight / gravity) to find mass 5. Put the chain in th ...
... 1. Set up lab as shown in diagram 2. Calibrate the force sensor 3. Take a paper clip and hook it on the force sensor and hook the bucket on the paperclip and open force sensor program 4. Find mass of bucket using force sensor program use formula (weight / gravity) to find mass 5. Put the chain in th ...
13. Kinetic Energy - Galileo and Einstein
... B. Other forces acting are always perpendicular to the direction of motion: so this will also be true for a roller coaster, ignoring friction. ...
... B. Other forces acting are always perpendicular to the direction of motion: so this will also be true for a roller coaster, ignoring friction. ...
03pp notes
... Yes, but only if both push equally. No. No, unless acceleration occurs. Explanation: However they push, the result is equal-magnitude forces on equal masses, which produce equal accelerations and, therefore, equal changes in speed. ...
... Yes, but only if both push equally. No. No, unless acceleration occurs. Explanation: However they push, the result is equal-magnitude forces on equal masses, which produce equal accelerations and, therefore, equal changes in speed. ...
Review C: Work and Kinetic Energy
... change of energy and so we search for physical laws that determine how each form of energy changes. The second point is that we must account for all the ways energy can change. If we observe a process, and the changes in energy do not add up to zero, then the laws for energy transformations are eith ...
... change of energy and so we search for physical laws that determine how each form of energy changes. The second point is that we must account for all the ways energy can change. If we observe a process, and the changes in energy do not add up to zero, then the laws for energy transformations are eith ...
12: Forces
... wagon stops? (Hint: Consider what it takes to change the velocity of the wagon and the marble.) ...
... wagon stops? (Hint: Consider what it takes to change the velocity of the wagon and the marble.) ...
Lecture 8: Forces & The Laws of Motion
... circles around the point halfway between them at a speed of 5.00 m/s. Treating the astronauts as particles… What is the magnitude of the angular momentum and the rotational energy of the system? By pulling on the rope, the astronauts shorten the distance between them to 5.00 m… What is the new angul ...
... circles around the point halfway between them at a speed of 5.00 m/s. Treating the astronauts as particles… What is the magnitude of the angular momentum and the rotational energy of the system? By pulling on the rope, the astronauts shorten the distance between them to 5.00 m… What is the new angul ...
Slides for Chapters 9, 10, 11 and Review
... cable around a solid cylinder with mass M and radius R. The cylinder rotates with negligible friction about a stationary horizontal axis. We tie the free and of the cable to a block of mass m and release the block from rest at distance h above the floor. As the block falls, the cable unwinds without ...
... cable around a solid cylinder with mass M and radius R. The cylinder rotates with negligible friction about a stationary horizontal axis. We tie the free and of the cable to a block of mass m and release the block from rest at distance h above the floor. As the block falls, the cable unwinds without ...
Wednesday, Apr. 3, 2002
... A car with a mass of 1300kg is constructed so that its frame is supported by four springs. Each spring has a force constant of 20,000N/m. If two peoploe riding in the car have a combined mass of 160kg, find the frequency of vibration of the car after it is driven over a pothole in the road. Let’s as ...
... A car with a mass of 1300kg is constructed so that its frame is supported by four springs. Each spring has a force constant of 20,000N/m. If two peoploe riding in the car have a combined mass of 160kg, find the frequency of vibration of the car after it is driven over a pothole in the road. Let’s as ...
Maximum Marks: 100
... 20. One similarity of DNA and RNA is that they both contain a) Nucleotide b) ATP c) Thymine d) Deoxyribose sugar 21. One of the characteristics of all living things is that they a) Require oxygen for respiration b) Originate from preexisting life c) Carry on heterotrophic nutrition d) Carry on autot ...
... 20. One similarity of DNA and RNA is that they both contain a) Nucleotide b) ATP c) Thymine d) Deoxyribose sugar 21. One of the characteristics of all living things is that they a) Require oxygen for respiration b) Originate from preexisting life c) Carry on heterotrophic nutrition d) Carry on autot ...
clicking here
... 20. One similarity of DNA and RNA is that they both contain a) Nucleotide b) ATP c) Thymine d) Deoxyribose sugar 21. One of the characteristics of all living things is that they a) Require oxygen for respiration b) Originate from preexisting life c) Carry on heterotrophic nutrition d) Carry on autot ...
... 20. One similarity of DNA and RNA is that they both contain a) Nucleotide b) ATP c) Thymine d) Deoxyribose sugar 21. One of the characteristics of all living things is that they a) Require oxygen for respiration b) Originate from preexisting life c) Carry on heterotrophic nutrition d) Carry on autot ...
Classical central-force problem
In classical mechanics, the central-force problem is to determine the motion of a particle under the influence of a single central force. A central force is a force that points from the particle directly towards (or directly away from) a fixed point in space, the center, and whose magnitude only depends on the distance of the object to the center. In many important cases, the problem can be solved analytically, i.e., in terms of well-studied functions such as trigonometric functions.The solution of this problem is important to classical physics, since many naturally occurring forces are central. Examples include gravity and electromagnetism as described by Newton's law of universal gravitation and Coulomb's law, respectively. The problem is also important because some more complicated problems in classical physics (such as the two-body problem with forces along the line connecting the two bodies) can be reduced to a central-force problem. Finally, the solution to the central-force problem often makes a good initial approximation of the true motion, as in calculating the motion of the planets in the Solar System.