DOE Chemistry 1
... Details the principles of ion exchange in the context of water purity. Discusses typical water treatment methods and the basis for these methods. Module 5 - Hazards of Chemicals and Gases Explains why certain chemicals are considered hazardous to facility personnel. Includes general safety rules on ...
... Details the principles of ion exchange in the context of water purity. Discusses typical water treatment methods and the basis for these methods. Module 5 - Hazards of Chemicals and Gases Explains why certain chemicals are considered hazardous to facility personnel. Includes general safety rules on ...
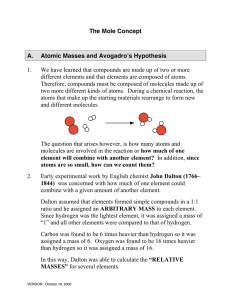
Mole Concept
... isotope, 6 C , which is assigned the mass of 12 amu exactly. Likewise 1 mole of 6 C has a mass of exactly 12 g. Atomic masses and molar masses of other isotopes are calculated based on their mass relative to that of Carbon-12. Masses of “average” atoms are found by summing isotopic masses, weighting ...
... isotope, 6 C , which is assigned the mass of 12 amu exactly. Likewise 1 mole of 6 C has a mass of exactly 12 g. Atomic masses and molar masses of other isotopes are calculated based on their mass relative to that of Carbon-12. Masses of “average” atoms are found by summing isotopic masses, weighting ...
Final Exam - KFUPM Faculty List
... lone pair in the tetrahedral arrangement. In H2O the tetrahedral angle between the bonds is further compressed to about 104o because of the 2 large lone pairs in the tetrahedral arrangement. Sec# 8-13 Grade# 60 Q22. What is the structure of SF4? A) See-saw B) Tetrahedral C) Square planar D) Trigonal ...
... lone pair in the tetrahedral arrangement. In H2O the tetrahedral angle between the bonds is further compressed to about 104o because of the 2 large lone pairs in the tetrahedral arrangement. Sec# 8-13 Grade# 60 Q22. What is the structure of SF4? A) See-saw B) Tetrahedral C) Square planar D) Trigonal ...
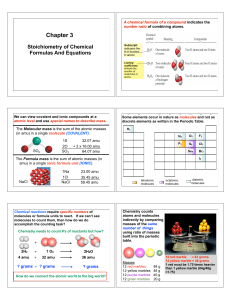
Chapter 3 2013
... What’s In A Chemical Formula? Urea, (NH2)2CO, is a nitrogen containing compound used as a fertilizer around the globe? Calculate the following for 25.6 g of urea: a) the molar mass of urea? b) the number of moles of urea in 25.6 g urea? b) # of molecules of urea in 25.6 g of urea? c) # hydrogen ato ...
... What’s In A Chemical Formula? Urea, (NH2)2CO, is a nitrogen containing compound used as a fertilizer around the globe? Calculate the following for 25.6 g of urea: a) the molar mass of urea? b) the number of moles of urea in 25.6 g urea? b) # of molecules of urea in 25.6 g of urea? c) # hydrogen ato ...
When wood, paper, and wax are burned, they ap
... amount of product(s) formed, called the yield, knowing how much reactant(s) was (were) used. This information is of great importance for reactions run on the laboratory or industrial scale. In practice, the actual yield is almost always less than that predicted from the equation because of various c ...
... amount of product(s) formed, called the yield, knowing how much reactant(s) was (were) used. This information is of great importance for reactions run on the laboratory or industrial scale. In practice, the actual yield is almost always less than that predicted from the equation because of various c ...
PART 3-ICHO 11-15
... washed, dried and calcinated. The mass of the precipitate after the calcination to constant mass, was 0.3265 g. An aqueous ammonia solution was added in excess to the solution obtained after separation of the precipitate. A compound of metal B remained in the solution while all the other metals prec ...
... washed, dried and calcinated. The mass of the precipitate after the calcination to constant mass, was 0.3265 g. An aqueous ammonia solution was added in excess to the solution obtained after separation of the precipitate. A compound of metal B remained in the solution while all the other metals prec ...
Part 1-ICHO-21-25
... tasks set in the ICHO in its fourty-year history is a contribution of the ICHO International Information Centre in Bratislava (Slovakia) to the development of this world known international competition. This Volume 2 contains 154 theoretical and 46 practical competition problems from the mentioned y ...
... tasks set in the ICHO in its fourty-year history is a contribution of the ICHO International Information Centre in Bratislava (Slovakia) to the development of this world known international competition. This Volume 2 contains 154 theoretical and 46 practical competition problems from the mentioned y ...
GCE Chemistry SAMs 2009 onwards pdf
... Reliable resources of energy need to be available in the future. A UK report anticipates the differing quantities of fuels needed in 50 years time. In this report three predictions are made based on different assumptions about future energy supply and demand. Among the assumptions the following were ...
... Reliable resources of energy need to be available in the future. A UK report anticipates the differing quantities of fuels needed in 50 years time. In this report three predictions are made based on different assumptions about future energy supply and demand. Among the assumptions the following were ...
Syllabus Cambridge IGCSE Chemistry (US) Syllabus Code 0439 For examination in 2013
... Teachers should note that there is an equal weighting of 50% for skills (including handling information; problem solving; practical, experimental, and investigative skills) and for knowledge and understanding. Teachers’ schemes of work (unit lesson plans) and the sequence of learning activities shou ...
... Teachers should note that there is an equal weighting of 50% for skills (including handling information; problem solving; practical, experimental, and investigative skills) and for knowledge and understanding. Teachers’ schemes of work (unit lesson plans) and the sequence of learning activities shou ...
Topic 3: Chemical Kinetics - Manitoba Education and Training
... (Topic 3: Chemical Reactions). Laboratory Activity Have students perform a lab activity to measure the change in mass of calcium carbonate as it reacts with 3 mol/L hydrochloric acid. See Appendix 3.1: Graphical Determination of Reaction Rate: Lab Activity. Using the data derived from the lab activi ...
... (Topic 3: Chemical Reactions). Laboratory Activity Have students perform a lab activity to measure the change in mass of calcium carbonate as it reacts with 3 mol/L hydrochloric acid. See Appendix 3.1: Graphical Determination of Reaction Rate: Lab Activity. Using the data derived from the lab activi ...
odd - WWW2
... but (x + y) = 5, the sum of the iron ions. Hence by substitution, x = 3 and y = 2. Thus there are three Fe2+ ions and two Fe3+ ions per formula. 14.29 Zeolites are used as ion exchangers for water; as adsorption agents, particularly for water in organic solvents; for gas separation, particularly dio ...
... but (x + y) = 5, the sum of the iron ions. Hence by substitution, x = 3 and y = 2. Thus there are three Fe2+ ions and two Fe3+ ions per formula. 14.29 Zeolites are used as ion exchangers for water; as adsorption agents, particularly for water in organic solvents; for gas separation, particularly dio ...
From Ultracold Atoms to Condensed Matter Physics
... magnetic, laser and evaporative cooling. The atoms are kept in place thanks to a harmonic confinement. On top of this harmonic trap, in analogy to the periodic potential felt by electrons in a solid, one can introduce a periodic potential using a combination of lasers. The lasers that create the la ...
... magnetic, laser and evaporative cooling. The atoms are kept in place thanks to a harmonic confinement. On top of this harmonic trap, in analogy to the periodic potential felt by electrons in a solid, one can introduce a periodic potential using a combination of lasers. The lasers that create the la ...
Answers - Pearson
... 2 Potash, soda, magnesia and barytes are compounds of Group 1 and 2 elements. These compounds were later broken down into their component elements by electrolysis. 3 The Schrödinger model: ...
... 2 Potash, soda, magnesia and barytes are compounds of Group 1 and 2 elements. These compounds were later broken down into their component elements by electrolysis. 3 The Schrödinger model: ...
Massachusetts Tests for Educator Licensure (MTEL )
... Correct Response: B. The environmental conditions are controlled, and the comparison stated is correct and sufficient to answer the question as to which plastic degrades more quickly. A is incorrect because the two plastics are not compared and degradation rates are theoretical. C is incorrect becau ...
... Correct Response: B. The environmental conditions are controlled, and the comparison stated is correct and sufficient to answer the question as to which plastic degrades more quickly. A is incorrect because the two plastics are not compared and degradation rates are theoretical. C is incorrect becau ...