101-Chem
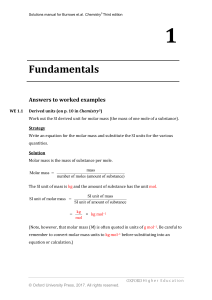
... Molecular Mass Sum of atomic masses of all atoms in compound’s formula 1 mole of molecule X = gram molecular mass of X ...
... Molecular Mass Sum of atomic masses of all atoms in compound’s formula 1 mole of molecule X = gram molecular mass of X ...
File
... less than what was expected. They identify and list the most likely errors in the activity. Which is a systematic error? A. B. C. D. ...
... less than what was expected. They identify and list the most likely errors in the activity. Which is a systematic error? A. B. C. D. ...
Solving Problems: A Chemistry Handbook
... sunburn. Ultraviolet radiation can also harm other animals and plants. In the 1980s, scientists documented that the ozone layer around Earth was becoming measurably thinner in some spots. In the 1970s, scientists had observed that large quantities of chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) had accumulated in Ear ...
... sunburn. Ultraviolet radiation can also harm other animals and plants. In the 1980s, scientists documented that the ozone layer around Earth was becoming measurably thinner in some spots. In the 1970s, scientists had observed that large quantities of chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) had accumulated in Ear ...
Major 01 - KFUPM Faculty List
... 2 mol SO2 reacts with 1 mol O2, thus 1.4047 mol SO2 use (1.4047/2) mol O2 = 0.7024 mol O2 So of the initial 3.125 mol O2, 0.7024 mol O2 are used and (3.125 - 0.7024) mol O2 = 2.4226 mol O2 are left over (in excess). This is 2.4226 mol x 32 g O2/mol = 77.5 g O2 are left over (choice A). 15. 1.00 mL ...
... 2 mol SO2 reacts with 1 mol O2, thus 1.4047 mol SO2 use (1.4047/2) mol O2 = 0.7024 mol O2 So of the initial 3.125 mol O2, 0.7024 mol O2 are used and (3.125 - 0.7024) mol O2 = 2.4226 mol O2 are left over (in excess). This is 2.4226 mol x 32 g O2/mol = 77.5 g O2 are left over (choice A). 15. 1.00 mL ...
Chapter 03 - KFUPM Faculty List
... Factors like 3/2 are ok, but usually not very much liked. So we multiply what we have (especially the 3/2) by 2: 2 NH3 + 2 O2 2 NO + 3 H2O: now N and H ok, but there are 4O atoms on the left and 5O atoms on the right so when we use (5/2) O2, then we have 5O atoms on the left and on the right side, ...
... Factors like 3/2 are ok, but usually not very much liked. So we multiply what we have (especially the 3/2) by 2: 2 NH3 + 2 O2 2 NO + 3 H2O: now N and H ok, but there are 4O atoms on the left and 5O atoms on the right so when we use (5/2) O2, then we have 5O atoms on the left and on the right side, ...
Chapter 3
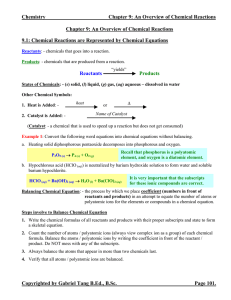
... element the same on both sides of the equation. Do not change the subscripts. 3. Start by balancing those elements that appear in only one reactant and one product. 4. Balance those elements that appear in two or more reactants or products. 4. Remove all fractions (generally by multiplying everythin ...
... element the same on both sides of the equation. Do not change the subscripts. 3. Start by balancing those elements that appear in only one reactant and one product. 4. Balance those elements that appear in two or more reactants or products. 4. Remove all fractions (generally by multiplying everythin ...
Fundamentals
... The average relative atomic mass is given by the weighted average of the masses of the individual isotopes. Average relative mass of 100 atoms of bromine ...
... The average relative atomic mass is given by the weighted average of the masses of the individual isotopes. Average relative mass of 100 atoms of bromine ...
Stoichiometry: Calculations with Chemical Formulas and Equations
... is one where the substance retains its identity. ...
... is one where the substance retains its identity. ...
Chemistry: Percent Yield
... 17: 3.4e Equal volumes of gases at the same temperature and pressure contain an equal number of particles. 33: 3.2b Types of chemical reactions include synthesis, decomposition, single replacement, and double replacement 36: M1.1C – Use algebraic and geometric representations to describe and compare ...
... 17: 3.4e Equal volumes of gases at the same temperature and pressure contain an equal number of particles. 33: 3.2b Types of chemical reactions include synthesis, decomposition, single replacement, and double replacement 36: M1.1C – Use algebraic and geometric representations to describe and compare ...
Chapter 09 An Overview of Chemical Reactions Notes
... CaCO3 (s) + 2 HCl (aq) → CaCl2 (aq) + H2O (l) + CO2 (g) a. How many moles of HCl (aq) are required to react with 2.5 mol of calcium carbonate? b. How many moles of carbon dioxide would be produced if 2.5 mol of calcium carbonate is used? 4. Aluminum reacts with hydrochloric acid, HCl (aq), to produc ...
... CaCO3 (s) + 2 HCl (aq) → CaCl2 (aq) + H2O (l) + CO2 (g) a. How many moles of HCl (aq) are required to react with 2.5 mol of calcium carbonate? b. How many moles of carbon dioxide would be produced if 2.5 mol of calcium carbonate is used? 4. Aluminum reacts with hydrochloric acid, HCl (aq), to produc ...
Answer Key - mrkelleher
... can be established. If Y replaces X but not Z, the series is Z > Y > X. If Y replaces Z but not X, the series is X > Y > Z. If Y reacts with neither solution, Y is at the bottom of the series. Next, put one chip of X into ZCl2(aq). If it reacts, the series is X > Z > Y. If it does not react, the ser ...
... can be established. If Y replaces X but not Z, the series is Z > Y > X. If Y replaces Z but not X, the series is X > Y > Z. If Y reacts with neither solution, Y is at the bottom of the series. Next, put one chip of X into ZCl2(aq). If it reacts, the series is X > Z > Y. If it does not react, the ser ...
File
... production; HNO3: important industrial chemical, used to form nitrogen-based explosives, strong acid and a very strong oxidizing agent. ...
... production; HNO3: important industrial chemical, used to form nitrogen-based explosives, strong acid and a very strong oxidizing agent. ...
Answers - logo Pre-U Chemistry Textbook
... The two things that affect the size of hydration energies are ionic radius and the charge on the ion. The higher the charge on the ion the more exothermic ∆hydrH. The value for Mg2+ is nearly five times as large as Na+. Al3+ is nearly two and a half times as big as Mg2+. By comparing the values for ...
... The two things that affect the size of hydration energies are ionic radius and the charge on the ion. The higher the charge on the ion the more exothermic ∆hydrH. The value for Mg2+ is nearly five times as large as Na+. Al3+ is nearly two and a half times as big as Mg2+. By comparing the values for ...
Specification and sample assessment material - Edexcel
... There are some practicals in the specification content, which students need to describe. Knowledge of these practicals, and the ability to interpret the resulting data, is required for the examinations. The teachers’ guide materials contain additional suggested practicals. Appendix 3 also contains s ...
... There are some practicals in the specification content, which students need to describe. Knowledge of these practicals, and the ability to interpret the resulting data, is required for the examinations. The teachers’ guide materials contain additional suggested practicals. Appendix 3 also contains s ...
Modern Chemistry
... the answer as 0.571429. a. Is the setup for calculating density correct? b. How many significant figures should the answer contain? 4. It was shown in the text that in a value such as 4000 g, the precision of the number is uncertain. The zeros may or may not be significant. a. Suppose that the mass ...
... the answer as 0.571429. a. Is the setup for calculating density correct? b. How many significant figures should the answer contain? 4. It was shown in the text that in a value such as 4000 g, the precision of the number is uncertain. The zeros may or may not be significant. a. Suppose that the mass ...
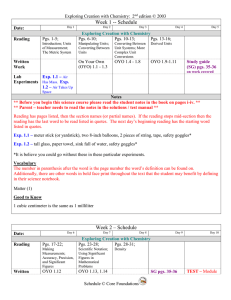
Week 1 -- Schedule
... Exp. 1.1 – meter stick (or yardstick), two 8-inch balloons, 2 pieces of string, tape, safety goggles* Exp. 1.2 – tall glass, paper towel, sink full of water, safety goggles* *It is believe you could go without these in these particular experiments. Vocabulary The number in parenthesis after the word ...
... Exp. 1.1 – meter stick (or yardstick), two 8-inch balloons, 2 pieces of string, tape, safety goggles* Exp. 1.2 – tall glass, paper towel, sink full of water, safety goggles* *It is believe you could go without these in these particular experiments. Vocabulary The number in parenthesis after the word ...
Practice Problems in Biomedical Organic Chemistry
... I: Integrated. These problems require the assimilation and integration of multiple core concepts to arrive at the correct solution to the problem. A: Applied. These problems test understanding of core concepts by applying them to data-driven and realworld problems in biology and other life scien ...
... I: Integrated. These problems require the assimilation and integration of multiple core concepts to arrive at the correct solution to the problem. A: Applied. These problems test understanding of core concepts by applying them to data-driven and realworld problems in biology and other life scien ...
Final Exam
... ____ 20. Which one of the following statements is INCORRECT? a. Ionization energy is always a positive value. ...
... ____ 20. Which one of the following statements is INCORRECT? a. Ionization energy is always a positive value. ...