Generation of quasistanding hypersonic wave in stimulated brillouin
... Apparently, a more detailed calculation of bubston cluster coalescence threshold requires that the dependence of bubston compressibility on frequency and their interaction potential be included. Note that this explanation of cavitation of a liquid in a broad-band pumping field differs from the theor ...
... Apparently, a more detailed calculation of bubston cluster coalescence threshold requires that the dependence of bubston compressibility on frequency and their interaction potential be included. Note that this explanation of cavitation of a liquid in a broad-band pumping field differs from the theor ...
Energy and angular momentum transfers from an
... or using interferences with plane waves [34] or self interferences using triangular apertures [35] or Young double slit experiments [36]. For review articles the reader can refer, for example, to [10, 11, 12, 37]. Concerning the applications, some authors take advantages of the vortex structure to g ...
... or using interferences with plane waves [34] or self interferences using triangular apertures [35] or Young double slit experiments [36]. For review articles the reader can refer, for example, to [10, 11, 12, 37]. Concerning the applications, some authors take advantages of the vortex structure to g ...
Test - Wave Optics
... Light is an electromagnetic wave phenomenon described by the same theoretical principles that govern all forms of electromagnetic radiation. Electromagnetic radiation propagates in the form of two mutually coupled vector waves, an electric-field wave and a magnetic-field wave. Nevertheless, it is po ...
... Light is an electromagnetic wave phenomenon described by the same theoretical principles that govern all forms of electromagnetic radiation. Electromagnetic radiation propagates in the form of two mutually coupled vector waves, an electric-field wave and a magnetic-field wave. Nevertheless, it is po ...
Superluminal group velocity in an anisotropic metamaterial
... the choice of sign of qz ensures that light power propagates away from the surface to the +z direction. Due to the anisotropy, the transmitted wave components may refract at slightly different angles. The values of refracted wave vector can be found by using the boundary condition and hyperbolic dis ...
... the choice of sign of qz ensures that light power propagates away from the surface to the +z direction. Due to the anisotropy, the transmitted wave components may refract at slightly different angles. The values of refracted wave vector can be found by using the boundary condition and hyperbolic dis ...
Doc - Department of Physics
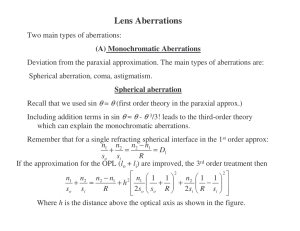
... Introduction to the Course unit The course comprises three parts: Waves, Geometrical Optics and an Introduction to Wave optics. A wave is a disturbance that transfers energy from one point to another without imparting net motion to the medium through which it propagates. Many examples of waves and o ...
... Introduction to the Course unit The course comprises three parts: Waves, Geometrical Optics and an Introduction to Wave optics. A wave is a disturbance that transfers energy from one point to another without imparting net motion to the medium through which it propagates. Many examples of waves and o ...
A demonstration of rotating sound waves in free space
... to establish a clear relation between matter waves and other familiar wave fields such as light, sound, and surface waves in liquids. One of the most interesting properties of rotating waves is that they carry angular momentum that can be transferred to matter, just as the linear momentum of traveli ...
... to establish a clear relation between matter waves and other familiar wave fields such as light, sound, and surface waves in liquids. One of the most interesting properties of rotating waves is that they carry angular momentum that can be transferred to matter, just as the linear momentum of traveli ...
Observation of optical polarization Möbius strips
... of –1/2 and –3/2. (A and C) The numerically calculated polarization topologies in the focal plane of the beam. (B and D) The experimentally observed polarization topologies in the focal plane of the beam. Our experiment was performed under tight-focusing (nonparaxial) conditions, which accentuates t ...
... of –1/2 and –3/2. (A and C) The numerically calculated polarization topologies in the focal plane of the beam. (B and D) The experimentally observed polarization topologies in the focal plane of the beam. Our experiment was performed under tight-focusing (nonparaxial) conditions, which accentuates t ...
Upholding the diffraction limit in the focusing of light and sound
... manipulation of fluorescence–based detection, such as stimulated emission depletion or on-andoff stochastic switching of fluorophore molecules [3], one can resolve subwavelength features of ...
... manipulation of fluorescence–based detection, such as stimulated emission depletion or on-andoff stochastic switching of fluorophore molecules [3], one can resolve subwavelength features of ...
Generalizing the Confocal Microscope via Heterodyne Interferometry and Digital Filtering
... Since this is a shearing system rather than a differential one, it is not limited to small phase shifts; it is equally accurate throughout 2π radians. As in any monochromatic-light interferometer, phase shifts larger than 2π introduce an ambiguity, which in this case is mitigated since depth-discrim ...
... Since this is a shearing system rather than a differential one, it is not limited to small phase shifts; it is equally accurate throughout 2π radians. As in any monochromatic-light interferometer, phase shifts larger than 2π introduce an ambiguity, which in this case is mitigated since depth-discrim ...
Optics in Confocal Microscopy
... compensated by adjustment of the mirror separation. However, the PSF is badly disturbed by the central occlusion and they are u ...
... compensated by adjustment of the mirror separation. However, the PSF is badly disturbed by the central occlusion and they are u ...
Dispersive Quantization
... kernel, which would effectively smooth out the coarser quantized times. Since the underlying partial differential equation is linear, with constant coefficients, derivatives and integrals of solutions are also solutions. In particular, integrating the solution (7) with respect to x a couple of times ...
... kernel, which would effectively smooth out the coarser quantized times. Since the underlying partial differential equation is linear, with constant coefficients, derivatives and integrals of solutions are also solutions. In particular, integrating the solution (7) with respect to x a couple of times ...
Polarization of light on reflection by some natural
... Attempts to detect ellipticity, if any, of the reflected light with the use of a combination of a quarter wave plate and a relatively broad-band interference filter did not yield meaningful results. Hence only the degree of linear polarization and relative intensity variations of the reflected light ...
... Attempts to detect ellipticity, if any, of the reflected light with the use of a combination of a quarter wave plate and a relatively broad-band interference filter did not yield meaningful results. Hence only the degree of linear polarization and relative intensity variations of the reflected light ...