Bright Field Microscopy
... plate introduces a relative retardation between O and E rays of exactly one wavelength for green wavelengths of 551 nm. Green wavelengths therefore emerge from the retardation plate linearly polarized in the same orientation as the polarizer and are blocked at the analyzer. O and E waves of all othe ...
... plate introduces a relative retardation between O and E rays of exactly one wavelength for green wavelengths of 551 nm. Green wavelengths therefore emerge from the retardation plate linearly polarized in the same orientation as the polarizer and are blocked at the analyzer. O and E waves of all othe ...
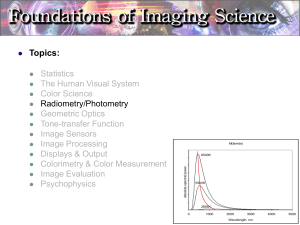
Overview
... -So, the index is a function of wavelength -Therefore, the amount of refraction is different -This effect is called chromatic dispersion ...
... -So, the index is a function of wavelength -Therefore, the amount of refraction is different -This effect is called chromatic dispersion ...
Lecture Series: Building the Future of Optical Modeling and Design
... concept for modeling the propagation of light through optical systems and gives an overview in theory and simulations of different modeling techniques to propagate light fields through for example homogeneous media, lenses, prisms, DOE’s, gratings and micro structures. Lecture 3: 29.08.2013 Modeling ...
... concept for modeling the propagation of light through optical systems and gives an overview in theory and simulations of different modeling techniques to propagate light fields through for example homogeneous media, lenses, prisms, DOE’s, gratings and micro structures. Lecture 3: 29.08.2013 Modeling ...
Off-Axis Aperture Camera: 3D Shape Reconstruction
... One can observe that the variation δπ[P(x)] in the above equation depends on the coordinates x. In particular, as kx − C1,2 k grows, also kδπ[P(x)]k grows. While in principle this behavior is acceptable, in practice it is an issue when using gradient-based techniques; part of the gradient of the cos ...
... One can observe that the variation δπ[P(x)] in the above equation depends on the coordinates x. In particular, as kx − C1,2 k grows, also kδπ[P(x)]k grows. While in principle this behavior is acceptable, in practice it is an issue when using gradient-based techniques; part of the gradient of the cos ...
What is a surface plasmon?
... quantitative phenomenological analysis of Wood anomalies. Phenomenology: using intuition then mathematics in order to describe quantitatively a phenomenon from the smallest number of parameters It allowed the discovery of the phenomenon of total absorption of light (Maystre and Petit, 1976, Hutley a ...
... quantitative phenomenological analysis of Wood anomalies. Phenomenology: using intuition then mathematics in order to describe quantitatively a phenomenon from the smallest number of parameters It allowed the discovery of the phenomenon of total absorption of light (Maystre and Petit, 1976, Hutley a ...
Volume Holographic Recording and Readout for 90
... where k refers to a propagation constant of light in the material, to be made more precise later. Also, the angle of the grating vector is terms in the surviving Laplace variable. It is pointed outthat the inverse transformation of 2-D Laplace functions as derived here is rather difficult even under ...
... where k refers to a propagation constant of light in the material, to be made more precise later. Also, the angle of the grating vector is terms in the surviving Laplace variable. It is pointed outthat the inverse transformation of 2-D Laplace functions as derived here is rather difficult even under ...
Waves & Oscillations Physics 42200 Spring 2013 Semester Lecture 30 – Geometric Optics
... An object is placed in front of two thin symmetrical coaxial lenses (lens 1 & lens 2) with focal lengths f1=+24 cm & f2=+9.0 cm, with a lens separation of L=10.0 cm. The object is 6.0 cm from lens 1. Where is the image of the object? Lens 1: ...
... An object is placed in front of two thin symmetrical coaxial lenses (lens 1 & lens 2) with focal lengths f1=+24 cm & f2=+9.0 cm, with a lens separation of L=10.0 cm. The object is 6.0 cm from lens 1. Where is the image of the object? Lens 1: ...
Integrated Optics
... • Integrated optics is a system of light-controlling components combined into a single device. The ultimate aim is to create miniature optical circuits similar to the silicon chips that have revolutionized the electronics industry. The advantage of the optical approach however is that data can be pr ...
... • Integrated optics is a system of light-controlling components combined into a single device. The ultimate aim is to create miniature optical circuits similar to the silicon chips that have revolutionized the electronics industry. The advantage of the optical approach however is that data can be pr ...
Gullstrand equation
... contact with solids. On this account, these three capillary menisci are known as liquid bridges (figure 5). Any moderately curved interface is determined by an intrinsic parameter (related to the media) and another purely geometrical one (principal radius of curvature on a reference point). In this ...
... contact with solids. On this account, these three capillary menisci are known as liquid bridges (figure 5). Any moderately curved interface is determined by an intrinsic parameter (related to the media) and another purely geometrical one (principal radius of curvature on a reference point). In this ...
Multiplexing in high-density optical data storage using the orbital
... The angular momentum of a (focused) beam of light comprises an intrinsic part due to the photon spin (units ± h or ± h / 2π per photon) and a part that can be associated with the geometrical structure of a light beam and we briefly recall the basic theory of this type of beams.2,3,4 Beams carrying n ...
... The angular momentum of a (focused) beam of light comprises an intrinsic part due to the photon spin (units ± h or ± h / 2π per photon) and a part that can be associated with the geometrical structure of a light beam and we briefly recall the basic theory of this type of beams.2,3,4 Beams carrying n ...
Analysis and Compensation of Four Wave Mixing Products in
... This article provides concepts of Four Wave Mixing which is a type of Nonlinearity. Due to the widespread growth in wireless communication, network operators are facing difficulty in accommodating the growing traffic. WDM appears to be a viable solution to such problems posed by the micro cellular s ...
... This article provides concepts of Four Wave Mixing which is a type of Nonlinearity. Due to the widespread growth in wireless communication, network operators are facing difficulty in accommodating the growing traffic. WDM appears to be a viable solution to such problems posed by the micro cellular s ...
Regenerating evanescent waves from a silver superlens
... interface, and W(θ,φ) the dipole function. When the incident frequency is fixed, the photon impinging on the metal surface can excite the collective oscillation of conductive electrons at certain wave vectors, i.e., the surface plasmon with maximum efficiency. Therefore by coupling with a hemispheri ...
... interface, and W(θ,φ) the dipole function. When the incident frequency is fixed, the photon impinging on the metal surface can excite the collective oscillation of conductive electrons at certain wave vectors, i.e., the surface plasmon with maximum efficiency. Therefore by coupling with a hemispheri ...
On the chromatic aberration of microlenses
... Similar to classical achromats an achromatic microlens does not show an achromatic behavior over the full wavelength range in-between λ1 and λ2. The variation of achromats inside the range between these two design wavelengths is usually called secondary color aberration [1]. In classical optics the ...
... Similar to classical achromats an achromatic microlens does not show an achromatic behavior over the full wavelength range in-between λ1 and λ2. The variation of achromats inside the range between these two design wavelengths is usually called secondary color aberration [1]. In classical optics the ...