b. optical wave breaking in the pcf
... which much closely match the corresponding experiment result shown in Fig.3 (c). Fig.5(b) is the simulated pulse shape from the PCF. A noteworthy feature of the pulse shape is that the rapid oscillations appear near the pulse edges, which are always accompanied by the sidelobes in the spectrum. The ...
... which much closely match the corresponding experiment result shown in Fig.3 (c). Fig.5(b) is the simulated pulse shape from the PCF. A noteworthy feature of the pulse shape is that the rapid oscillations appear near the pulse edges, which are always accompanied by the sidelobes in the spectrum. The ...
Real-time digital holographic microscopy Ventseslav Sainov and Elena Stoykova
... and an object spherical wave U lR (r ) = A lR exp{− jk (x − x l )2 + ( y − y l )2 / 2 R} in paraxial approximation, r ...
... and an object spherical wave U lR (r ) = A lR exp{− jk (x − x l )2 + ( y − y l )2 / 2 R} in paraxial approximation, r ...
Phase distortions in sum- and difference
... with zero intensity its output phase will be independent of the intensities of the input waves and will depend only on DkL, where L is the crystal length. The output phases of the other two waves will be intensity dependent if Dk fi 0. If there is linear absorption the phase of the wave that started ...
... with zero intensity its output phase will be independent of the intensities of the input waves and will depend only on DkL, where L is the crystal length. The output phases of the other two waves will be intensity dependent if Dk fi 0. If there is linear absorption the phase of the wave that started ...
Aberrations
... The Aberration Polynomial: So far, we haven’t asked what the functional form of W might be. If we restrict ourselves to rotationally symmetric optical systems, we can limit the possible forms W might take. If we assume a 2-Dimensional polynomial form for W, and eliminate all terms and combination of ...
... The Aberration Polynomial: So far, we haven’t asked what the functional form of W might be. If we restrict ourselves to rotationally symmetric optical systems, we can limit the possible forms W might take. If we assume a 2-Dimensional polynomial form for W, and eliminate all terms and combination of ...
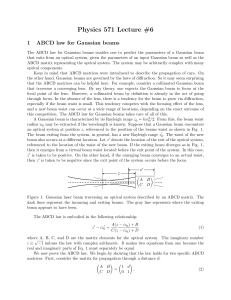
Using ray matrices to derive analytical expressions of optical
... Ray matrix formalism is a useful theory applied to paraxial geometrical optics, which employs 2×2 matrices to describe optical systems [1,2]. This formulation allows complex, multi-element, optical systems to be analyzed and simplified using easy calculations. This matrix theory is also very useful ...
... Ray matrix formalism is a useful theory applied to paraxial geometrical optics, which employs 2×2 matrices to describe optical systems [1,2]. This formulation allows complex, multi-element, optical systems to be analyzed and simplified using easy calculations. This matrix theory is also very useful ...
Solitons, Shock Waves and Conservation Laws of Rosenau
... fundamental pulses that travel through the optical fibers for transcontinental and transoceanic distances. The modern telecommunication system in information sciences has advanced because of the progress in the research on optical solitons [9, 12]. Apart from nonlinear optics, solitons are also obse ...
... fundamental pulses that travel through the optical fibers for transcontinental and transoceanic distances. The modern telecommunication system in information sciences has advanced because of the progress in the research on optical solitons [9, 12]. Apart from nonlinear optics, solitons are also obse ...
Physical Optics
... Introduction and structure of the course. The study of light has been an important part of science from its beginning. The ancient Greeks and, prior to the Middle Ages, Islamic scholars provided important insights. With the coming of the Scientific Revolution in the 16th and 17th centuries, optics, ...
... Introduction and structure of the course. The study of light has been an important part of science from its beginning. The ancient Greeks and, prior to the Middle Ages, Islamic scholars provided important insights. With the coming of the Scientific Revolution in the 16th and 17th centuries, optics, ...
Engineering biphoton wave packets with an electromagnetically
... sample that act as an amplitude grating and by which the joint Stokes and anti-Stokes wave packet can be shaped. Compared with previous proposals ascribed before, several interesting features appear in the present one. First, such a medium may exert both amplitude and phase modulations on biphoton w ...
... sample that act as an amplitude grating and by which the joint Stokes and anti-Stokes wave packet can be shaped. Compared with previous proposals ascribed before, several interesting features appear in the present one. First, such a medium may exert both amplitude and phase modulations on biphoton w ...
Negative refraction - Condensed Matter Theory group
... All the properties of these double negative materials are consistent with a negative refractive index, and it is now common to use the term ‘negatively refracting’ to describe these double negative materials. In view of the role of causality in guiding us to physically correct solutions, we shall he ...
... All the properties of these double negative materials are consistent with a negative refractive index, and it is now common to use the term ‘negatively refracting’ to describe these double negative materials. In view of the role of causality in guiding us to physically correct solutions, we shall he ...
Waves
... Light is only a small part of the electromagnetic spectrum (see picture on next slide). All the different parts of the electromagnetic spectrum differ from light only in frequency (and thus period) and wavelength. Since light does not need a medium to propagate, and ALL other waves do, we can classi ...
... Light is only a small part of the electromagnetic spectrum (see picture on next slide). All the different parts of the electromagnetic spectrum differ from light only in frequency (and thus period) and wavelength. Since light does not need a medium to propagate, and ALL other waves do, we can classi ...