Lecture 6 – Bloch`s theorem
... completely filled or partially filled bands. The Fermi surface is obtained from the condition that εn (k) = εF • Band gap If some bands are completely filled and all others remain empty, the gap between the highest occupied level and the lowest unoccupied level is called the band gap. In this case, ...
... completely filled or partially filled bands. The Fermi surface is obtained from the condition that εn (k) = εF • Band gap If some bands are completely filled and all others remain empty, the gap between the highest occupied level and the lowest unoccupied level is called the band gap. In this case, ...
New compound shows unusual conducting properties
... valence band in diamond that electrons do not have sufficient energy to move - the 'band gap' is large - therefore no electric current can be carried. In recent years, researchers have become interested in materials called topological insulators (TIs), which act as insulators on the inside, but are ...
... valence band in diamond that electrons do not have sufficient energy to move - the 'band gap' is large - therefore no electric current can be carried. In recent years, researchers have become interested in materials called topological insulators (TIs), which act as insulators on the inside, but are ...
Section 4.8: The Structure and Properties of Solids
... 6. (a) A metallic solid conducts electricity and has a high melting point. (b) An ionic solid does not conduct electricity as a solid but does when dissolved in heat. (c) A covalent network solid does not conduct electricity and has a high boiling point. (d) A molecular solid does not conduct electr ...
... 6. (a) A metallic solid conducts electricity and has a high melting point. (b) An ionic solid does not conduct electricity as a solid but does when dissolved in heat. (c) A covalent network solid does not conduct electricity and has a high boiling point. (d) A molecular solid does not conduct electr ...
Experimental
... The most powerful tool for the characterization of coordination solids is the single crystal X-ray crystallography. This technique provides us with an accurate account of the structure and properties of materials in crystalline state. Additional advanced analytical and graphical tools associated wit ...
... The most powerful tool for the characterization of coordination solids is the single crystal X-ray crystallography. This technique provides us with an accurate account of the structure and properties of materials in crystalline state. Additional advanced analytical and graphical tools associated wit ...
303004BIP_supl_mtr
... which had a mean-square roughness less than 3 nm. The main principle of the method is the excitation of the quartz crystal at its resonant frequency, so that the crystal starts oscillating. By applying a RF voltage across the electrodes near the resonant frequency a layer, which is adsorbed to the g ...
... which had a mean-square roughness less than 3 nm. The main principle of the method is the excitation of the quartz crystal at its resonant frequency, so that the crystal starts oscillating. By applying a RF voltage across the electrodes near the resonant frequency a layer, which is adsorbed to the g ...
Polymers composed of a large number of repeating units. Isomers
... Monel needs to be turned and worked at slow speeds and low feed rates. It is resistant to corrosion and acids and hardens very quickly. ...
... Monel needs to be turned and worked at slow speeds and low feed rates. It is resistant to corrosion and acids and hardens very quickly. ...
4.1.4 Summary to: 4.1 Input to Si Processing in an...
... 4.1.4 Summary to: 4.1 Input to Si Processing in an Industrial Environment Semiconductor technology happens in factories. They need special materials, "reticles" (= structures), "know-how" and huge amoundt of money (= capital) as major inputs It's always about money! Only mass production will recover ...
... 4.1.4 Summary to: 4.1 Input to Si Processing in an Industrial Environment Semiconductor technology happens in factories. They need special materials, "reticles" (= structures), "know-how" and huge amoundt of money (= capital) as major inputs It's always about money! Only mass production will recover ...
Ettringite - Sulfato - ltmufrgs
... that too. It will commonly form well shaped hexagonal prisms that are topped by a hexagonal pyramid, which in turn is often truncated by the flat face of a pinacoid. Its chemistry is interesting. Four out of every five atoms in this mineral is either a part of a water molecule or an hydroxide. It's ...
... that too. It will commonly form well shaped hexagonal prisms that are topped by a hexagonal pyramid, which in turn is often truncated by the flat face of a pinacoid. Its chemistry is interesting. Four out of every five atoms in this mineral is either a part of a water molecule or an hydroxide. It's ...
JaegerCh01overview2015
... • displaced along the body diagonal of the larger cube by one quarter of the body diagonal. The diamond lattice therefore is a face-centered-cubic lattice with a basis containing two identical atoms. ...
... • displaced along the body diagonal of the larger cube by one quarter of the body diagonal. The diamond lattice therefore is a face-centered-cubic lattice with a basis containing two identical atoms. ...
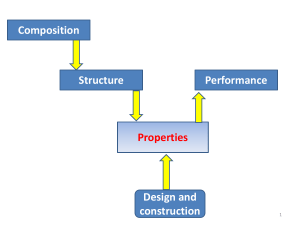
follow up solids
... 5. Do these arrangements promote certain mechanisms for electronic or atomic motions? 6. How do these mechanisms give rise to the observed properties? ...
... 5. Do these arrangements promote certain mechanisms for electronic or atomic motions? 6. How do these mechanisms give rise to the observed properties? ...
Semiconductor Modelling
... These crystals take up to 14 days to grow. In the absence, the ingredients don’t separate readily and the molten material tends to pull away from the container shortly. Not sure about how commercial this will get, but John Walker and his colleagues would like to show that growing crystals in space c ...
... These crystals take up to 14 days to grow. In the absence, the ingredients don’t separate readily and the molten material tends to pull away from the container shortly. Not sure about how commercial this will get, but John Walker and his colleagues would like to show that growing crystals in space c ...
The Potential of Computed Crystal Energy Landscapes to
... A key first step in developing a solid oral dosage form is to identify crystalline forms of the drug molecule, generally through some form of crystallization screening. Crystallization provides a means to purify and recover the drug substance coming out of the final step of the synthesis and to isol ...
... A key first step in developing a solid oral dosage form is to identify crystalline forms of the drug molecule, generally through some form of crystallization screening. Crystallization provides a means to purify and recover the drug substance coming out of the final step of the synthesis and to isol ...
The structure of RNase E at the core of the RNA
... derivative was prepared by soaking the native crystals with cis-amino platinum, which was not useful for phasing, but in difference maps corroborated the position of an exposed histidine side chain. Higher resolution data were collected from native crystals at the Zn absorption edge, and anomalous ...
... derivative was prepared by soaking the native crystals with cis-amino platinum, which was not useful for phasing, but in difference maps corroborated the position of an exposed histidine side chain. Higher resolution data were collected from native crystals at the Zn absorption edge, and anomalous ...
Crystal structure

In mineralogy and crystallography, a crystal structure is a unique arrangement of atoms, ions or molecules in a crystalline liquid or solid. It describes a highly ordered structure, occurring due to the intrinsic nature of its constituents to form symmetric patterns.The crystal lattice can be thought of as an array of 'small boxes' infinitely repeating in all three spatial directions. Such a unit cell is the smallest unit of volume that contains all of the structural and symmetry information to build-up the macroscopic structure of the lattice by translation.Patterns are located upon the points of a lattice, which is an array of points repeating periodically in three dimensions. The lengths of the edges of a unit cell and the angles between them are called the lattice parameters. The symmetry properties of the crystal are embodied in its space group.A crystal's structure and symmetry play a role in determining many of its physical properties, such as cleavage, electronic band structure, and optical transparency.