PREM NMHU Highlights - FY 14-15
... The promise of low-cost processing and flexible circuitry has driven intense research in carbon-based electronics. The performance of carbon-based materials can be effectively tuned by the application of redox reagents dopants, through increasing the conductivity and decreasing the injection barrier ...
... The promise of low-cost processing and flexible circuitry has driven intense research in carbon-based electronics. The performance of carbon-based materials can be effectively tuned by the application of redox reagents dopants, through increasing the conductivity and decreasing the injection barrier ...
Chapter 4
... •Material permanently deforms as dislocation moves through the crystal. • Bonds break and reform, but only along the dislocation line at any point in time, not along the whole plane at once. • Dislocation line separates slipped and unslipped material. ...
... •Material permanently deforms as dislocation moves through the crystal. • Bonds break and reform, but only along the dislocation line at any point in time, not along the whole plane at once. • Dislocation line separates slipped and unslipped material. ...
Electro-optic modulators
... Operation of electro-optic modulators is based on the principle of induced birefringence. Pockels cell is such device which can produce controllable birefringence by applying voltage to the cell. The cell contains uniaxial crystal, which becomes biaxial when electric field is applied. If new axes in ...
... Operation of electro-optic modulators is based on the principle of induced birefringence. Pockels cell is such device which can produce controllable birefringence by applying voltage to the cell. The cell contains uniaxial crystal, which becomes biaxial when electric field is applied. If new axes in ...
PHYS 4740 Lecture notes 1
... For example, consider a lattice formed by X and M ions. Suppose an M ion leaves the M sublattice, leaving the X sublattice unchanged. The number of interstitials formed will equal the number of vacancies formed. One form of a Frenkel defect reaction in MgO with the oxygen ion leaving the lattice and ...
... For example, consider a lattice formed by X and M ions. Suppose an M ion leaves the M sublattice, leaving the X sublattice unchanged. The number of interstitials formed will equal the number of vacancies formed. One form of a Frenkel defect reaction in MgO with the oxygen ion leaving the lattice and ...
Crystal Structure of Mixed-metal Phosphite, Pb2Ga(HPIIIO3)3(PVO3)
... active lone pairs. The Pb−O and Ga-O distances range from 2.510(6) to 2.702(5) Å, 1.957 (5) to 1.966 (7) Å, respectively. All of these bond distances are comparable to those reported for other lead(II) phosphites [20] and gallium phosphites [9,21]. The calculated total bond valences for Pb(1), Ga(1) ...
... active lone pairs. The Pb−O and Ga-O distances range from 2.510(6) to 2.702(5) Å, 1.957 (5) to 1.966 (7) Å, respectively. All of these bond distances are comparable to those reported for other lead(II) phosphites [20] and gallium phosphites [9,21]. The calculated total bond valences for Pb(1), Ga(1) ...
Magnetic Materials Background: 5. Properties
... In a crystalline magnetic material the magnetic properties will vary depending on the crystallographic direction in which the magnetic dipoles are aligned. Figure 4 demonstrates this effect for a single crystal of cobalt. The hexagonal crystal structure of Co can be magnetised easily in the [0001] d ...
... In a crystalline magnetic material the magnetic properties will vary depending on the crystallographic direction in which the magnetic dipoles are aligned. Figure 4 demonstrates this effect for a single crystal of cobalt. The hexagonal crystal structure of Co can be magnetised easily in the [0001] d ...
Read more (docx 14 kB)
... Title: Nonlinear Photonic Crystals Abstract: Photonic crystals are materials patterned with periodic dielectric structures. Since they were first proposed, in 1987, they have grown into a burgeoning research field. Nowadays, their engineerable response is already used in a broad range of application ...
... Title: Nonlinear Photonic Crystals Abstract: Photonic crystals are materials patterned with periodic dielectric structures. Since they were first proposed, in 1987, they have grown into a burgeoning research field. Nowadays, their engineerable response is already used in a broad range of application ...
Chapter 5 2004.ppt
... adjacent faces of quartz is always exactly the same. Other minerals were also found to have this regularity. This observation became known as the law of constancy of interfacial angles. • Atoms of different minerals are clustered into geometric forms such as cubes, bricks, hexagons, etc. and so the ...
... adjacent faces of quartz is always exactly the same. Other minerals were also found to have this regularity. This observation became known as the law of constancy of interfacial angles. • Atoms of different minerals are clustered into geometric forms such as cubes, bricks, hexagons, etc. and so the ...
1.2 Atomic mass and molar fractions Solution 1.22 BCC and FCC
... b. Suppose that a substance (compound or an alloy) is composed of N elements, A, B, C,... and that we know their atomic (or molar) fractions n A , n B n C , .... Show that the weight fractions w A , w B , w C ,....are given by ...
... b. Suppose that a substance (compound or an alloy) is composed of N elements, A, B, C,... and that we know their atomic (or molar) fractions n A , n B n C , .... Show that the weight fractions w A , w B , w C ,....are given by ...
Size effects
... The misfit between adjacent crystallites in the grain boundaries changes the atomic structure (e.g. the average atomic density, the nearestneighbor coordination, etc.) of materials. At high defect densities the volume fraction of defects becomes comparable with the volume fraction of the crystalline ...
... The misfit between adjacent crystallites in the grain boundaries changes the atomic structure (e.g. the average atomic density, the nearestneighbor coordination, etc.) of materials. At high defect densities the volume fraction of defects becomes comparable with the volume fraction of the crystalline ...
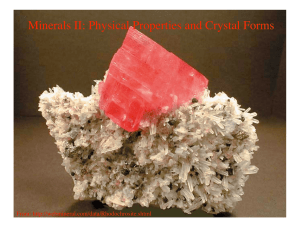
Physical properties of minerals
... • Hardness - This is the resistance of the mineral to abrasion or scratching. This property doesn't vary greatly from sample to sample of the same mineral, and thus is highly diagnostic. It also is a direct reflection of the bonding type and internal atomic arrangement. A value is obtained by compar ...
... • Hardness - This is the resistance of the mineral to abrasion or scratching. This property doesn't vary greatly from sample to sample of the same mineral, and thus is highly diagnostic. It also is a direct reflection of the bonding type and internal atomic arrangement. A value is obtained by compar ...
What is a mineral - group items
... crystalline structure.” p. 86 The Earth’s crust contains more than 100 naturally occurring elements. Earth’s crust is composed of 3000 different minerals. Minerals may be metallic, like gold, or nonmetallic, like talc. Most have to be compounds or there couldn’t be that many. ...
... crystalline structure.” p. 86 The Earth’s crust contains more than 100 naturally occurring elements. Earth’s crust is composed of 3000 different minerals. Minerals may be metallic, like gold, or nonmetallic, like talc. Most have to be compounds or there couldn’t be that many. ...
Ceramic Glass
... each other. As the melt cools, thermal vibrational energy decreases and the chains can’t move as easily so the structure becomes more rigid. Silica is the most important constituent of glass, but other oxides are added to change certain physical characteristics or to lower the melting point. Glass i ...
... each other. As the melt cools, thermal vibrational energy decreases and the chains can’t move as easily so the structure becomes more rigid. Silica is the most important constituent of glass, but other oxides are added to change certain physical characteristics or to lower the melting point. Glass i ...
Using APL format - Massachusetts Institute of Technology
... planar-layer structure is the ‘‘layer-by-layer’’10 共or ‘‘woodpile’’11兲 design: dielectric ‘‘logs’’ stacked in alternating perpendicular directions with a four-layer period, forming an fcc crystal oriented in the 100 direction. Any given plane, however, does not have high rotational symmetry, meaning ...
... planar-layer structure is the ‘‘layer-by-layer’’10 共or ‘‘woodpile’’11兲 design: dielectric ‘‘logs’’ stacked in alternating perpendicular directions with a four-layer period, forming an fcc crystal oriented in the 100 direction. Any given plane, however, does not have high rotational symmetry, meaning ...
CRYSTALLINITY
... CRYSTAL SYSTEM (INTERNAL STRUCTURE) The most symmetric system is cubic system. Other six systems, in order of decreasing symmetry, are hexagonal, tetragonal, rhombohedral (also known as trigonal), orthorhombic, monoclinic and triclinic. Thus there are fourteen types of unit cell called as the Brava ...
... CRYSTAL SYSTEM (INTERNAL STRUCTURE) The most symmetric system is cubic system. Other six systems, in order of decreasing symmetry, are hexagonal, tetragonal, rhombohedral (also known as trigonal), orthorhombic, monoclinic and triclinic. Thus there are fourteen types of unit cell called as the Brava ...
Minerals - TeacherWeb
... solids, with definite structure and composition; made of one or more elements ...
... solids, with definite structure and composition; made of one or more elements ...
Crystal structure

In mineralogy and crystallography, a crystal structure is a unique arrangement of atoms, ions or molecules in a crystalline liquid or solid. It describes a highly ordered structure, occurring due to the intrinsic nature of its constituents to form symmetric patterns.The crystal lattice can be thought of as an array of 'small boxes' infinitely repeating in all three spatial directions. Such a unit cell is the smallest unit of volume that contains all of the structural and symmetry information to build-up the macroscopic structure of the lattice by translation.Patterns are located upon the points of a lattice, which is an array of points repeating periodically in three dimensions. The lengths of the edges of a unit cell and the angles between them are called the lattice parameters. The symmetry properties of the crystal are embodied in its space group.A crystal's structure and symmetry play a role in determining many of its physical properties, such as cleavage, electronic band structure, and optical transparency.