How do atoms arrange themselves to form solids? • Fundamental
... atoms as being hard spheres with well-defined radii. In this hard-sphere model, the shortest distance between two like atoms is one diameter of the hard sphere. 2R ...
... atoms as being hard spheres with well-defined radii. In this hard-sphere model, the shortest distance between two like atoms is one diameter of the hard sphere. 2R ...
How do atoms arrange themselves to form solids? • Fundamental
... Since the entire crystal can be generated by the repetition of the unit cell, the density of a crystalline material, ρ = the density of the unit cell = (atoms in the unit cell, n ) × (mass of an atom, M) / (the volume of the cell, Vc) Atoms in the unit cell, n = 2 (BCC); 4 (FCC); 6 (HCP) Mass of an ...
... Since the entire crystal can be generated by the repetition of the unit cell, the density of a crystalline material, ρ = the density of the unit cell = (atoms in the unit cell, n ) × (mass of an atom, M) / (the volume of the cell, Vc) Atoms in the unit cell, n = 2 (BCC); 4 (FCC); 6 (HCP) Mass of an ...
CRYSTALLINE MATERIALS
... A beam of light may consist of two plane-polarized wave trains Planes of polarization at right angles to each other May also be out of phase Electric vector at a given point in space is constant in amplitude but rotates with angular frequency ...
... A beam of light may consist of two plane-polarized wave trains Planes of polarization at right angles to each other May also be out of phase Electric vector at a given point in space is constant in amplitude but rotates with angular frequency ...
Basic aproximations in the band theory of solid state
... SUPERFLUIDITY OF LIQUID HELLIUM. THE CONSTANT CURRENT JOSEPHSON EFFECT. 14. SURFACE PHYSICS: REFLECTION DIFFRACTION OF HIGH ENERGY ELECTRONS (RHEED). ELECTRON STRUCTURE OF SURFACE, WORK FUNCTION, ...
... SUPERFLUIDITY OF LIQUID HELLIUM. THE CONSTANT CURRENT JOSEPHSON EFFECT. 14. SURFACE PHYSICS: REFLECTION DIFFRACTION OF HIGH ENERGY ELECTRONS (RHEED). ELECTRON STRUCTURE OF SURFACE, WORK FUNCTION, ...
Dniester is the main artery of the Republic of Moldova, with a
... determined. The values of ZT calculated for n-type (111) and (100) QWs are 0.89 and 1.40, respectively, which are two and three times higher than those in bulk PbTe. In a separate task, a method for calculating xe in quasi-one-dimensional (Q1D) organic crystals has been developed. It included the in ...
... determined. The values of ZT calculated for n-type (111) and (100) QWs are 0.89 and 1.40, respectively, which are two and three times higher than those in bulk PbTe. In a separate task, a method for calculating xe in quasi-one-dimensional (Q1D) organic crystals has been developed. It included the in ...
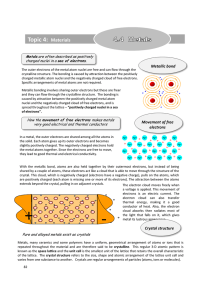
Topic 4: Materials - Education Umbrella
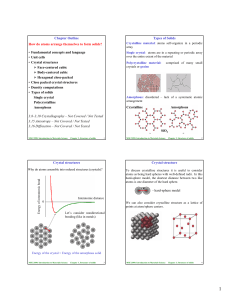
... Metals, many ceramics and some polymers have a uniform, geometrical arrangement of atoms or ions that is repeated throughout the material and are therefore said to be crystalline. This regular 3‐D atomic pattern is known as the space lattice and the unit cell is the smallest unit of the lattice that ...
... Metals, many ceramics and some polymers have a uniform, geometrical arrangement of atoms or ions that is repeated throughout the material and are therefore said to be crystalline. This regular 3‐D atomic pattern is known as the space lattice and the unit cell is the smallest unit of the lattice that ...
Color of a mineral in its powdered form
... Tendency to break along planes of weak bonding Produces flat, shiny surfaces Described by resulting geometric shapes -Number of planes -Angles between adjacent planes ...
... Tendency to break along planes of weak bonding Produces flat, shiny surfaces Described by resulting geometric shapes -Number of planes -Angles between adjacent planes ...
Metal
... tend to be densely packed. Reasons for dense packing: ● Typically, only one element is present, so all atomic radii are the same. ● bonding is not directional. ● nearest neighbor distances tend to be small in order to reduce bond energy (energy minimization). ● electron cloud shields cores from each ...
... tend to be densely packed. Reasons for dense packing: ● Typically, only one element is present, so all atomic radii are the same. ● bonding is not directional. ● nearest neighbor distances tend to be small in order to reduce bond energy (energy minimization). ● electron cloud shields cores from each ...
5.2 Composition and Structure of Minerals
... Crystal Structure Cont’d • If space is limited when a mineral is forming, there may not be enough room for crystal faces to develop fully, or “grow” • The mineral fills the available space • Still crystalline, but faces are not visible ...
... Crystal Structure Cont’d • If space is limited when a mineral is forming, there may not be enough room for crystal faces to develop fully, or “grow” • The mineral fills the available space • Still crystalline, but faces are not visible ...
Sample PDF
... that the spheres cover the octahedral voids, a layer different from first (A) and second (B) is produced. If we continue packing in this manner, then a packing is obtained where the spheres in every fourth layer will vertically aligned. This pattern of packing spheres is called ABCABC..... pattern o ...
... that the spheres cover the octahedral voids, a layer different from first (A) and second (B) is produced. If we continue packing in this manner, then a packing is obtained where the spheres in every fourth layer will vertically aligned. This pattern of packing spheres is called ABCABC..... pattern o ...
Basics of Material Sciences - E
... 19Method used in producing synthetic fibres is _______. (1) melt extrution (2) wet spinning (3) dry spinning(4) all 20Rayon fibres are produced by ________ method. (1) melt extrusion (2) wet spinning (3) dry spinning(4) all 21_________ is a laminated composite material. ...
... 19Method used in producing synthetic fibres is _______. (1) melt extrution (2) wet spinning (3) dry spinning(4) all 20Rayon fibres are produced by ________ method. (1) melt extrusion (2) wet spinning (3) dry spinning(4) all 21_________ is a laminated composite material. ...
of minerals!
... with a definite composition (or range of compositions), usually possessing a regular, internal crystalline structure. ...
... with a definite composition (or range of compositions), usually possessing a regular, internal crystalline structure. ...
Instructions how to Prepare a One Page Abstract for the European
... become the most promising material for the production of next generation thin and flexible electronic components. However, these properties depend on the presence of topological defects in the graphene lattice. In order to provide a model of graphene behavior allowing to study the birth and evolutio ...
... become the most promising material for the production of next generation thin and flexible electronic components. However, these properties depend on the presence of topological defects in the graphene lattice. In order to provide a model of graphene behavior allowing to study the birth and evolutio ...
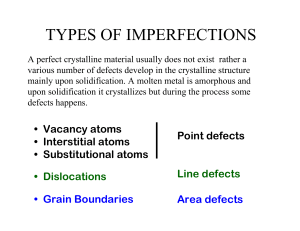
TYPES OF IMPERFECTIONS
... 2. Crystal structure. For appreciable solid solubility the crystal structures for metals of both atom types must be the same. 3. Electronegativity. The more electropositive one element and the more elec- tronegative the other, the greater is the likelihood that they will form an intrmetallic compoun ...
... 2. Crystal structure. For appreciable solid solubility the crystal structures for metals of both atom types must be the same. 3. Electronegativity. The more electropositive one element and the more elec- tronegative the other, the greater is the likelihood that they will form an intrmetallic compoun ...
110 mid-term 2011Solutions
... level. These excitations relax back down to a lower, possibly not ground state, energy level – the energy difference is emitted as an emission particle with X-ray energy lower than the incident but specific to the excitation. Every element has different possible transitions between ground and higher ...
... level. These excitations relax back down to a lower, possibly not ground state, energy level – the energy difference is emitted as an emission particle with X-ray energy lower than the incident but specific to the excitation. Every element has different possible transitions between ground and higher ...
Crystal Structures
... • Waves REFLECTED from the crystal planes INTERFERE with each other * In a manner that depends on the SPACING (d) of the crystal planes * The interference also depends on the WAVELENGTH () of the waves And the ANGLE () at which they are incident on the crystal * Consider the case of waves reflec ...
... • Waves REFLECTED from the crystal planes INTERFERE with each other * In a manner that depends on the SPACING (d) of the crystal planes * The interference also depends on the WAVELENGTH () of the waves And the ANGLE () at which they are incident on the crystal * Consider the case of waves reflec ...
Metallic Crystal Structure
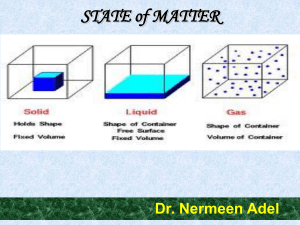
... ceramic materials, and certain polymers form crystalline structures under normal solidification conditions. For those that do not crystallize, this long-range atomic order is absent; these noncrystalline or amorphous materials. Crystalline and Noncrystalline Materials For a crystalline solid, when t ...
... ceramic materials, and certain polymers form crystalline structures under normal solidification conditions. For those that do not crystallize, this long-range atomic order is absent; these noncrystalline or amorphous materials. Crystalline and Noncrystalline Materials For a crystalline solid, when t ...
Crystal structure

In mineralogy and crystallography, a crystal structure is a unique arrangement of atoms, ions or molecules in a crystalline liquid or solid. It describes a highly ordered structure, occurring due to the intrinsic nature of its constituents to form symmetric patterns.The crystal lattice can be thought of as an array of 'small boxes' infinitely repeating in all three spatial directions. Such a unit cell is the smallest unit of volume that contains all of the structural and symmetry information to build-up the macroscopic structure of the lattice by translation.Patterns are located upon the points of a lattice, which is an array of points repeating periodically in three dimensions. The lengths of the edges of a unit cell and the angles between them are called the lattice parameters. The symmetry properties of the crystal are embodied in its space group.A crystal's structure and symmetry play a role in determining many of its physical properties, such as cleavage, electronic band structure, and optical transparency.