L6-Imperfections
... The strain fields surrounding dislocations in close proximity to one another may interact such that forces are imposed on each dislocation by the combined interactions of all its neighboring dislocations. ...
... The strain fields surrounding dislocations in close proximity to one another may interact such that forces are imposed on each dislocation by the combined interactions of all its neighboring dislocations. ...
Crystal growth and characterization of a new NLO
... great deal of attention, as they have large optical susceptibilities, inherent ultra-fast response times and high optical thresholds for laser power as compared with inorganic materials [3,4]. Organic molecules with significant nonlinear optical activity generally consist of a π – electron conjugate ...
... great deal of attention, as they have large optical susceptibilities, inherent ultra-fast response times and high optical thresholds for laser power as compared with inorganic materials [3,4]. Organic molecules with significant nonlinear optical activity generally consist of a π – electron conjugate ...
Three-Dimensional Electron Realm in Crystalline Solids Revealed
... Experimental band structure E(k). – Fig. 2 (b-c) shows an experimental ARPES intensity images of E(k) measured along two layer-parallel and layer-perpendicular directions in k-space with hv varying around 900 eV. The electrons are seen to occupy a wide energy range below certain maximal so-called Fe ...
... Experimental band structure E(k). – Fig. 2 (b-c) shows an experimental ARPES intensity images of E(k) measured along two layer-parallel and layer-perpendicular directions in k-space with hv varying around 900 eV. The electrons are seen to occupy a wide energy range below certain maximal so-called Fe ...
Chapter505.ppt
... adjacent faces of quartz is always exactly the same. Other minerals were also found to have this regularity. This observation became known as the law of constancy of interfacial angles. • Atoms of different minerals are clustered into geometric forms such as cubes, bricks, hexagons, etc. and so the ...
... adjacent faces of quartz is always exactly the same. Other minerals were also found to have this regularity. This observation became known as the law of constancy of interfacial angles. • Atoms of different minerals are clustered into geometric forms such as cubes, bricks, hexagons, etc. and so the ...
Key to Writing Assignment #1
... atoms are more closely packed than those in quartz. All three are SiO2 polymorphs. 12. Why are the physical properties of diamond and graphite so different? These polymorphs of carbon have very different internal structure and bonding. Diamonds bonds are much stronger. 13. What’s the difference betw ...
... atoms are more closely packed than those in quartz. All three are SiO2 polymorphs. 12. Why are the physical properties of diamond and graphite so different? These polymorphs of carbon have very different internal structure and bonding. Diamonds bonds are much stronger. 13. What’s the difference betw ...
Structural basis for bending of organic crystals{
... materials is in terms of similar homologous temperature5a (equal to T/Tm, where T is the temperature of deformation), we repeated the bending experiment at 403 K. Bending occurred as it did for 3 at room temperature. An interesting sidelight here is that the bend in the crystal propagates when the s ...
... materials is in terms of similar homologous temperature5a (equal to T/Tm, where T is the temperature of deformation), we repeated the bending experiment at 403 K. Bending occurred as it did for 3 at room temperature. An interesting sidelight here is that the bend in the crystal propagates when the s ...
Enthalpy - Career Launcher
... Coordination number and ionic radii Coordination no. increases with ...
... Coordination number and ionic radii Coordination no. increases with ...
Earth Unit
... material where the molecules fit together in a repeating pattern mineral: made are made of one thing ...
... material where the molecules fit together in a repeating pattern mineral: made are made of one thing ...
Crystal Properties and Growth of Semiconductors
... primitive vectors. Note that, in a primitive cell, the lattice points at the corners are shared with adjacent cells; thus, the effective number of lattice points belonging to the primitive cell is always unity. Since there are many different ways of placing atoms in a volume, the distances and orien ...
... primitive vectors. Note that, in a primitive cell, the lattice points at the corners are shared with adjacent cells; thus, the effective number of lattice points belonging to the primitive cell is always unity. Since there are many different ways of placing atoms in a volume, the distances and orien ...
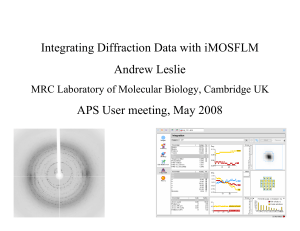
Integrating Diffraction Data with iMOSFLM Andrew Leslie - NE-CAT
... If the scattering vectors are projected along a real space axis direction (such as a, b or c) all the projected vectors for spots in the same reciprocal space plane will have the same length, as will all those spots in the next plane etc. This will give a large peak in the Fourier transform. In othe ...
... If the scattering vectors are projected along a real space axis direction (such as a, b or c) all the projected vectors for spots in the same reciprocal space plane will have the same length, as will all those spots in the next plane etc. This will give a large peak in the Fourier transform. In othe ...
Crystal Ceramic Material
... The transformation from crystalline to the crystalline form of a shift transformation, where the transformation of this form is identical to the reaction martensit. Silica with drastically changed the structure of the Crystal due to distortion of the unit cell on the small contiguous parts or from t ...
... The transformation from crystalline to the crystalline form of a shift transformation, where the transformation of this form is identical to the reaction martensit. Silica with drastically changed the structure of the Crystal due to distortion of the unit cell on the small contiguous parts or from t ...
Minerals
... • A few dozen minerals are called the rockforming minerals • These minerals can be grouped according to ...
... • A few dozen minerals are called the rockforming minerals • These minerals can be grouped according to ...
C41021922
... method at room temperature. The bright, transparent and colourless crystal was obtained with average dimension of 11 × 0.7 × 0.3 cm3. The elemental analysis of the compound confirms the stoichiometric ratio of the compound. The sharp and well defined Bragg peaks obtained in the powder X-ray diffract ...
... method at room temperature. The bright, transparent and colourless crystal was obtained with average dimension of 11 × 0.7 × 0.3 cm3. The elemental analysis of the compound confirms the stoichiometric ratio of the compound. The sharp and well defined Bragg peaks obtained in the powder X-ray diffract ...
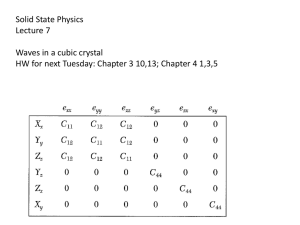
Solid State Physics Lectures 7 Waves in a cubic crystal
... Take a crystal for which C12 ≠ C13, but otherwise has all the same matrix elements as for a cubic crystal. How do you modify the equations for u and v? ...
... Take a crystal for which C12 ≠ C13, but otherwise has all the same matrix elements as for a cubic crystal. How do you modify the equations for u and v? ...
Problems
... 2. (10 points) Calculate the depth of cloud required for an ice crystal, which starts off as a plane plate with an effective diameter of 1 mm and a mass of 0.01 mg, to grow into a spherical graupel particle 1 mm in diameter if it falls through the cloud layer which contains a liquid water content of ...
... 2. (10 points) Calculate the depth of cloud required for an ice crystal, which starts off as a plane plate with an effective diameter of 1 mm and a mass of 0.01 mg, to grow into a spherical graupel particle 1 mm in diameter if it falls through the cloud layer which contains a liquid water content of ...
Chapter 3
... Ex. An Opal is not a mineral because it atoms are Not all solids are minerals. not all arranged in a definite, repeating pattern (even though it is a naturally occurring, inorganic solid). ...
... Ex. An Opal is not a mineral because it atoms are Not all solids are minerals. not all arranged in a definite, repeating pattern (even though it is a naturally occurring, inorganic solid). ...
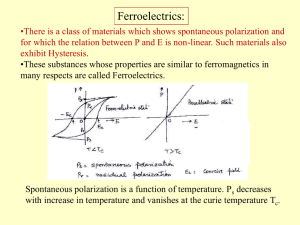
Dielectric loss
... ferromagnetic material respond mechanically to magnetic fields. This effect, called magnetostriction, is responsible for the familiar hum of transformers and other AC devices containing iron cores. ...
... ferromagnetic material respond mechanically to magnetic fields. This effect, called magnetostriction, is responsible for the familiar hum of transformers and other AC devices containing iron cores. ...
Introduction To Materials Science, Chapter 3
... Both FCC and HCP crystal structures have atomic packing factors of 0.74 (maximum possible value) Both FCC and HCP crystal structures may be generated by the stacking of close-packed planes The difference between the two structures is in the ...
... Both FCC and HCP crystal structures have atomic packing factors of 0.74 (maximum possible value) Both FCC and HCP crystal structures may be generated by the stacking of close-packed planes The difference between the two structures is in the ...
Basics of material sciece - E
... probability density are specified by three of these quantum numbers. Furthermore, Bohr energy levels separate into electron subshells, and quantum numbers dictate the number of states within each subshell. Shells are specified by a principal quantum number n, which may take on integral values begin ...
... probability density are specified by three of these quantum numbers. Furthermore, Bohr energy levels separate into electron subshells, and quantum numbers dictate the number of states within each subshell. Shells are specified by a principal quantum number n, which may take on integral values begin ...
Read the full Psuedo Polymorph Application Note (M-2-126)
... The first step towards defining any crystallization process is choosing the solvent. If a solvent that might give a pseudo polymorph is selected, the non-solvated form might be less stable than the solvent, and problems might be encountered getting this form out during the process. Knowledge of pseu ...
... The first step towards defining any crystallization process is choosing the solvent. If a solvent that might give a pseudo polymorph is selected, the non-solvated form might be less stable than the solvent, and problems might be encountered getting this form out during the process. Knowledge of pseu ...
Crystal structure

In mineralogy and crystallography, a crystal structure is a unique arrangement of atoms, ions or molecules in a crystalline liquid or solid. It describes a highly ordered structure, occurring due to the intrinsic nature of its constituents to form symmetric patterns.The crystal lattice can be thought of as an array of 'small boxes' infinitely repeating in all three spatial directions. Such a unit cell is the smallest unit of volume that contains all of the structural and symmetry information to build-up the macroscopic structure of the lattice by translation.Patterns are located upon the points of a lattice, which is an array of points repeating periodically in three dimensions. The lengths of the edges of a unit cell and the angles between them are called the lattice parameters. The symmetry properties of the crystal are embodied in its space group.A crystal's structure and symmetry play a role in determining many of its physical properties, such as cleavage, electronic band structure, and optical transparency.