GEOL 2311
... C) There are 64 32 possible combinations of symmetry operations that define external symmetry of crystals D) The 222 point group (or crystal class) occurs in triclinic orthorhombic crystal system E) Crystals containing a combination of 4-fold, 3-fold and 2-fold rotation axes can only occur in the is ...
... C) There are 64 32 possible combinations of symmetry operations that define external symmetry of crystals D) The 222 point group (or crystal class) occurs in triclinic orthorhombic crystal system E) Crystals containing a combination of 4-fold, 3-fold and 2-fold rotation axes can only occur in the is ...
Crystal Modelling
... Make a crystal of the substance. The crystal must be very pure and perfect. Stage 2 ...
... Make a crystal of the substance. The crystal must be very pure and perfect. Stage 2 ...
solid state - einstein classes
... CSS – 3 Q. Explain briefly ionic solids. Solution : Ions are the constituent particles of ionic solids. Such solids are formed by the three dimensional arrangements of cations and anions bound by strong coulombic (electrostatic) forces. These solids are hard and brittle in nature. They have high me ...
... CSS – 3 Q. Explain briefly ionic solids. Solution : Ions are the constituent particles of ionic solids. Such solids are formed by the three dimensional arrangements of cations and anions bound by strong coulombic (electrostatic) forces. These solids are hard and brittle in nature. They have high me ...
Department of Civil Engineering
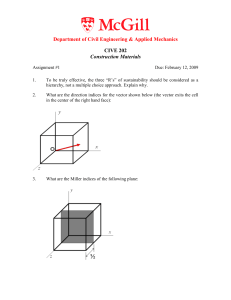
... To be truly effective, the three “R’s” of sustainability should be considered as a hierarchy, not a multiple choice approach. Explain why. ...
... To be truly effective, the three “R’s” of sustainability should be considered as a hierarchy, not a multiple choice approach. Explain why. ...
Piezo Technology
... for use in keyboards. Their sensitivity is so extreme, that the switching cycle can even be produced through 4 mm thick panels, which can be made from many different materials. We have perfected piezo technology. In the past, ceramic elements have been incorported in the technical parts of a keyboar ...
... for use in keyboards. Their sensitivity is so extreme, that the switching cycle can even be produced through 4 mm thick panels, which can be made from many different materials. We have perfected piezo technology. In the past, ceramic elements have been incorported in the technical parts of a keyboar ...
IOSR Journal of Applied Physics (IOSR-JAP)
... functional groups in the synthesized compound. FTIR spectrum was recorded using spectrophotometer by kBr pellet technique in the region 4000-500 cm-1. For the organic molecule, the FTIR region has been divided into fractional group and fingerprint region. The fingerprint regions are those lying betw ...
... functional groups in the synthesized compound. FTIR spectrum was recorded using spectrophotometer by kBr pellet technique in the region 4000-500 cm-1. For the organic molecule, the FTIR region has been divided into fractional group and fingerprint region. The fingerprint regions are those lying betw ...
Substitution, Solid Solutions, and an Introduction to Silicate Mineral
... only a distortion of the crystal structure. Order-disorder polymorphism occurs as a result of the change in site occupancy for a given cation, say Al3+ vs. Si4+ in the 4fold sites in K-feldspar. NB that cation disorder usually increases w/ inc. T. ...
... only a distortion of the crystal structure. Order-disorder polymorphism occurs as a result of the change in site occupancy for a given cation, say Al3+ vs. Si4+ in the 4fold sites in K-feldspar. NB that cation disorder usually increases w/ inc. T. ...
Chapter 5: Atoms to Minerals
... The opposite charge will then attract Ion – a charged atom A metal looses electrons easily to form positive ions. Therefore they can not join with other metals. Nonmetals gain electrons easily to form negative ions. This makes them want to bond to the positive metals. ...
... The opposite charge will then attract Ion – a charged atom A metal looses electrons easily to form positive ions. Therefore they can not join with other metals. Nonmetals gain electrons easily to form negative ions. This makes them want to bond to the positive metals. ...
G070376-00
... RbTiOAsO4, Appl. Phys. B 79, 77 (2004), b) Crystal Technology, Inc., c) only one value given, no axis specified. ...
... RbTiOAsO4, Appl. Phys. B 79, 77 (2004), b) Crystal Technology, Inc., c) only one value given, no axis specified. ...
Lewis Acid Catalyzed Z to E Isomerization of 1, 2
... obvious model. The differences in catalytic activi ties are thus correlated with the acceptor properties of the Group 13 trihalides. It should be noted that reactions of Z-dppee with BrNnsted acids like trifluoromethanesulfonic or tetrafluoroboric acid also lead to a quatemisation at the phosphorus ...
... obvious model. The differences in catalytic activi ties are thus correlated with the acceptor properties of the Group 13 trihalides. It should be noted that reactions of Z-dppee with BrNnsted acids like trifluoromethanesulfonic or tetrafluoroboric acid also lead to a quatemisation at the phosphorus ...
Structure function
... materials. A beam of Xrays are used to bombard a specimen from various angles. The Xrays are diffracted as they are reflected from successive planes formed by the crystal lattice of the material. By varying angles a diffraction pattern emerges that is characteristic of the samples. It can then be fu ...
... materials. A beam of Xrays are used to bombard a specimen from various angles. The Xrays are diffracted as they are reflected from successive planes formed by the crystal lattice of the material. By varying angles a diffraction pattern emerges that is characteristic of the samples. It can then be fu ...
geology - MabryOnline.org
... What is really inside the Earth? What is a mineral? A rock? What is the difference? What is a crystal? How do minerals/rocks form? Why are minerals/rocks important? ...
... What is really inside the Earth? What is a mineral? A rock? What is the difference? What is a crystal? How do minerals/rocks form? Why are minerals/rocks important? ...
Crystal-field induced dipoles in heteropolar crystals
... normally presupposed that the two charges have no considerable overlap, which is by no means the case for the nucleus of charge qN and the electron distribution of charge qe- On the contrary, the nucleus is totally embedded within the electron cloud and the approach seems hardly reliable. Most proba ...
... normally presupposed that the two charges have no considerable overlap, which is by no means the case for the nucleus of charge qN and the electron distribution of charge qe- On the contrary, the nucleus is totally embedded within the electron cloud and the approach seems hardly reliable. Most proba ...
R-29_ChenYQ.pdf
... A general numerical approach is developed to simulate the failure process of structure or heterogeneous material, in which different local failure models are defined for different structures and materials to describe the failure of structure joint or material element. A two-parameter Weibull distrib ...
... A general numerical approach is developed to simulate the failure process of structure or heterogeneous material, in which different local failure models are defined for different structures and materials to describe the failure of structure joint or material element. A two-parameter Weibull distrib ...
Crystal structure

In mineralogy and crystallography, a crystal structure is a unique arrangement of atoms, ions or molecules in a crystalline liquid or solid. It describes a highly ordered structure, occurring due to the intrinsic nature of its constituents to form symmetric patterns.The crystal lattice can be thought of as an array of 'small boxes' infinitely repeating in all three spatial directions. Such a unit cell is the smallest unit of volume that contains all of the structural and symmetry information to build-up the macroscopic structure of the lattice by translation.Patterns are located upon the points of a lattice, which is an array of points repeating periodically in three dimensions. The lengths of the edges of a unit cell and the angles between them are called the lattice parameters. The symmetry properties of the crystal are embodied in its space group.A crystal's structure and symmetry play a role in determining many of its physical properties, such as cleavage, electronic band structure, and optical transparency.